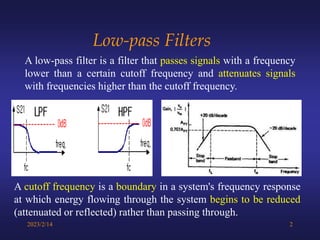
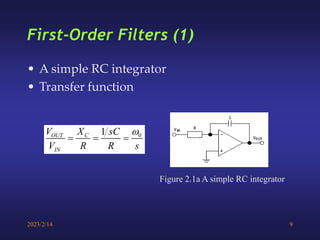
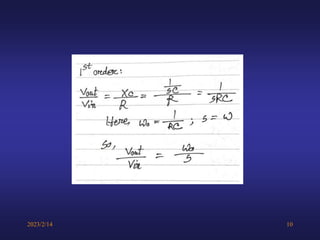
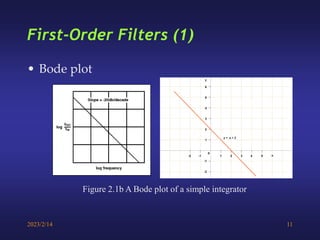
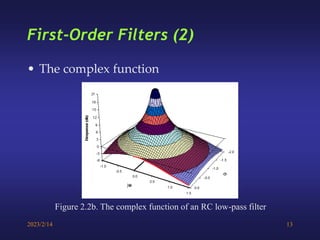
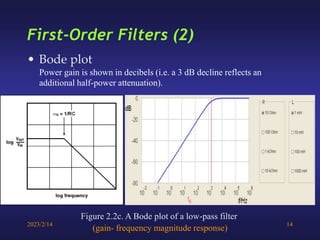
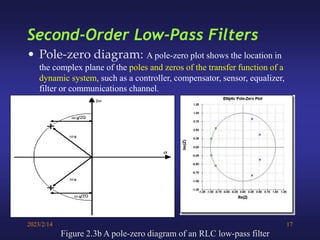
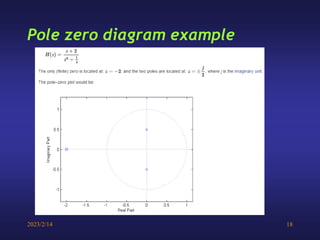
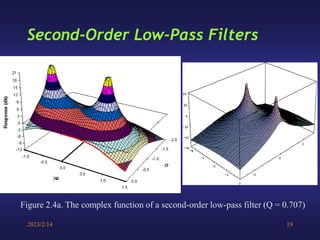
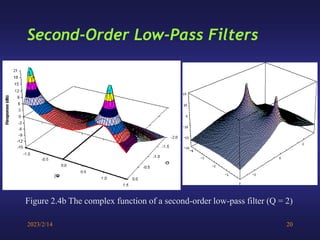
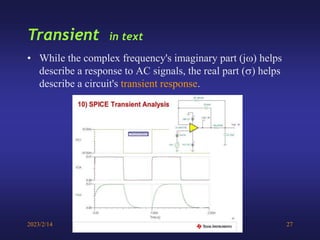
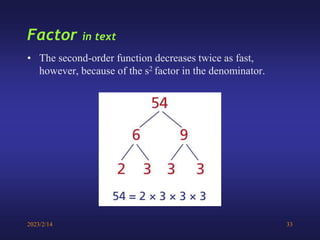
A low-pass filter passes signals with frequencies lower than a cutoff frequency and attenuates higher frequencies. A first order filter has one reactive component like a capacitor or inductor affecting its frequency response, while a second order filter has two reactive components. The document discusses low-pass filters including their transfer functions, Bode plots, pole-zero diagrams, and key terminology like Laplace transform, quality factor and decaying exponential response.