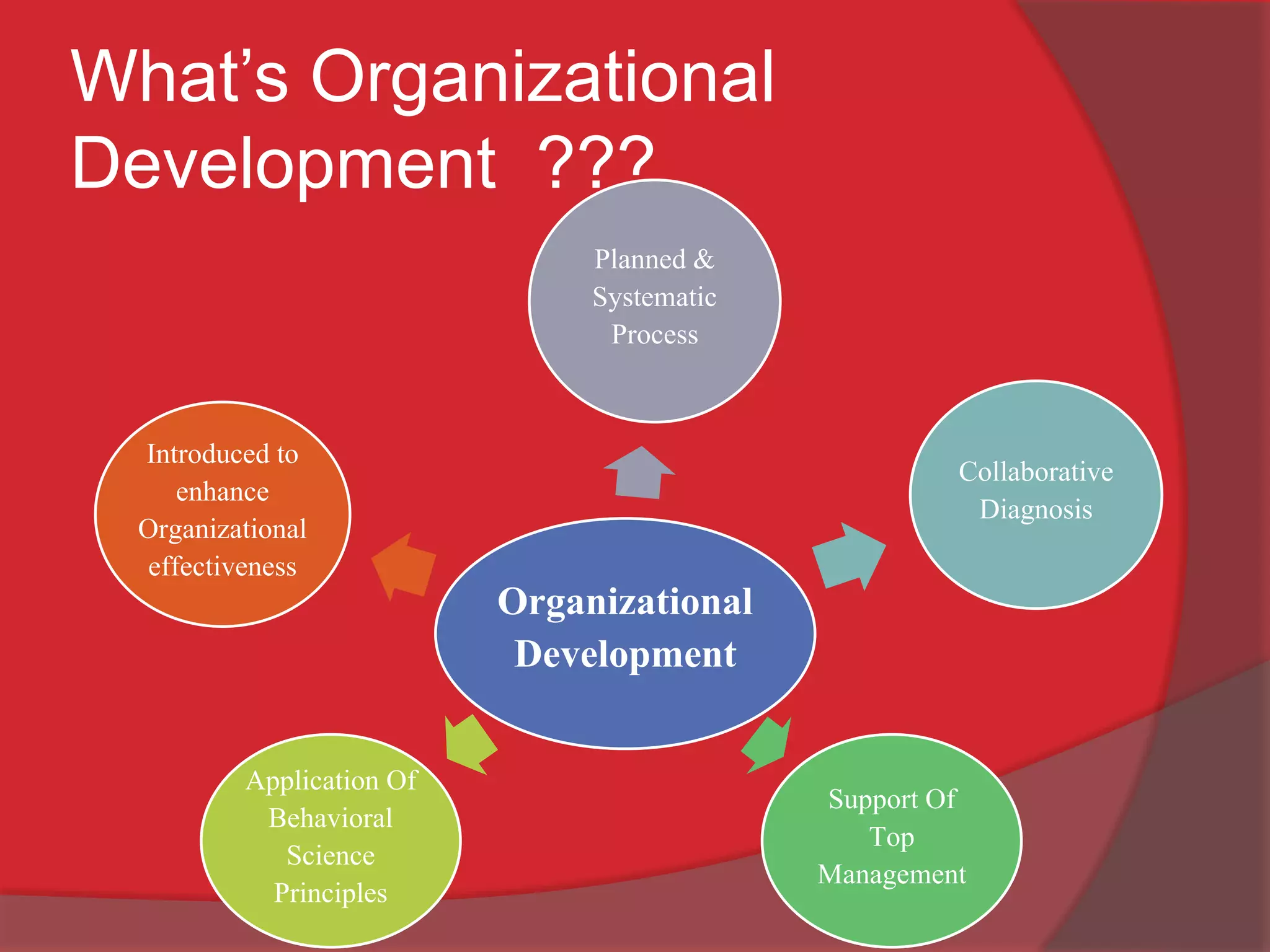
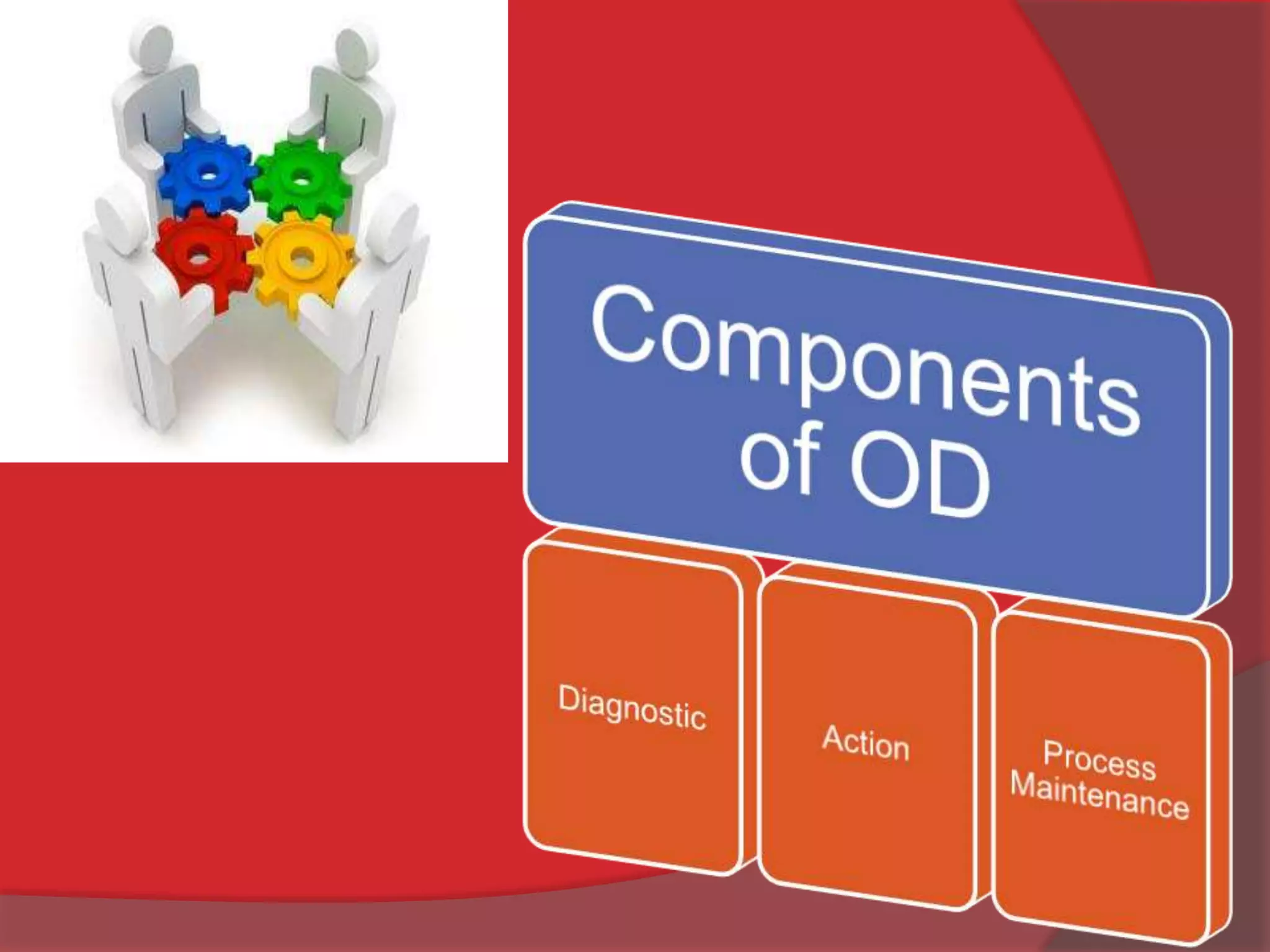
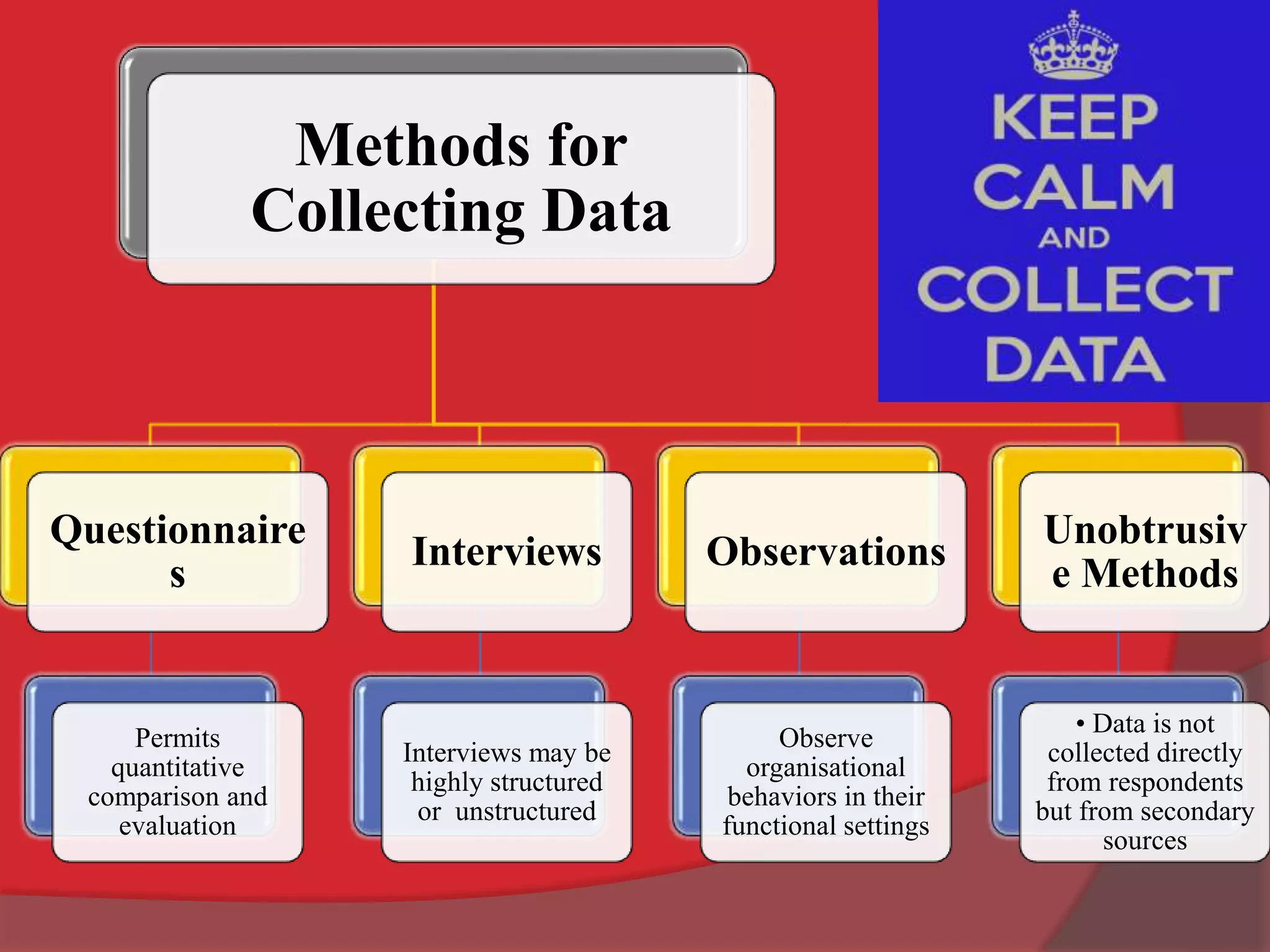
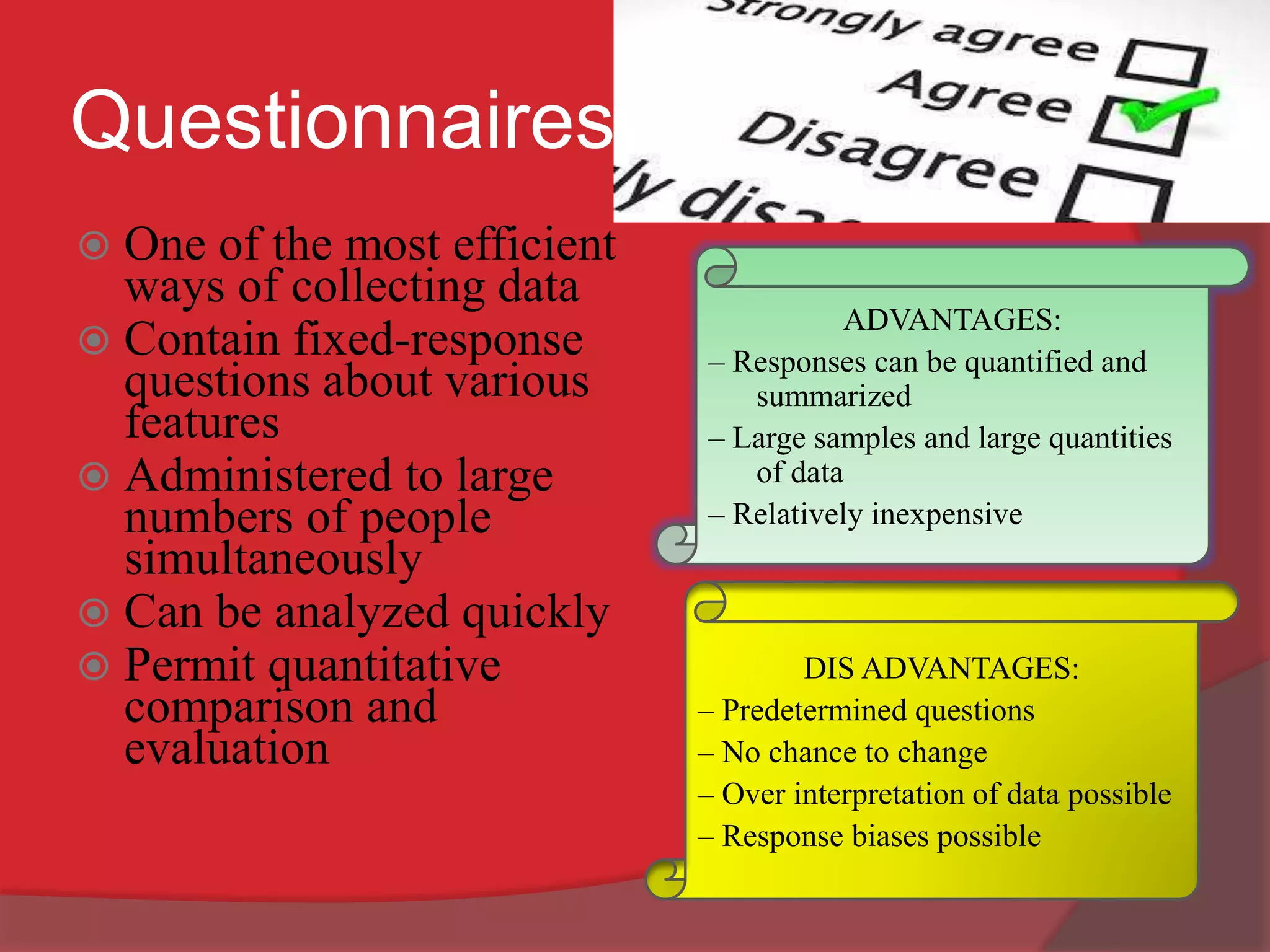
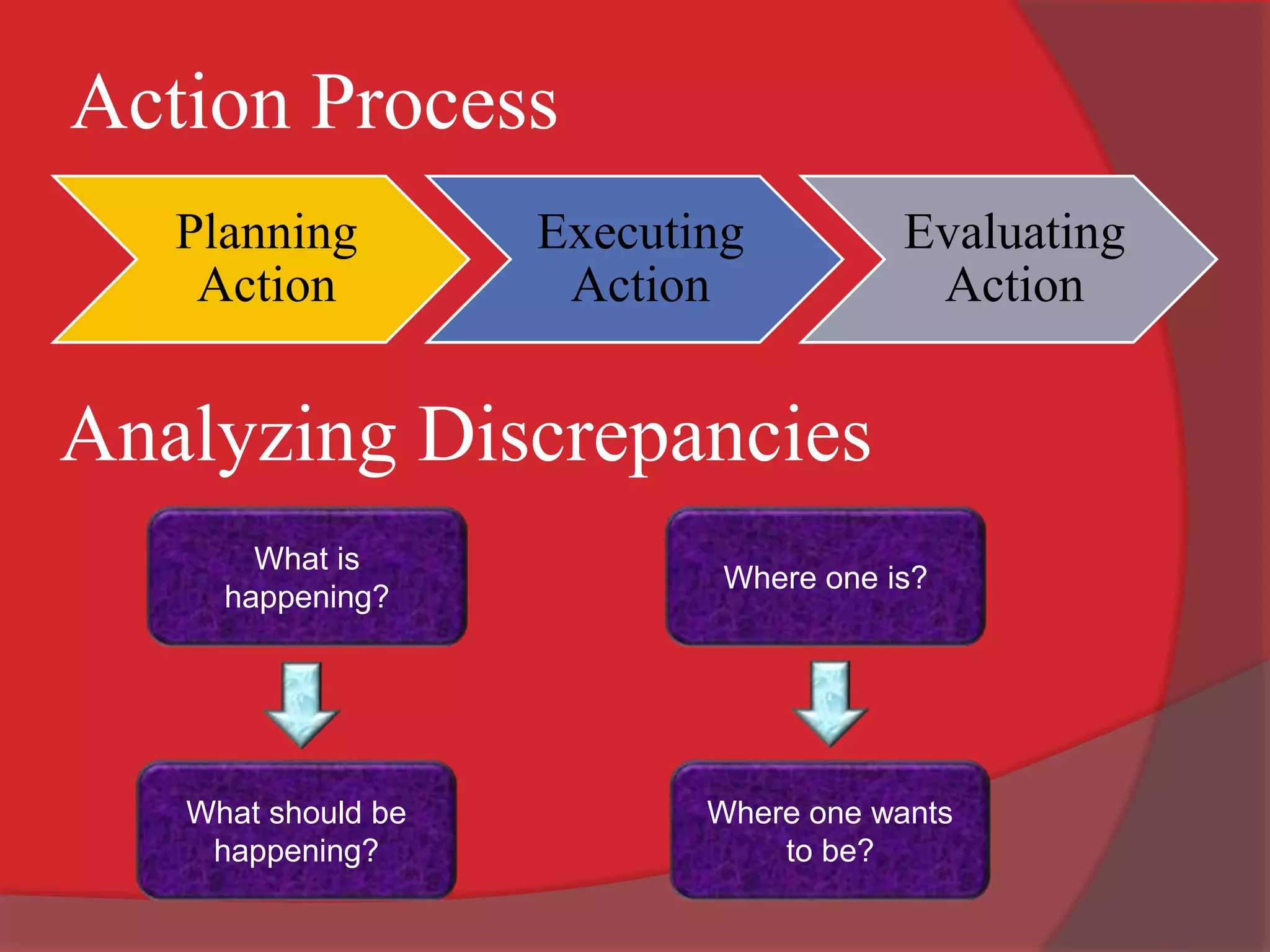
This document discusses organizational development (OD) and the diagnostic process used in OD. It defines OD as a planned, systematic, and collaborative process that applies behavioral science principles to improve organizational effectiveness. The diagnostic process involves collecting information through methods like questionnaires, interviews, observations, and unobtrusive measures in order to analyze issues and plan interventions. The interventions are then implemented and evaluated in an ongoing process of maintenance to continuously monitor and improve the organization.