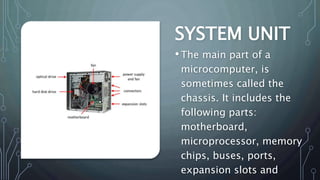
The document introduces the basics of CAD software and computer hardware, explaining the division between hardware and peripherals. It details essential hardware components like the system unit, keyboard, monitor, hard disk drive, mouse, and printer, as well as the distinction between operating system software and application software. The document emphasizes the importance of both hardware and software in operating a computer system and performing tasks.