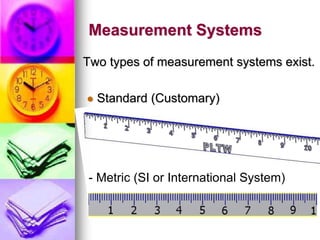
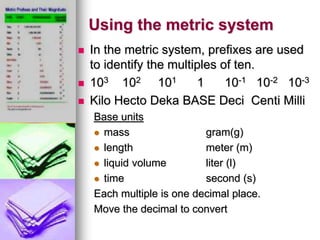
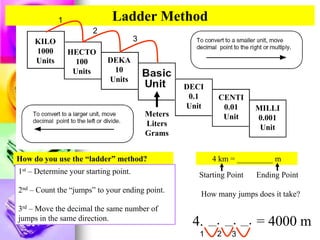
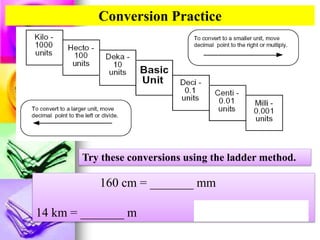
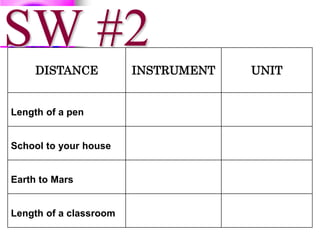
This document provides information about measuring distance using standard metric units. It discusses why measuring distance is important, the two main measurement systems, and focuses on the International System of Units (SI or metric system). Key points include that the metric system uses multiples of ten as prefixes for units of measurement. The base units for length, mass, time and other quantities are defined. Examples show how to use the "ladder method" to convert between metric units like centimeters to millimeters. Students complete practice problems converting between units of distance.