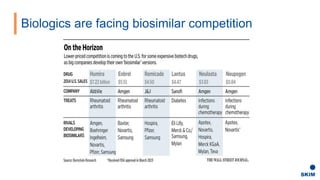
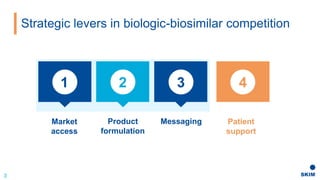
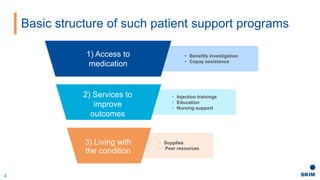
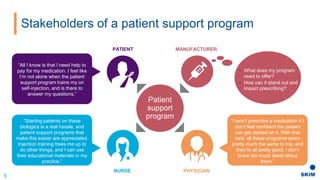
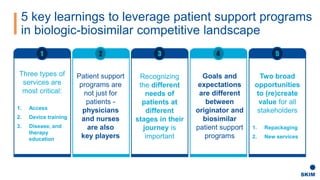
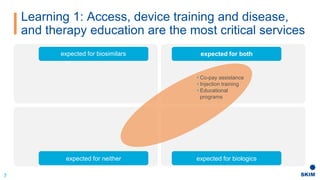
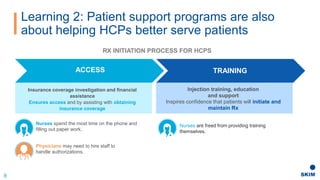
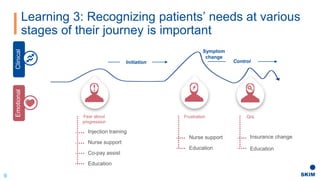
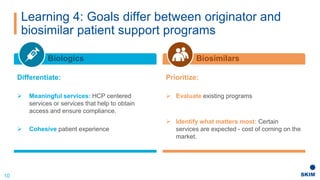
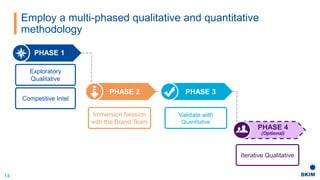
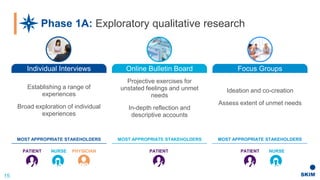
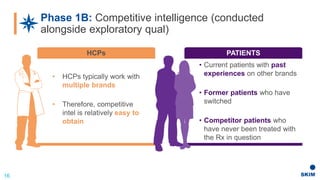
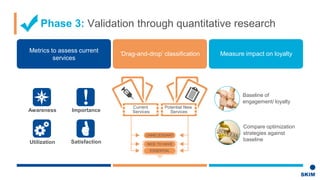
The document discusses the importance of patient support programs in the biologic-biosimilar competitive landscape, highlighting three critical services: access, device training, and disease education. It emphasizes the need to recognize patients' varied needs throughout their treatment journey and the different goals for originator and biosimilar programs. Key learnings suggest that effective patient support not only aids patients but also assists healthcare providers in managing prescriptions and addressing their needs more efficiently.