lecture14.ppt
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•8 views
This document discusses node analysis, which is a method to determine all voltages and currents in a circuit. It involves selecting a reference node and writing Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) equations at each other node in terms of the node voltages. Once the node voltages are solved, the currents can be determined using Ohm's Law. The document provides examples of writing KCL equations at nodes and using techniques like super nodes to solve circuits with dependent sources.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
BEF 12403 - Week 12 - Nodal Analysis Method.ppt

Nodal analysis is a circuit analysis technique where each node in the circuit is assigned a voltage and equations are written for each node using Kirchhoff's Current Law. Ohm's law is used to relate the branch currents to the node voltages. A reference node is selected and its voltage is set to zero. Node voltage equations are set up and solved to find the unknown node voltages. Key steps are to define the nodes and reference node, write KCL equations, apply Ohm's law, and solve the resulting system of equations. Worked examples are provided to demonstrate applying nodal analysis to calculate unknown node voltages.
Network theorems for electrical engineering

The document discusses several circuit analysis theorems and methods. Kirchhoff's laws describe the conservation of charge and energy in circuits. Mesh analysis and nodal analysis are methods to solve circuits by assigning currents or voltages and setting up equations based on Kirchhoff's laws. The superposition theorem allows analyzing circuits with multiple sources by solving for each source independently and summing the results.
node analysis.pptx

1. The document discusses various circuit analysis techniques for AC circuits including nodal analysis, mesh analysis, and network theorems. It provides explanations and examples of applying these techniques.
2. Key topics covered include node and mesh definitions, the steps of nodal and mesh analysis, supernode and supermesh concepts, and applications of network theorems like superposition, Thevenin's, and Norton's theorems.
3. The document also introduces phasor analysis for AC circuits, defining phasors and discussing phasor relationships for circuit elements like resistors, inductors, and capacitors. It provides the phasor representations of voltage and current in these components.
L 05(gdr)(et) ((ee)nptel)

The document describes the steps of node voltage analysis of circuits. It begins by explaining that node voltage analysis is a technique for circuit analysis that uses Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) to write equations at each node. It then provides an example circuit and shows how to:
1) Identify and label the nodes, choosing one as the reference node.
2) Write KCL equations for each node in terms of the node voltages.
3) Solve the simultaneous equations to determine the node voltages and then use these to find branch currents.
Kirchoff's Law

The document discusses Kirchhoff's laws, which are two fundamental laws of circuit analysis:
1) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop is equal to zero.
2) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of the currents entering and leaving any node in a circuit is equal to zero.
The document provides examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze circuits and solve for unknown voltages and currents. It also includes a quiz on Kirchhoff's laws.
Kirchoff's Law

The document discusses Kirchhoff's laws, which are two fundamental laws of circuit analysis:
1) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop is equal to zero.
2) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of the currents entering and leaving any node in a circuit is equal to zero.
The document provides examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze circuits and solve for unknown voltages and currents. It also includes a quiz on Kirchhoff's laws.
CSL (1).pptx

The document describes experiments performed in PS-Pice to verify various circuit theorems. Experiment 1 introduces PS-Pice and describes its basic functions. Experiment 2 uses PS-Pice to verify Kirchhoff's Current and Voltage Laws in a DC circuit by comparing analytical and simulated results. Experiment 3 verifies the Superposition Theorem for dependent and independent sources by calculating voltages using individual source contributions. Experiment 4 verifies Thevenin's Theorem for an independent source DC network by deriving the equivalent circuit representation.
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS PROBLEM SOLUTION IN MATLAB

THIS PPT IS MAINLY BASED ON ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS PROBLEM AND THIS PPT ALSO SOLVED THEORETICALLY AND SOLVED BY USING THE MATLAB SOFTWARE AND THIS ALSO CONTAINS THE CODE AND RESULTS ARE ALSO THERE.SO THIS IS USEFUL
Recommended
BEF 12403 - Week 12 - Nodal Analysis Method.ppt

Nodal analysis is a circuit analysis technique where each node in the circuit is assigned a voltage and equations are written for each node using Kirchhoff's Current Law. Ohm's law is used to relate the branch currents to the node voltages. A reference node is selected and its voltage is set to zero. Node voltage equations are set up and solved to find the unknown node voltages. Key steps are to define the nodes and reference node, write KCL equations, apply Ohm's law, and solve the resulting system of equations. Worked examples are provided to demonstrate applying nodal analysis to calculate unknown node voltages.
Network theorems for electrical engineering

The document discusses several circuit analysis theorems and methods. Kirchhoff's laws describe the conservation of charge and energy in circuits. Mesh analysis and nodal analysis are methods to solve circuits by assigning currents or voltages and setting up equations based on Kirchhoff's laws. The superposition theorem allows analyzing circuits with multiple sources by solving for each source independently and summing the results.
node analysis.pptx

1. The document discusses various circuit analysis techniques for AC circuits including nodal analysis, mesh analysis, and network theorems. It provides explanations and examples of applying these techniques.
2. Key topics covered include node and mesh definitions, the steps of nodal and mesh analysis, supernode and supermesh concepts, and applications of network theorems like superposition, Thevenin's, and Norton's theorems.
3. The document also introduces phasor analysis for AC circuits, defining phasors and discussing phasor relationships for circuit elements like resistors, inductors, and capacitors. It provides the phasor representations of voltage and current in these components.
L 05(gdr)(et) ((ee)nptel)

The document describes the steps of node voltage analysis of circuits. It begins by explaining that node voltage analysis is a technique for circuit analysis that uses Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) to write equations at each node. It then provides an example circuit and shows how to:
1) Identify and label the nodes, choosing one as the reference node.
2) Write KCL equations for each node in terms of the node voltages.
3) Solve the simultaneous equations to determine the node voltages and then use these to find branch currents.
Kirchoff's Law

The document discusses Kirchhoff's laws, which are two fundamental laws of circuit analysis:
1) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop is equal to zero.
2) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of the currents entering and leaving any node in a circuit is equal to zero.
The document provides examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze circuits and solve for unknown voltages and currents. It also includes a quiz on Kirchhoff's laws.
Kirchoff's Law

The document discusses Kirchhoff's laws, which are two fundamental laws of circuit analysis:
1) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltages around any closed loop is equal to zero.
2) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of the currents entering and leaving any node in a circuit is equal to zero.
The document provides examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze circuits and solve for unknown voltages and currents. It also includes a quiz on Kirchhoff's laws.
CSL (1).pptx

The document describes experiments performed in PS-Pice to verify various circuit theorems. Experiment 1 introduces PS-Pice and describes its basic functions. Experiment 2 uses PS-Pice to verify Kirchhoff's Current and Voltage Laws in a DC circuit by comparing analytical and simulated results. Experiment 3 verifies the Superposition Theorem for dependent and independent sources by calculating voltages using individual source contributions. Experiment 4 verifies Thevenin's Theorem for an independent source DC network by deriving the equivalent circuit representation.
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS PROBLEM SOLUTION IN MATLAB

THIS PPT IS MAINLY BASED ON ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS PROBLEM AND THIS PPT ALSO SOLVED THEORETICALLY AND SOLVED BY USING THE MATLAB SOFTWARE AND THIS ALSO CONTAINS THE CODE AND RESULTS ARE ALSO THERE.SO THIS IS USEFUL
4 kirchoff law

Kirchoff's laws are foundational circuit analysis techniques. Kirchoff announced two laws in 1854:
(1) Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node equals the sum leaving;
(2) Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) states that the algebraic sum of voltages in a closed loop is zero.
Circuit analysis methods like Node Analysis and Mesh Analysis apply KCL and KVL to write equations relating currents and voltages in a circuit.
beee final.ppt

Nodal analysis is a method for analyzing electrical circuits by writing Kirchhoff's current law equations at each node. It involves selecting a reference node, assigning voltages to other nodes, writing KCL equations for each non-reference node, and solving the equations simultaneously to determine the node voltages. Examples show how to set up KCL equations at each node, including combining nodes connected by a voltage source into a supernode. Solving the nodal analysis equations provides the voltage across every element in the circuit.
3- Ch03- Methods Of Analysis-Sadiku

1) Nodal analysis is a circuit analysis technique that uses node voltages as variables. It involves applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) at each node to obtain equations relating the node voltages.
2) To perform nodal analysis, a reference node is selected and assigned a voltage of 0 V. Voltages of other nodes are assigned with respect to the reference node. Then, KCL is applied at each non-reference node to obtain equations.
3) Ohm's law is used to express branch currents in terms of node voltages. This results in a system of simultaneous equations that can be solved for the unknown node voltages.
Circuit laws & network theorems

Kirchhoff's laws deal with the conservation of charge and energy in electrical circuits. There are two Kirchhoff's laws:
1. Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of currents in a network meeting at a point is zero.
2. Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the directed sum of the potential differences around any closed network is zero.
Circuit analysis methods like mesh analysis, nodal analysis, and superposition theorem can be used to solve circuits using Kirchhoff's laws. Mesh analysis uses KVL to analyze loops in a planar circuit. Nodal analysis uses KCL to analyze connections (nodes) in a circuit. Superposition
Circuitlaws i-120122051920-phpapp01

Kirchhoff's laws describe the conservation of electric charge and energy in electrical circuits. There are two Kirchhoff's laws: 1) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of currents in a network meeting at a point is zero. 2) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the directed sum of the potential differences around any closed network loop is zero. Mesh analysis and nodal analysis are methods used to solve planar circuits using KCL and KVL. Thevenin's theorem states that any linear electrical network can be reduced to an equivalent circuit of a voltage source in series with a resistor at its terminals.
unit 1.ppt

This document provides an overview of the concepts of Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), Kirchhoff's current law (KCL), and nodal analysis that will be used in a lab involving circuit simulation and calculations. It includes:
- An outline of the lab activities over two weeks involving building circuits in Multisim, measuring voltages and currents, verifying KVL and KCL, and performing nodal analysis calculations.
- Explanations and examples of KVL, KCL, wye-delta transformations, and the definitions of current entering and leaving a node in nodal analysis.
- Examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze simple circuits and setting up the nodal
ECA - Lecture 03

1) The document discusses basic circuit analysis techniques including circuit abstraction, voltage, current, resistance, nodes, branches, loops, and Kirchhoff's laws.
2) Key circuit concepts covered are open and short circuits, voltage and current division, and mesh analysis.
3) Mesh analysis involves identifying all loops in a circuit, labeling loop currents, applying Kirchhoff's laws, and solving equations to determine the currents through each component.
KVL & KCL

This is a ppt of a college project of the topic kvl and kcl ..do read this..i have such interest in science projects and do maake aa lot of money by doing freelancing in embedded system so make sure to check this ppt for more updtes
Nodal Analysis.pptx

The document discusses nodal analysis, a technique for solving electrical circuits using node voltages as variables. It provides examples to demonstrate the steps of nodal analysis: 1) selecting a reference node, 2) assigning node voltages, 3) writing nodal equations using Kirchhoff's Current Law, and 4) solving the nodal equations to determine the node voltages. Additional examples show how to use nodal analysis to find branch currents and power dissipation once the node voltages are known. The document also introduces the inspection method for nodal analysis, which involves converting voltage sources to current sources and defining self and mutual conductances between nodes.
Circuit theory 1-c3-analysis methods

1. Nodal analysis can be used to analyze the circuit. There are 3 non-reference nodes so 3 node voltage equations are required. (2) The node voltage equations relate the node voltages (v1, v2, v3) to the independent current sources (I1, I2) through the conductance matrix. (3) Writing the equations in matrix form produces: Gv=i where G is the 3x3 conductance matrix, v is the 3x1 node voltage vector, and i is the 3x1 independent current source vector.
99992505.pdf

This document discusses biasing circuits for BJTs. It begins by explaining that biasing circuits apply DC voltages to establish fixed operating points for transistors. This allows them to operate in the linear region. It then discusses several common biasing circuits: fixed bias, emitter-stabilized bias, and voltage divider bias. The fixed bias circuit uses two resistors and provides DC paths. The emitter-stabilized bias adds a resistor at the emitter for improved stability. The voltage divider bias uses a voltage divider network to provide DC voltages, making the operating point largely independent of transistor beta. It analyzes examples of each circuit type and discusses how to determine key voltages and currents like the Q-point, VCE, and
Network theorems by adi

This document discusses several network theorems used in circuit analysis including:
- Kirchhoff's laws which deal with conservation of charge and energy. Kirchhoff's current law states the algebraic sum of currents at a node is zero. Kirchhoff's voltage law states the algebraic sum of voltages around a closed loop is zero.
- Mesh and nodal analysis which use Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's law to set up systems of equations to solve for unknown currents and voltages.
- The superposition theorem which allows breaking a circuit with multiple sources into simpler circuits with one source each in order to determine the total response as the sum of the individual source responses. It applies to linear circuits but not power calculations
Circuit lab 6 kirchoff’s current law (kcl)@taj

Circuit lab 6 kirchoff’s current law (kcl)@taj
.
This lecture is from my class lectures in IIT-JU.
.
Find me:
Website: https://www.tajimiitju.blogspot.com
Linked in: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tajimiitju
Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tajim_Md_Niamat_Ullah_Akhund
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/tajimiitju?sub_confirmation=1
Slideshare: https://www.slideshare.net/TajimMdNiamatUllahAk
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tajim.mohammad
Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/users/tajimiitju
Google+: plus.google.com/+tajimiitju
Email: tajim.mohammad.3@gmail.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Tajim53
Example an op amp circuit analysis lecture

This document discusses analyzing an op-amp circuit to determine the output voltage. It presents the circuit and walks through applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) along with device equations to set up 12 equations with 12 unknowns. It solves the equations step-by-step to arrive at the "right equation" of vout = 14/3vin - 2vin. Alternatively, the document shows the circuit can be analyzed using superposition to obtain the same output voltage equation.
Topic 1 b_basic_concepts_and_theorem

This document provides an overview of equivalent circuits and circuit analysis techniques including node-voltage analysis, mesh analysis, and dealing with dependent and independent sources. It defines equivalent circuits as circuits that can replace one another without changing the external behavior of the overall circuit. It also describes node-voltage and mesh analysis, specifying how to write equations for each method by applying Kirchhoff's laws. Techniques for handling dependent sources and circuits with no path to ground are discussed. Examples demonstrate transforming between delta-wye configurations and using the different analysis methods to solve for voltages and currents.
Circuit lab 5 kirchoff’s voltage law (kvl)@taj

Circuit lab 5 kirchoff’s voltage law (kvl)@taj
.
This lecture is from my class lectures in IIT-JU.
.
Find me:
Website: https://www.tajimiitju.blogspot.com
Linked in: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tajimiitju
Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tajim_Md_Niamat_Ullah_Akhund
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/tajimiitju?sub_confirmation=1
Slideshare: https://www.slideshare.net/TajimMdNiamatUllahAk
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tajim.mohammad
Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/users/tajimiitju
Google+: plus.google.com/+tajimiitju
Email: tajim.mohammad.3@gmail.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Tajim53
Bai thi nghiem_linear_circuit_cttt

This document provides instructions for an experiment involving Kirchhoff's Current and Voltage Laws. The objectives are to learn and apply Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, obtain further practice with electrical measurements, and compare results with calculations and simulations. The experiment uses a circuit with four resistors to apply the two Kirchhoff's Laws and calculate voltages and currents at various points. Students are instructed to use the laws to derive equations relating node voltages, solve them through calculation and simulation, measure resistor values, and compare results.
Capacitors and inductors linear circuit analysis

This document provides an introduction to capacitors and inductors. It discusses how capacitors store electric charge and inductors store magnetic energy. Key points include:
- Capacitors oppose changes in voltage by accumulating electric charge on conducting plates separated by a dielectric. The capacitance depends on the plate area, distance between plates, and dielectric material.
- Inductors oppose changes in current. They are formed from coils of conducting wire that generate magnetic fields when current flows.
- Circuit analysis techniques used for resistors can also be applied to circuits containing capacitors and inductors. Energy can be stored in the electric fields of capacitors and magnetic fields of inductors.
- Capacitors and inductors
STATE-SPACE AVERAGING METHOD 

Prof. Cuk invited talk at APEC 2011 plenary session to celebrate
35 years of his creation of this modeling and analysis method.
This talk was also recorded on video by IEEE.tv and can be viewed together. Here is a link to that video.
https://youtu.be/BLx57J2fF5w
Note: first few minutes of the video is Prof. Cuk's interview made after his presentation. This is thern followed by full 25 minutes presentation, which can be followed by the enclosed 67 slides.
Lecture 4 methods_of_analysis

This document discusses node and mesh analysis techniques for solving circuit problems. Node analysis involves applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) at nodes and solving the resulting equations. Mesh analysis involves labeling mesh currents, applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) in each mesh, and solving for the unknown currents. Examples are provided for both node and mesh analysis. Common methods for solving the linear equations generated include substitution, determinants, calculators, and numerical methods.
BBR 2024 Summer Sessions Interview Training

Qualitative research interview training by Professor Katrina Pritchard and Dr Helen Williams
ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...

Denis is a dynamic and results-driven Chief Information Officer (CIO) with a distinguished career spanning information systems analysis and technical project management. With a proven track record of spearheading the design and delivery of cutting-edge Information Management solutions, he has consistently elevated business operations, streamlined reporting functions, and maximized process efficiency.
Certified as an ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) Lead Implementer, Data Protection Officer, and Cyber Risks Analyst, Denis brings a heightened focus on data security, privacy, and cyber resilience to every endeavor.
His expertise extends across a diverse spectrum of reporting, database, and web development applications, underpinned by an exceptional grasp of data storage and virtualization technologies. His proficiency in application testing, database administration, and data cleansing ensures seamless execution of complex projects.
What sets Denis apart is his comprehensive understanding of Business and Systems Analysis technologies, honed through involvement in all phases of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). From meticulous requirements gathering to precise analysis, innovative design, rigorous development, thorough testing, and successful implementation, he has consistently delivered exceptional results.
Throughout his career, he has taken on multifaceted roles, from leading technical project management teams to owning solutions that drive operational excellence. His conscientious and proactive approach is unwavering, whether he is working independently or collaboratively within a team. His ability to connect with colleagues on a personal level underscores his commitment to fostering a harmonious and productive workplace environment.
Date: May 29, 2024
Tags: Information Security, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, Artificial Intelligence, GDPR
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Find out more about ISO training and certification services
Training: ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management System - EN | PECB
ISO/IEC 42001 Artificial Intelligence Management System - EN | PECB
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - Training Courses - EN | PECB
Webinars: https://pecb.com/webinars
Article: https://pecb.com/article
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more information about PECB:
Website: https://pecb.com/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/pecb/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PECBInternational/
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/PECBCERTIFICATION
More Related Content
Similar to lecture14.ppt
4 kirchoff law

Kirchoff's laws are foundational circuit analysis techniques. Kirchoff announced two laws in 1854:
(1) Kirchoff's Current Law (KCL) states that the sum of currents entering a node equals the sum leaving;
(2) Kirchoff's Voltage Law (KVL) states that the algebraic sum of voltages in a closed loop is zero.
Circuit analysis methods like Node Analysis and Mesh Analysis apply KCL and KVL to write equations relating currents and voltages in a circuit.
beee final.ppt

Nodal analysis is a method for analyzing electrical circuits by writing Kirchhoff's current law equations at each node. It involves selecting a reference node, assigning voltages to other nodes, writing KCL equations for each non-reference node, and solving the equations simultaneously to determine the node voltages. Examples show how to set up KCL equations at each node, including combining nodes connected by a voltage source into a supernode. Solving the nodal analysis equations provides the voltage across every element in the circuit.
3- Ch03- Methods Of Analysis-Sadiku

1) Nodal analysis is a circuit analysis technique that uses node voltages as variables. It involves applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) at each node to obtain equations relating the node voltages.
2) To perform nodal analysis, a reference node is selected and assigned a voltage of 0 V. Voltages of other nodes are assigned with respect to the reference node. Then, KCL is applied at each non-reference node to obtain equations.
3) Ohm's law is used to express branch currents in terms of node voltages. This results in a system of simultaneous equations that can be solved for the unknown node voltages.
Circuit laws & network theorems

Kirchhoff's laws deal with the conservation of charge and energy in electrical circuits. There are two Kirchhoff's laws:
1. Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of currents in a network meeting at a point is zero.
2. Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the directed sum of the potential differences around any closed network is zero.
Circuit analysis methods like mesh analysis, nodal analysis, and superposition theorem can be used to solve circuits using Kirchhoff's laws. Mesh analysis uses KVL to analyze loops in a planar circuit. Nodal analysis uses KCL to analyze connections (nodes) in a circuit. Superposition
Circuitlaws i-120122051920-phpapp01

Kirchhoff's laws describe the conservation of electric charge and energy in electrical circuits. There are two Kirchhoff's laws: 1) Kirchhoff's current law (KCL) states that the algebraic sum of currents in a network meeting at a point is zero. 2) Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) states that the directed sum of the potential differences around any closed network loop is zero. Mesh analysis and nodal analysis are methods used to solve planar circuits using KCL and KVL. Thevenin's theorem states that any linear electrical network can be reduced to an equivalent circuit of a voltage source in series with a resistor at its terminals.
unit 1.ppt

This document provides an overview of the concepts of Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL), Kirchhoff's current law (KCL), and nodal analysis that will be used in a lab involving circuit simulation and calculations. It includes:
- An outline of the lab activities over two weeks involving building circuits in Multisim, measuring voltages and currents, verifying KVL and KCL, and performing nodal analysis calculations.
- Explanations and examples of KVL, KCL, wye-delta transformations, and the definitions of current entering and leaving a node in nodal analysis.
- Examples of applying KVL and KCL to analyze simple circuits and setting up the nodal
ECA - Lecture 03

1) The document discusses basic circuit analysis techniques including circuit abstraction, voltage, current, resistance, nodes, branches, loops, and Kirchhoff's laws.
2) Key circuit concepts covered are open and short circuits, voltage and current division, and mesh analysis.
3) Mesh analysis involves identifying all loops in a circuit, labeling loop currents, applying Kirchhoff's laws, and solving equations to determine the currents through each component.
KVL & KCL

This is a ppt of a college project of the topic kvl and kcl ..do read this..i have such interest in science projects and do maake aa lot of money by doing freelancing in embedded system so make sure to check this ppt for more updtes
Nodal Analysis.pptx

The document discusses nodal analysis, a technique for solving electrical circuits using node voltages as variables. It provides examples to demonstrate the steps of nodal analysis: 1) selecting a reference node, 2) assigning node voltages, 3) writing nodal equations using Kirchhoff's Current Law, and 4) solving the nodal equations to determine the node voltages. Additional examples show how to use nodal analysis to find branch currents and power dissipation once the node voltages are known. The document also introduces the inspection method for nodal analysis, which involves converting voltage sources to current sources and defining self and mutual conductances between nodes.
Circuit theory 1-c3-analysis methods

1. Nodal analysis can be used to analyze the circuit. There are 3 non-reference nodes so 3 node voltage equations are required. (2) The node voltage equations relate the node voltages (v1, v2, v3) to the independent current sources (I1, I2) through the conductance matrix. (3) Writing the equations in matrix form produces: Gv=i where G is the 3x3 conductance matrix, v is the 3x1 node voltage vector, and i is the 3x1 independent current source vector.
99992505.pdf

This document discusses biasing circuits for BJTs. It begins by explaining that biasing circuits apply DC voltages to establish fixed operating points for transistors. This allows them to operate in the linear region. It then discusses several common biasing circuits: fixed bias, emitter-stabilized bias, and voltage divider bias. The fixed bias circuit uses two resistors and provides DC paths. The emitter-stabilized bias adds a resistor at the emitter for improved stability. The voltage divider bias uses a voltage divider network to provide DC voltages, making the operating point largely independent of transistor beta. It analyzes examples of each circuit type and discusses how to determine key voltages and currents like the Q-point, VCE, and
Network theorems by adi

This document discusses several network theorems used in circuit analysis including:
- Kirchhoff's laws which deal with conservation of charge and energy. Kirchhoff's current law states the algebraic sum of currents at a node is zero. Kirchhoff's voltage law states the algebraic sum of voltages around a closed loop is zero.
- Mesh and nodal analysis which use Kirchhoff's laws and Ohm's law to set up systems of equations to solve for unknown currents and voltages.
- The superposition theorem which allows breaking a circuit with multiple sources into simpler circuits with one source each in order to determine the total response as the sum of the individual source responses. It applies to linear circuits but not power calculations
Circuit lab 6 kirchoff’s current law (kcl)@taj

Circuit lab 6 kirchoff’s current law (kcl)@taj
.
This lecture is from my class lectures in IIT-JU.
.
Find me:
Website: https://www.tajimiitju.blogspot.com
Linked in: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tajimiitju
Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tajim_Md_Niamat_Ullah_Akhund
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/tajimiitju?sub_confirmation=1
Slideshare: https://www.slideshare.net/TajimMdNiamatUllahAk
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tajim.mohammad
Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/users/tajimiitju
Google+: plus.google.com/+tajimiitju
Email: tajim.mohammad.3@gmail.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Tajim53
Example an op amp circuit analysis lecture

This document discusses analyzing an op-amp circuit to determine the output voltage. It presents the circuit and walks through applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) along with device equations to set up 12 equations with 12 unknowns. It solves the equations step-by-step to arrive at the "right equation" of vout = 14/3vin - 2vin. Alternatively, the document shows the circuit can be analyzed using superposition to obtain the same output voltage equation.
Topic 1 b_basic_concepts_and_theorem

This document provides an overview of equivalent circuits and circuit analysis techniques including node-voltage analysis, mesh analysis, and dealing with dependent and independent sources. It defines equivalent circuits as circuits that can replace one another without changing the external behavior of the overall circuit. It also describes node-voltage and mesh analysis, specifying how to write equations for each method by applying Kirchhoff's laws. Techniques for handling dependent sources and circuits with no path to ground are discussed. Examples demonstrate transforming between delta-wye configurations and using the different analysis methods to solve for voltages and currents.
Circuit lab 5 kirchoff’s voltage law (kvl)@taj

Circuit lab 5 kirchoff’s voltage law (kvl)@taj
.
This lecture is from my class lectures in IIT-JU.
.
Find me:
Website: https://www.tajimiitju.blogspot.com
Linked in: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tajimiitju
Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tajim_Md_Niamat_Ullah_Akhund
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/tajimiitju?sub_confirmation=1
Slideshare: https://www.slideshare.net/TajimMdNiamatUllahAk
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tajim.mohammad
Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/users/tajimiitju
Google+: plus.google.com/+tajimiitju
Email: tajim.mohammad.3@gmail.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Tajim53
Bai thi nghiem_linear_circuit_cttt

This document provides instructions for an experiment involving Kirchhoff's Current and Voltage Laws. The objectives are to learn and apply Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, obtain further practice with electrical measurements, and compare results with calculations and simulations. The experiment uses a circuit with four resistors to apply the two Kirchhoff's Laws and calculate voltages and currents at various points. Students are instructed to use the laws to derive equations relating node voltages, solve them through calculation and simulation, measure resistor values, and compare results.
Capacitors and inductors linear circuit analysis

This document provides an introduction to capacitors and inductors. It discusses how capacitors store electric charge and inductors store magnetic energy. Key points include:
- Capacitors oppose changes in voltage by accumulating electric charge on conducting plates separated by a dielectric. The capacitance depends on the plate area, distance between plates, and dielectric material.
- Inductors oppose changes in current. They are formed from coils of conducting wire that generate magnetic fields when current flows.
- Circuit analysis techniques used for resistors can also be applied to circuits containing capacitors and inductors. Energy can be stored in the electric fields of capacitors and magnetic fields of inductors.
- Capacitors and inductors
STATE-SPACE AVERAGING METHOD 

Prof. Cuk invited talk at APEC 2011 plenary session to celebrate
35 years of his creation of this modeling and analysis method.
This talk was also recorded on video by IEEE.tv and can be viewed together. Here is a link to that video.
https://youtu.be/BLx57J2fF5w
Note: first few minutes of the video is Prof. Cuk's interview made after his presentation. This is thern followed by full 25 minutes presentation, which can be followed by the enclosed 67 slides.
Lecture 4 methods_of_analysis

This document discusses node and mesh analysis techniques for solving circuit problems. Node analysis involves applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) at nodes and solving the resulting equations. Mesh analysis involves labeling mesh currents, applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) in each mesh, and solving for the unknown currents. Examples are provided for both node and mesh analysis. Common methods for solving the linear equations generated include substitution, determinants, calculators, and numerical methods.
Similar to lecture14.ppt (20)
Recently uploaded
BBR 2024 Summer Sessions Interview Training

Qualitative research interview training by Professor Katrina Pritchard and Dr Helen Williams
ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...

Denis is a dynamic and results-driven Chief Information Officer (CIO) with a distinguished career spanning information systems analysis and technical project management. With a proven track record of spearheading the design and delivery of cutting-edge Information Management solutions, he has consistently elevated business operations, streamlined reporting functions, and maximized process efficiency.
Certified as an ISO/IEC 27001: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) Lead Implementer, Data Protection Officer, and Cyber Risks Analyst, Denis brings a heightened focus on data security, privacy, and cyber resilience to every endeavor.
His expertise extends across a diverse spectrum of reporting, database, and web development applications, underpinned by an exceptional grasp of data storage and virtualization technologies. His proficiency in application testing, database administration, and data cleansing ensures seamless execution of complex projects.
What sets Denis apart is his comprehensive understanding of Business and Systems Analysis technologies, honed through involvement in all phases of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). From meticulous requirements gathering to precise analysis, innovative design, rigorous development, thorough testing, and successful implementation, he has consistently delivered exceptional results.
Throughout his career, he has taken on multifaceted roles, from leading technical project management teams to owning solutions that drive operational excellence. His conscientious and proactive approach is unwavering, whether he is working independently or collaboratively within a team. His ability to connect with colleagues on a personal level underscores his commitment to fostering a harmonious and productive workplace environment.
Date: May 29, 2024
Tags: Information Security, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, Artificial Intelligence, GDPR
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Find out more about ISO training and certification services
Training: ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management System - EN | PECB
ISO/IEC 42001 Artificial Intelligence Management System - EN | PECB
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) - Training Courses - EN | PECB
Webinars: https://pecb.com/webinars
Article: https://pecb.com/article
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
For more information about PECB:
Website: https://pecb.com/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/pecb/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/PECBInternational/
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/PECBCERTIFICATION
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/y977uz6bpd3af4qsebv7r9b7s21935vdCommunity pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5

Covered community pharmacy topic of the subject Social and preventive pharmacy for Diploma and Bachelor of pharmacy
ANATOMY AND BIOMECHANICS OF HIP JOINT.pdf

it describes the bony anatomy including the femoral head , acetabulum, labrum . also discusses the capsule , ligaments . muscle that act on the hip joint and the range of motion are outlined. factors affecting hip joint stability and weight transmission through the joint are summarized.
Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling

Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective UpskillingExcellence Foundation for South Sudan
Strategies for Effective Upskilling is a presentation by Chinwendu Peace in a Your Skill Boost Masterclass organisation by the Excellence Foundation for South Sudan on 08th and 09th June 2024 from 1 PM to 3 PM on each day.How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

Odoo provides an option for creating a module by using a single line command. By using this command the user can make a whole structure of a module. It is very easy for a beginner to make a module. There is no need to make each file manually. This slide will show how to create a module using the scaffold method.
How to Make a Field Mandatory in Odoo 17

In Odoo, making a field required can be done through both Python code and XML views. When you set the required attribute to True in Python code, it makes the field required across all views where it's used. Conversely, when you set the required attribute in XML views, it makes the field required only in the context of that particular view.
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশের অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা ২০২৪ [Bangladesh Economic Review 2024 Bangla.pdf] কম্পিউটার , ট্যাব ও স্মার্ট ফোন ভার্সন সহ সম্পূর্ণ বাংলা ই-বুক বা pdf বই " সুচিপত্র ...বুকমার্ক মেনু 🔖 ও হাইপার লিংক মেনু 📝👆 যুক্ত ..
আমাদের সবার জন্য খুব খুব গুরুত্বপূর্ণ একটি বই ..বিসিএস, ব্যাংক, ইউনিভার্সিটি ভর্তি ও যে কোন প্রতিযোগিতা মূলক পরীক্ষার জন্য এর খুব ইম্পরট্যান্ট একটি বিষয় ...তাছাড়া বাংলাদেশের সাম্প্রতিক যে কোন ডাটা বা তথ্য এই বইতে পাবেন ...
তাই একজন নাগরিক হিসাবে এই তথ্য গুলো আপনার জানা প্রয়োজন ...।
বিসিএস ও ব্যাংক এর লিখিত পরীক্ষা ...+এছাড়া মাধ্যমিক ও উচ্চমাধ্যমিকের স্টুডেন্টদের জন্য অনেক কাজে আসবে ...
Pengantar Penggunaan Flutter - Dart programming language1.pptx

Pengantar Penggunaan Flutter - Dart programming language1.pptx
South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)

South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)Academy of Science of South Africa
A workshop hosted by the South African Journal of Science aimed at postgraduate students and early career researchers with little or no experience in writing and publishing journal articles.RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS Template 2023-2024 by: Irene S. Rueco
Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Advanced Java[Extra Concepts, Not Difficult].docx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
This is part 2 of my Java Learning Journey. This contains Hashing, ArrayList, LinkedList, Date and Time Classes, Calendar Class and more.
Hindi varnamala | hindi alphabet PPT.pdf

हिंदी वर्णमाला पीपीटी, hindi alphabet PPT presentation, hindi varnamala PPT, Hindi Varnamala pdf, हिंदी स्वर, हिंदी व्यंजन, sikhiye hindi varnmala, dr. mulla adam ali, hindi language and literature, hindi alphabet with drawing, hindi alphabet pdf, hindi varnamala for childrens, hindi language, hindi varnamala practice for kids, https://www.drmullaadamali.com
Recently uploaded (20)
ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...

ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 42001, and GDPR: Best Practices for Implementation and...
BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...

BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ TIẾNG ANH 8 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUCCESS - NĂM HỌC 2023-2024 (CÓ FI...
Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design

Digital Artefact 1 - Tiny Home Environmental Design
Community pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5

Community pharmacy- Social and preventive pharmacy UNIT 5
Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling

Your Skill Boost Masterclass: Strategies for Effective Upskilling
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method
বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf

বাংলাদেশ অর্থনৈতিক সমীক্ষা (Economic Review) ২০২৪ UJS App.pdf
Pengantar Penggunaan Flutter - Dart programming language1.pptx

Pengantar Penggunaan Flutter - Dart programming language1.pptx
Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie

Film vocab for eal 3 students: Australia the movie
South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)

South African Journal of Science: Writing with integrity workshop (2024)
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3
lecture14.ppt
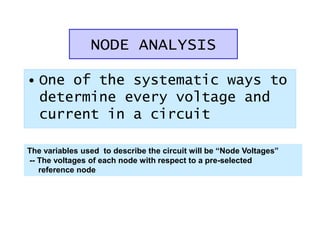
- 1. NODE ANALYSIS • One of the systematic ways to determine every voltage and current in a circuit The variables used to describe the circuit will be “Node Voltages” -- The voltages of each node with respect to a pre-selected reference node
- 2. IT IS INSTRUCTIVE TO START THE PRESENTATION WITH A RECAP OF A PROBLEM SOLVED BEFORE USING SERIES/ PARALLEL RESISTOR COMBINATIONS COMPUTE ALL THE VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS IN THIS CIRCUIT
- 3. SECOND: “BACKTRACK” USING KVL, KCL OHM’S k V I a 6 2 : S OHM' 0 3 2 1 I I I : KCL 3 * 3 I k Vb : S OHM' …OTHER OPTIONS... 4 3 4 * 4 12 4 12 I k V I I b 5 3 4 5 * 3 0 I k V I I I C : S OHM' : KCL k 12 k k 12 || 4 k 6 k k 6 || 6 k V I 12 12 1 ) 12 ( 9 3 3 a V 3 I FIRST REDUCE TO A SINGLE LOOP CIRCUIT
- 4. THE NODE ANALYSIS PERSPECTIVE THERE ARE FIVE NODES. IF ONE NODE IS SELECTED AS REFERENCE THEN THERE ARE FOUR VOLTAGES WITH RESPECT TO THE REFERENCE NODE THEOREM: IF ALL NODE VOLTAGES WITH RESPECT TO A COMMON REFERENCE NODE ARE KNOWN THEN ONE CAN DETERMINE ANY OTHER ELECTRICAL VARIABLE FOR THE CIRCUIT a S a S V V V V V V 1 1 0 b a b a V V V V V V 3 3 0 ______ ca V QUESTION DRILL REFERENCE S V a V b V c V 1 V KVL 3 V KVL 5 V WHAT IS THE PATTERN??? KVL 0 5 b c V V V ONCE THE VOLTAGES ARE KNOWN THE CURRENTS CAN BE COMPUTED USING OHM’S LAW A GENERAL VIEW R v N m R v v v 5 b c V V V
- 5. THE REFERENCE DIRECTION FOR CURRENTS IS IRRELEVANT ' i R v USING THE LEFT-RIGHT REFERENCE DIRECTION THE VOLTAGE DROP ACROSS THE RESISTOR MUST HAVE THE POLARITY SHOWN R v v i N m LAW S OHM' IF THE CURRENT REFERENCE DIRECTION IS REVERSED ... ' R v THE PASSIVE SIGN CONVENTION WILL ASSIGN THE REVERSE REFERENCE POLARITY TO THE VOLTAGE ACROSS THE RESISTOR R v v i m N ' LAW S OHM' ' i i PASSIVE SIGN CONVENTION RULES!
- 6. DEFINING THE REFERENCE NODE IS VITAL S MEANINGLES IS 4V V STATEMENT THE 1 UNTIL THE REFERENCE POINT IS DEFINED BY CONVENTION THE GROUND SYMBOL SPECIFIES THE REFERENCE POINT. V 4 ALL NODE VOLTAGES ARE MEASURED WITH RESPECT TO THAT REFERENCE POINT V 2 _____? 12 V 12 V
- 7. THE STRATEGY FOR NODE ANALYSIS 1. IDENTIFY ALL NODES AND SELECT A REFERENCE NODE 2. IDENTIFY KNOWN NODE VOLTAGES 3. AT EACH NODE WITH UNKNOWN VOLTAGE WRITE A KCL EQUATION (e.g.,SUM OF CURRENT LEAVING =0) 0 : @ 3 2 1 I I I Va 4. REPLACE CURRENTS IN TERMS OF NODE VOLTAGES 0 3 6 9 k V V k V k V V b a a s a AND GET ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS IN THE NODE VOLTAGES ... REFERENCE S V a V b V c V 0 : @ 5 4 3 I I I Vb 0 : @ 6 5 I I Vc 0 9 4 3 k V V k V k V V c b b a b 0 3 9 k V k V V c b c SHORTCUT: SKIP WRITING THESE EQUATIONS... AND PRACTICE WRITING THESE DIRECTLY
- 8. a b c d a V b V c V d V 1 R 3 R 2 R WHEN WRITING A NODE EQUATION... AT EACH NODE ONE CAN CHOSE ARBITRARY DIRECTIONS FOR THE CURRENTS AND SELECT ANY FORM OF KCL. WHEN THE CURRENTS ARE REPLACED IN TERMS OF THE NODE VOLTAGES THE NODE EQUATIONS THAT RESULT ARE THE SAME OR EQUIVALENT 0 0 3 2 1 3 2 1 R V V R V V R V V I I I c b d b b a 0 LEAVING CURRENTS 0 0 3 2 1 3 2 1 R V V R V V R V V I I I c b d b b a 0 NODE INTO CURRENTS 2 I 3 I 1 I a b c d a V b V c V d V 1 R 3 R 2 R ' 2 I ' 3 I ' 1 I 0 0 3 2 1 ' 3 ' 2 ' 1 R V V R V V R V V I I I b c d b a b 0 LEAVING CURRENTS 0 0 3 2 1 ' 3 ' 2 ' 1 R V V R V V R V V I I I b c d b a b 0 NODE INTO CURRENTS WHEN WRITING THE NODE EQUATIONS WRITE THE EQUATION DIRECTLY IN TERMS OF THE NODE VOLTAGES. BY DEFAULT USE KCL IN THE FORM SUM-OF-CURRENTS-LEAVING = 0 THE REFERENCE DIRECTION FOR THE CURRENTS DOES NOT AFFECT THE NODE EQUATION
- 9. CIRCUITS WITH ONLY INDEPENDENT SOURCES HINT: THE FORMAL MANIPULATION OF EQUATIONS MAY BE SIMPLER IF ONE USES CONDUCTANCES INSTEAD OF RESISTANCES. @ NODE 1 0 2 2 1 1 1 R v v R v iA S RESISTANCE USING 0 ) ( 2 1 2 1 1 v v G v G iA ES CONDUCTANC WITH REORDERING TERMS @ NODE 2 REORDERING TERMS THE MODEL FOR THE CIRCUIT IS A SYSTEM OF ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS
- 10. EXAMPLE @ NODE 1 WE VISUALIZE THE CURRENTS LEAVING AND WRITE THE KCL EQUATION REPEAT THE PROCESS AT NODE 2 0 3 1 2 4 1 2 2 R v v R v v i OR VISUALIZE CURRENTS GOING INTO NODE WRITE THE KCL EQUATIONS
- 11. mA 15 A B C k 8 k 8 k 2 k 2 SELECT AS REFERENCE A V B V MARK THE NODES (TO INSURE THAT NONE IS MISSING) ANOTHER EXAMPLE OF WRITING NODE EQUATIONS WRITE KCL AT EACH NODE IN TERMS OF NODE VOLTAGES 0 15 8 2 @ mA k V k V A A A 0 15 2 8 @ mA k V k V B B B
- 12. k V V k V mA V 12 6 4 : @ 2 1 1 1 USING KCL 0 12 6 2 : @ 1 2 2 2 k V V k V mA V BY “INSPECTION” mA V k V k k 4 12 1 12 1 6 1 2 1 mA V k k k 2 12 1 6 1 12 1 2 LEARNING EXTENSION
- 13. mA 6 1 I 2 I 3 I 0 3 6 6 : @ 2 2 2 k V k V mA V 2 12 V V CURRENTS COULD BE COMPUTED DIRECTLY USING KCL AND CURRENT DIVIDER!! 1 2 3 8 3 (6 ) 2 3 6 6 (6 ) 4 3 6 I mA k I mA mA k k k I mA mA k k LEARNING EXTENSION IN MOST CASES THERE ARE SEVERAL DIFFERENT WAYS OF SOLVING A PROBLEM NODE EQS. BY INSPECTION mA V V k 6 2 0 2 1 2 1 mA V k k V 6 3 1 6 1 0 2 1 1 16 V V k V I k V I k V I 3 6 2 2 3 2 2 1 1 Once node voltages are known 1 1 @ : 2 6 0 2 V V mA mA k Node analysis
- 14. 3 nodes plus the reference. In principle one needs 3 equations... …but two nodes are connected to the reference through voltage sources. Hence those node voltages are known!!! …Only one KCL is necessary 0 12 12 6 1 2 3 2 2 k V V k V V k V ] [ 5 . 1 ] [ 6 4 0 ) ( ) ( 2 2 2 1 2 3 2 2 V V V V V V V V V EQUATIONS THE SOLVING Hint: Each voltage source connected to the reference node saves one node equation CIRCUITS WITH INDEPENDENT VOLTAGE SOURCES ] [ 6 ] [ 12 3 1 V V V V THESE ARE THE REMAINING TWO NODE EQUATIONS
- 15. We will use this example to introduce the concept of a SUPERNODE Conventional node analysis requires all currents at a node @V_1 0 6 6 1 S I k V mA @V_2 0 12 4 2 k V mA IS 2 eqs, 3 unknowns...Panic!! The current through the source is not related to the voltage of the source Math solution: add one equation ] [ 6 2 1 V V V Efficient solution: enclose the source, and all elements in parallel, inside a surface. Apply KCL to the surface!!! 0 4 12 6 6 2 1 mA k V k V mA The source current is interior to the surface and is not required We STILL need one more equation ] [ 6 2 1 V V V Only 2 eqs in two unknowns!!! SUPERNODE THE SUPERNODE TECHNIQUE S I
- 16. k 12 / * ] [ 6 0 4 6 12 6 2 1 2 1 V V V mA mA k V k V (2) (1) Equations The ALGEBRAIC DETAILS ... by Multiply Eq(1). in rs denominato Eliminate 1. Solution ] [ 6 ] [ 24 2 2 1 2 1 V V V V V V ] [ 10 ] [ 30 3 1 1 V V V V 2 V eliminate to equations Add 2. ] [ 4 ] [ 6 1 2 V V V V 2 V compute to Eq(2) Use 3.
- 18. V V V V 4 6 4 1 SOURCES CONNECTED TO THE REFERENCE SUPERNODE CONSTRAINT EQUATION V V V 12 2 3 KCL @ SUPERNODE 0 2 ) 4 ( 2 1 2 6 3 3 2 2 k V k V k V k V k 2 / * V V V 2 2 3 3 2 V V V 12 3 2 add and 3 / * V V 38 5 3 mA k V IO 8 . 3 2 3 LAW S OHM' O I V FOR NEEDED NOT IS 2