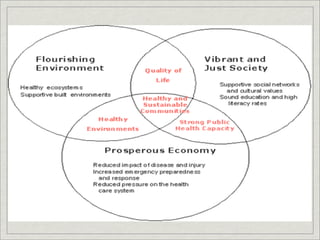
The document discusses environmental ethics, laws, and principles, outlining how ethics considers human relationships with the non-human world and influences many disciplines. It examines ethical decisions regarding the environment and lists environmental laws and international treaties. Sustainable development aims to improve quality of life while protecting the environment for future generations.