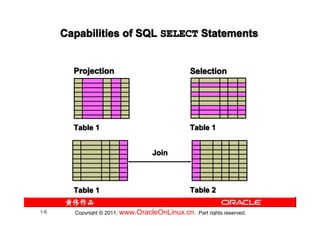
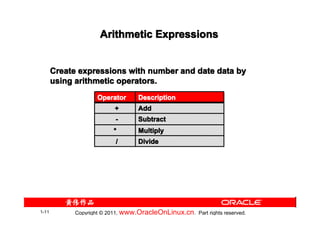
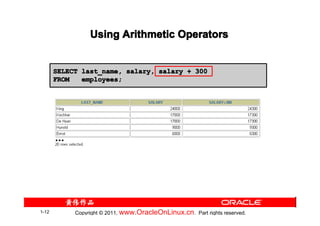
The document provides training content for the Oracle OCP 1Z0-007 exam. It covers topics like retrieving data using the SQL SELECT statement, including basic SELECT statements, column aliases, arithmetic expressions, null values, concatenation operators, and using the DESCRIBE command. It also discusses the differences between SQL statements and iSQL*Plus commands, and provides examples of interacting with iSQL*Plus and script files. Practice questions at the end test understanding of concepts like SQL statement capabilities, column alias usage, and iSQL*Plus features.




![Basic SELECT Statement
SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...}
FROM table;
• SELECT identifies the columns to be displayed
• FROM identifies the table containing those columns
1-6 Copyright © 2011, www.OracleOnLinux.cn . Part rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson01-111207192720-phpapp01/85/Lesson01-SQL-6-320.jpg)








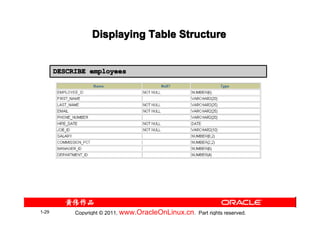
![Displaying Table Structure
Use the iSQL*Plus DESCRIBE command to display the
SQL*
structure of a table:
DESC[RIBE] tablename
1-28 Copyright © 2011, www.OracleOnLinux.cn . Part rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson01-111207192720-phpapp01/85/Lesson01-SQL-28-320.jpg)
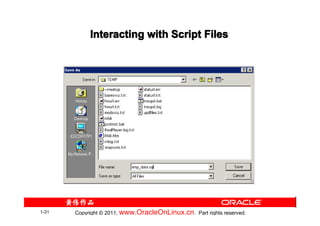

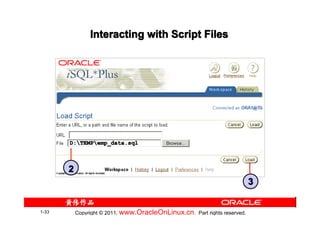
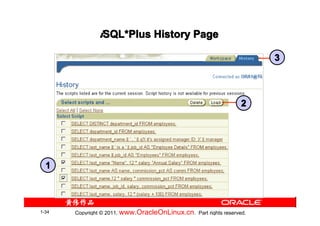
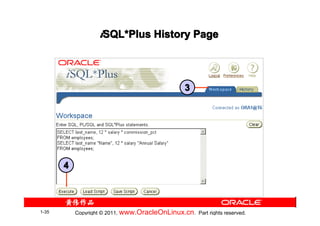

![Summary
In this lesson, you should have learned how to:
• Write a SELECT statement that:
– Returns all rows and columns from a table
– Returns specified columns from a table
– Uses column aliases to display more descriptive
column headings
• Use the iSQL*Plus environment to write, save, and
SQL*
execute SQL statements and iSQL*Plus
SQL*
commands
SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...}
FROM table;
1-38 Copyright © 2011, www.OracleOnLinux.cn . Part rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson01-111207192720-phpapp01/85/Lesson01-SQL-38-320.jpg)







