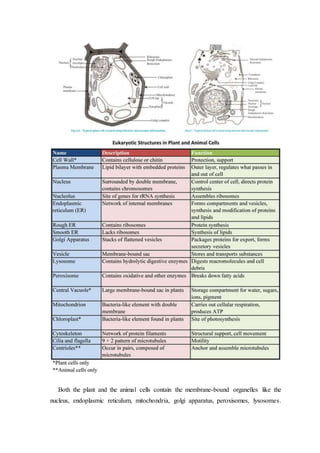
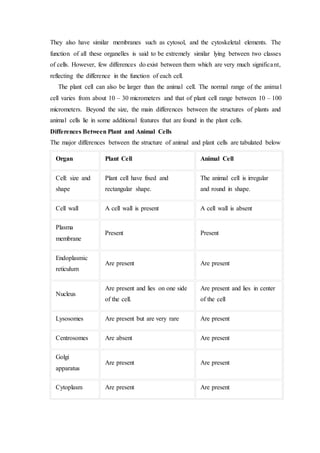
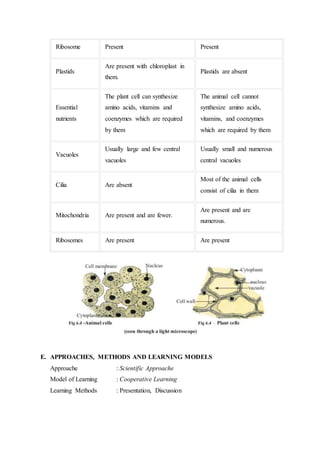
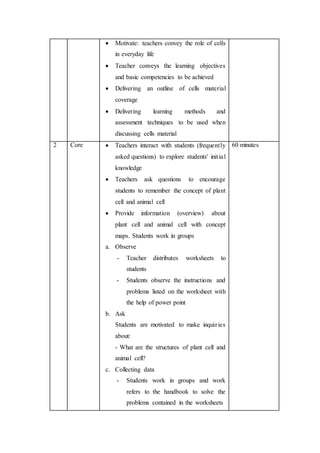
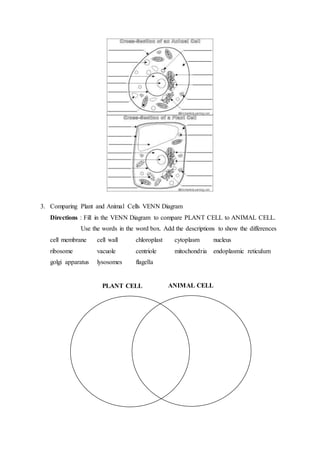
This lesson plan outlines a biology lesson for 11th grade students on plant and animal cells. The lesson will last 2 periods of 45 minutes each. Students will learn about the characteristics, structures, and functions of plant and animal cells. They will also compare and contrast the differences between plant and animal cells. Activities include a presentation, group work reviewing concepts and structures, a worksheet, and a concluding discussion. Student understanding and participation will be assessed through observation, tests, presentations, and worksheets.