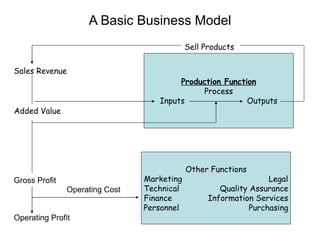
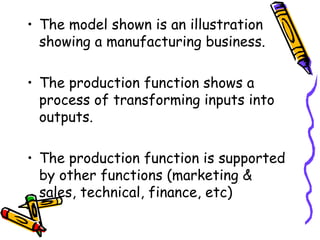
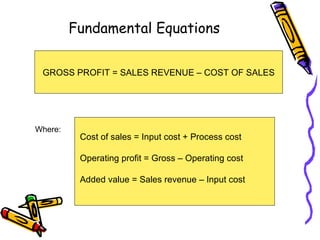
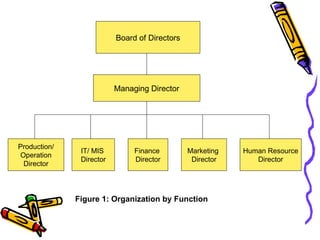
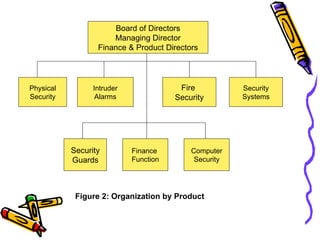
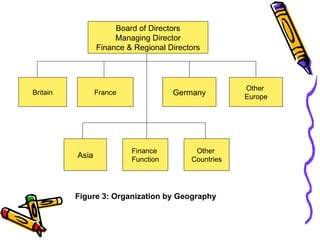
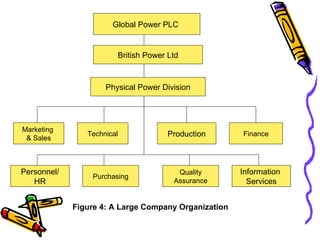
A business transforms inputs into outputs through various functions like production, marketing, finance, etc. to generate sales revenue and profit. The key functions include production of goods/services, marketing and sales, finance, human resources, purchasing, and legal. A business can be classified by the product or service, size as tiny, small, medium or large, and by ownership type like sole proprietorship, partnership or limited liability company.