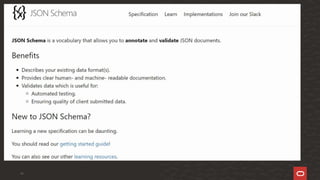
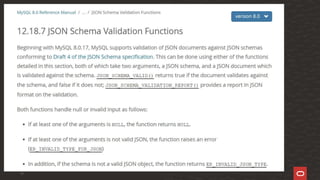
The document discusses JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) as a widely used data format for transmitting data objects, emphasizing its language independence and applications. It also covers validation practices in MySQL for ensuring data integrity via JSON schemas, detailing functions like json_schema_valid and json_schema_validation_report to validate JSON documents against specified schemas. Various SQL examples illustrate the implementation of these validation techniques and their importance in maintaining clean and accurate data.






![OBJECTS are enclosed in {}
JSON: OBJECTS versus ARRAYS
7
Arrays are enclosed in []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsonvalidationperconalive2021-210513180254/85/Validating-JSON-Percona-Live-2021-presentation-7-320.jpg)











![CREATE TABLE `testx` (
`col` JSON,
CONSTRAINT `myage_inRange`
CHECK (JSON_SCHEMA_VALID('{"type": "object",
"properties": {
"myage": {
"type" : "number",
"minimum": 28,
"maximum": 99
}
},"required": ["myage"]
}', `col`) = 1)
);
REQUIRE Fields
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsonvalidationperconalive2021-210513180254/85/Validating-JSON-Percona-Live-2021-presentation-22-320.jpg)
![CREATE TABLE `testx` (
`col` JSON,
CONSTRAINT `myage_inRange`
CHECK (JSON_SCHEMA_VALID('{"type": "object",
"properties": {
"myage": {
"type" : "number",
"minimum": 28,
"maximum": 99
}
},"required": ["myage"]
}', `col`) = 1)
);
REQUIRE Fields
23
insert into testx values('{"myage":27}');
ERROR 3819 (HY000):
Check constraint 'myage_inRange' is
violated.
insert into testx values('{"myage":97}');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsonvalidationperconalive2021-210513180254/85/Validating-JSON-Percona-Live-2021-presentation-23-320.jpg)