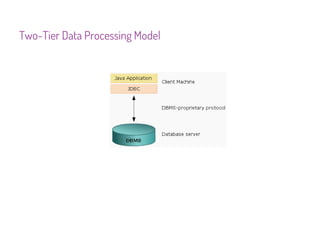
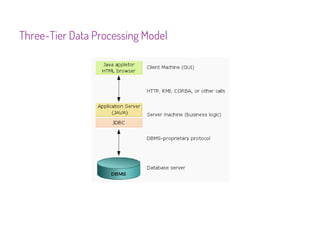
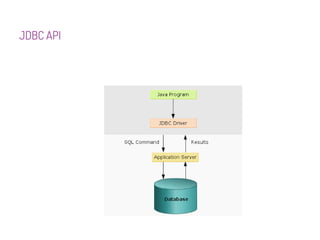
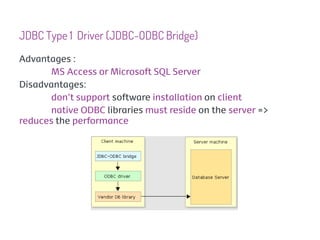
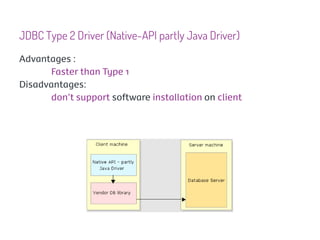
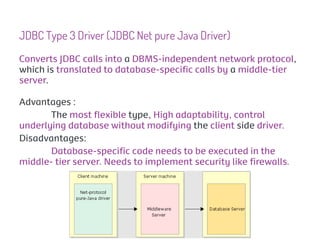
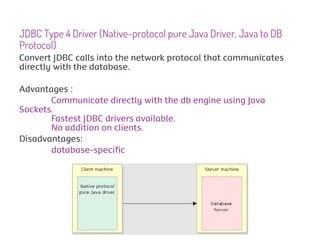
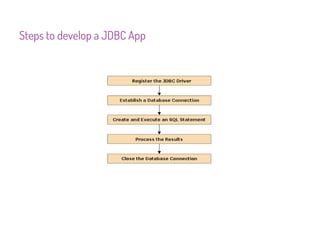
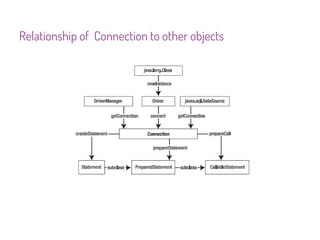
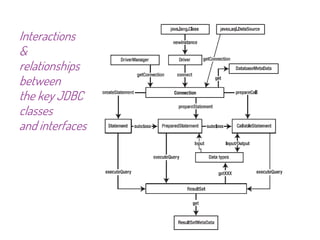
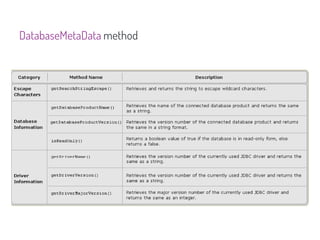
JDBC is a Java API that provides interfaces for connecting to and working with databases. It allows Java applications to execute SQL statements and process the results by providing a standard interface for database access that is independent of database vendors. The key classes and interfaces in JDBC include Connection, Statement, PreparedStatement, CallableStatement, and ResultSet. JDBC drivers convert JDBC calls into database-specific protocols to communicate with the database.