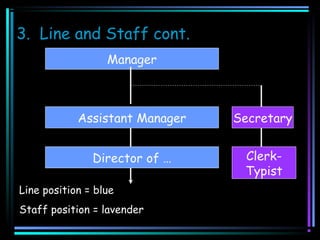
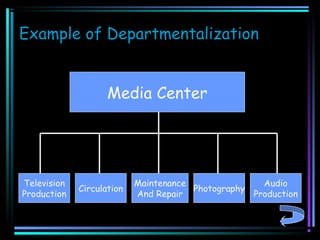
This document outlines key concepts related to organizational structure and decision making. It defines the purpose and elements of an organizational chart, including vertical/horizontal dimensions, chain of command, line/staff positions, authority levels, power, responsibility, and departmentalization. Five steps of decision making are described: identify the problem, analyze alternatives, review alternatives, implement, and evaluate. Effective decision makers are said to have good judgment, experience, creativity, analytic skills, insight, and seek outside input.