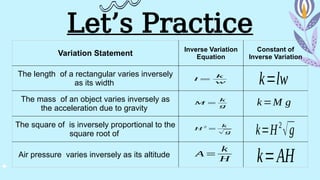
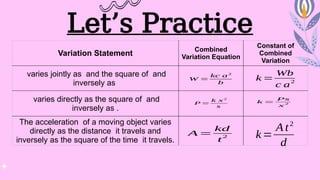
The document outlines the types of variations in mathematics: direct, inverse, joint, and combined variation, providing definitions and equations for each. It explains how each type relates variables to one another, including practical examples for better understanding. Exercises are included to practice translating variation statements into mathematical equations.