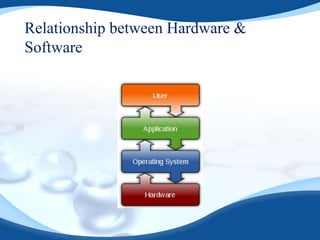
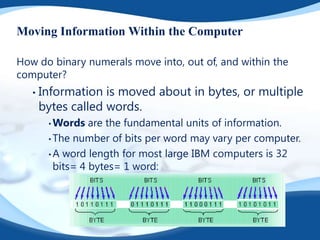
The document provides a detailed overview of hardware and software components essential to computers. It explains various hardware components like the CPU, RAM, sound and video cards, input/output devices, and storage devices, and also outlines the nature of software, its types, and its key features. The conclusion emphasizes the interdependence of hardware and software in enabling computers to function effectively.