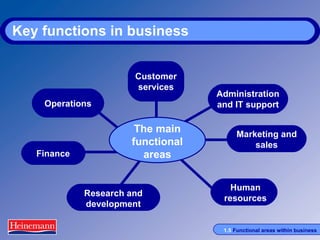
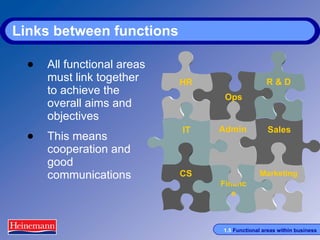
The document discusses the key functional areas within businesses including operations, finance, research and development, human resources, marketing and sales, administration and IT support, and customer services. It explains that in small businesses these functions are typically performed by individuals while in larger businesses they are divided into departments. All functional areas must work together to achieve business objectives through cooperation and communication. The roles and responsibilities of each functional area are then outlined in further detail.