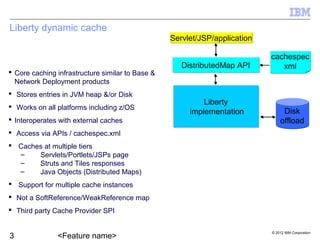
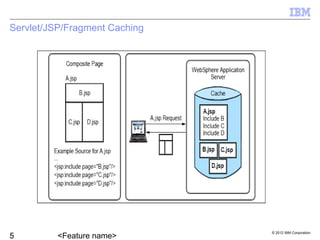
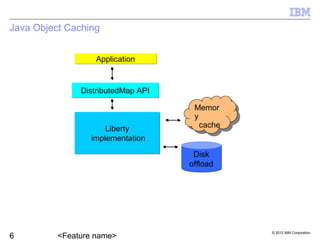
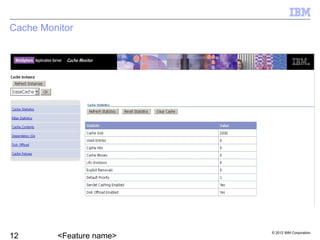
Liberty provides dynamic caching capabilities through configuration in server.xml and properties files. Caches can store entries in memory or disk and work across multiple tiers like servlets and Java objects. The Cache Monitor displays metrics and configurations for all cache instances. There are some restrictions around features like replication and caching for certain workloads.