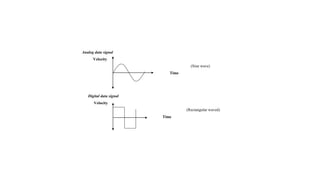
This document covers topics related to data communication, including different types of data signals, signal modulation and demodulation, multiplexing and demultiplexing, frequency, baud rate, bandwidth, guardband, baseband signals, broadband transmission, and attenuation. The learner is expected to differentiate between analog and digital signals and understand concepts like modulation, demodulation, multiplexing, and attenuation. Assessment will be done through online presentations, CATs, class practicals, and examinations. Relevant journals and textbooks are also provided.