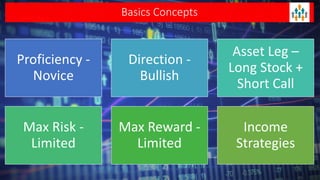
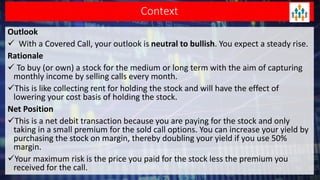
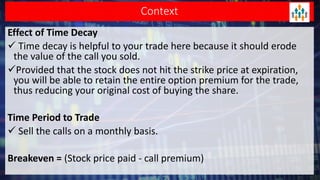
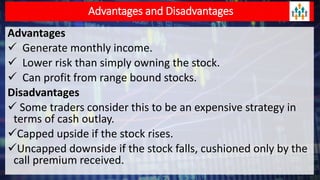
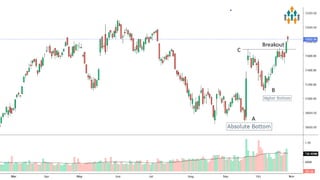
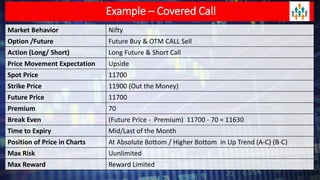
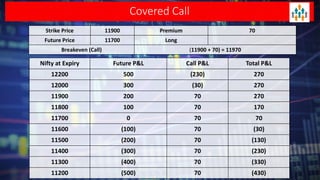
Lecture no 6 discusses the covered call strategy, emphasizing that it is a straightforward yet effective way to generate income while holding stocks, with limited risk and reward profiles. The strategy involves owning a stock and selling call options monthly, generating premium income and employing time decay to benefit. Key points include managing positions according to market trends and the implications of stock movements relative to the strike price.