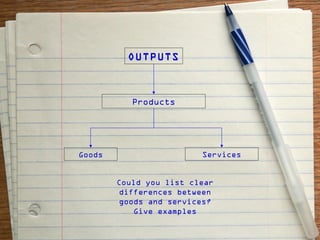
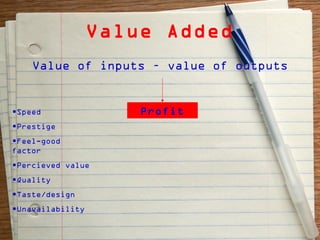
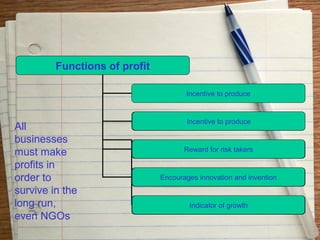
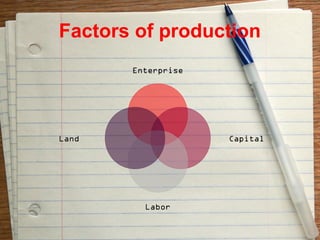
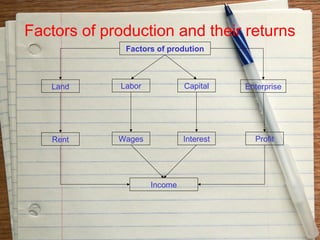
The document provides an overview of the key functions of a business. It discusses the nature of business activities and decision making as well as inputs such as goods, services, and customers, and outputs such as products. It then summarizes the main business functions of production, marketing, finance, and human resources which are responsible for converting materials into goods, identifying customer needs, managing finances, and overseeing personnel respectively.