Embed presentation
Download to read offline





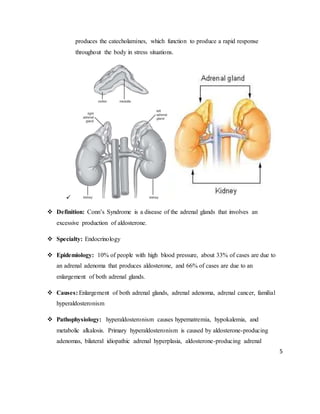








Conn's syndrome, also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, refers to excessive production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels. This causes high blood pressure, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis. Symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, headaches, and vision problems. Diagnosis involves measuring aldosterone and renin levels. Treatment options include medications that block aldosterone like spironolactone, or surgical removal of an adrenal tumor if present. Left untreated, complications of Conn's syndrome can include heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and abnormal heart rhythms.














