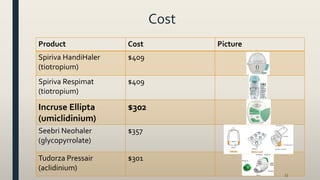
This document provides an overview of newly available COPD medications, including long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) and LAMA/long-acting beta-2 agonist (LABA) combinations. It summarizes the mechanisms of action, clinical evidence and costs of medications like Incruse Ellipta, Seebri Neohaler, Tudorza Pressair, and combinations of LAMAs and LABAs. It recommends Incruse Ellipta as the preferred new LAMA therapy based on lower cost and statistically significant improvement in lung function compared to Spiriva.

















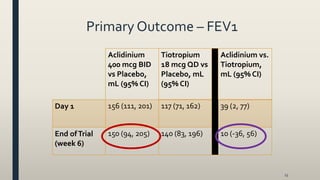





![Primary Outcome –Trough FEV1Value
30
Day 2 28 56 84 85
Drug Umec Tio Umec Tio Umec Tio Umec Tio Umec Tio
n 469 471 453 454 425 432 402 420 392 416
Mean Change from
baseline (mL) [SE]
103
[±8]
91 [±8] 144
[±10]
102
[±10]
136
[±11]
89
[±11]
142
[±11]
86
[±11]
154
[±11]
95 [±11]
Difference vsTio
(mL)
[95% CI]
13 [-9,35] N/A 42
[14,69]
N/A 46
[17,76]
N/A 56
[26,85]
N/A 59
[29,88]
N/A
P -Value 0.254 0.003 0.002 <0.001 <0.001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-30-320.jpg)















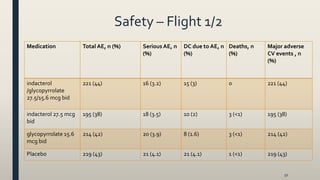
![Results Flight 1/2
51
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly
improved FEV1 AUC0-12 h at week 12 vs mono-components
[103 mL (indacterol 24.8 mcg bid) and 88 mL
(glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid), respectively; all p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved breathlessness at week 12
• Improvement exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) of 1.64 according to transition dyspnea
index (TDI) unit vs placebo [p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid provided a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in health-
related quality of life vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid (1.7 [p=0.019] and 1.5 [p=0.033]unit
improvement according to St. George's respiratory questionnaire (SGRQ), respectively)
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid significantly reduced rescue medication use over 12 weeks vs indacterol 24.8 mcg
bid and glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid by 0.33 and 0.5 puffs/day [p<0.05], respectively](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-51-320.jpg)
![Results
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved FEV1AUC0-12 h at week 12 vs mono-components [103 mL (indacterol 24.8 mcg
bid) and 88 mL (glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid), respectively; all p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly
improved breathlessness at week 12
• Improvement exceeded the minimal clinically important
difference (MCID) of 1.64 according to transition dyspnea index
(TDI) unit vs placebo [p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid provided a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in health-related
quality of life vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid (1.7 [p=0.019] and 1.5 [p=0.033]unit improvement
according to St. George's respiratory questionnaire (SGRQ), respectively)
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid significantly reduced rescue medication use over 12 weeks vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and
glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid by 0.33 and 0.5 puffs/day [p<0.05], respectively
52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-52-320.jpg)
![Results
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved FEV1 AUC0-12 h at week 12 vs mono-components [103 mL (indacterol 24.8 mcg bid) and 88
mL (glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid), respectively; all p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved breathlessness at week 12
• Improvement exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) of 1.64 according to transition dyspnea index (TDI) unit vs placebo [p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid provided a statistically
significant and clinically meaningful improvement in health-
related quality of life vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and
glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid (1.7 [p=0.019] and 1.5 [p=0.033]unit
improvement according to St. George's respiratory questionnaire
(SGRQ), respectively)
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid significantly reduced rescue medication use over 12 weeks vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and glycopyrrolate
15.6 mcg bid by 0.33 and 0.5 puffs/day [p<0.05], respectively
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-53-320.jpg)
![Results
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved FEV1AUC0-12 h at week 12 vs mono-components [103 mL (indacterol 24.8 mcg
bid) and 88 mL (glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid), respectively; all p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate 27.5/15.6 mcg bid significantly improved breathlessness at week 12
• Improvement exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) of 1.64 according to transition dyspnea index (TDI) unit vs placebo
[p<0.001]
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid provided a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in health-related quality of life vs
indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid (1.7 [p=0.019] and 1.5 [p=0.033]unit improvement according to St. George's respiratory
questionnaire (SGRQ), respectively)
• indacterol /glycopyrrolate mcg bid significantly reduced rescue
medication use over 12 weeks vs indacterol 24.8 mcg bid and
glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg bid by 0.33 and 0.5 puffs/day [p<0.05],
respectively
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-54-320.jpg)
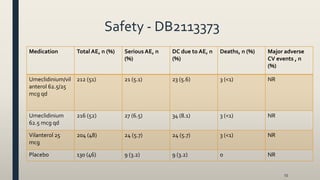
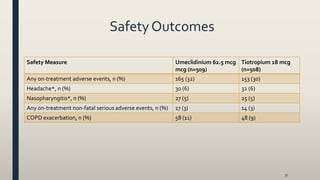
![Results - DB2113373
56
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd significantly improved
trough FEV1 = 52 and 95 mL at week 24 compared with mono-
components (p=0.004 and p<0.001), respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improvedTDI total score at 24 weeks compared with mono-components (0.03 and 0.4 units, respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improved SGRQ total score compared with mono-components at 24 weeks (0.82 and 0.32 units, respectively)
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd reduced rescue medication use over 24 weeks compared with Umeclidinium 62.5 mcg qd (0.6 puffs/day
[p≤0.001]); however, increased use with vilanterol 25 mcg qd (0.1 puffs/day [p<0.05]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-56-320.jpg)
![Result
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd significantly improved trough FEV1 = 52 and 95 mL at week 24
compared with mono-components (p=0.004 and p<0.001), respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd
improvedTDI total score at 24 weeks compared
with mono-components (0.03 and 0.4 units,
respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improved SGRQ total score compared with mono-
components at 24 weeks (0.82 and 0.32 units, respectively)
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd reduced rescue medication use over 24 weeks
compared with Umeclidinium 62.5 mcg qd (0.6 puffs/day [p≤0.001]); however, increased use
with vilanterol 25 mcg qd (0.1 puffs/day [p<0.05]
57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-57-320.jpg)
![Result
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd significantly improved trough FEV1 = 52 and 95 mL at week 24
compared with mono-components (p=0.004 and p<0.001), respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improvedTDI total score at 24 weeks compared with
mono-components (0.03 and 0.4 units, respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improved SGRQ
total score compared with mono-components at 24 weeks
(0.82 and 0.32 units, respectively)
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd reduced rescue medication use over 24 weeks
compared with Umeclidinium 62.5 mcg qd (0.6 puffs/day [p≤0.001]); however, increased use
with vilanterol 25 mcg qd (0.1 puffs/day [p<0.05]
58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-58-320.jpg)
![Result
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd significantly improved trough FEV1 = 52 and
95 mL at week 24 compared with mono-components (p=0.004 and p<0.001),
respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improvedTDI total score at 24 weeks compared with
mono-components (0.03 and 0.4 units, respectively
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd improved SGRQ total score compared with mono-
components at 24 weeks (0.82 and 0.32 units, respectively)
• Umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg qd reduced rescue
medication use over 24 weeks compared with
Umeclidinium 62.5 mcg qd (0.6 puffs/day [p≤0.001]);
however, increased with vilanterol 25 mcg qd (0.1
puffs/day [p<0.05] 59](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-59-320.jpg)
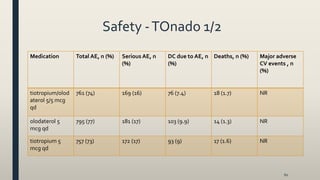
![Results -TOnado 1/2
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved
both primary end points at 24 weeks compared with mono-
components (FEV1= 85 and 60 mL for olodaterol 5 mcg qd
and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively [all p<0.001]
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improvedTDI score at week 24 compared with mono-components (0.42
units [p<0.005] and 0.36 units [p<0.05] vs olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved SGRQ total score compared with olodaterol 5 mcg qd and
tiotropium 5 mcg qd (1.7 units [p<0.01] and 1.2 [p<0.05], respectively)
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd reduced the weekly mean daily (24 h) rescue medication use vs the mono-
components throughout the 52 week treatment, but no values or statistical analysis has been reported
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-61-320.jpg)
![Results
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved both primary end points and 24 weeks compared with mono-components
(FEV1= 85 and 60 mL for olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively [all p<0.001]
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improvedTDI
score at week 24 compared with mono-components (0.42 units
[p<0.005] and 0.36 units [p<0.05] vs olodaterol 5 mcg qd and
tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved SGRQ total score compared with olodaterol 5 mcg qd and
tiotropium 5 mcg qd (1.7 units [p<0.01] and 1.2 [p<0.05], respectively)
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd reduced the weekly mean daily (24 h) rescue medication use vs the mono-
components throughout the 52 week treatment, but no values or statistical analysis has been reported
62](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-62-320.jpg)
![Results
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved both primary end points and 24 weeks compared with mono-components (FEV1= 85 and 60
mL for olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively [all p<0.001]
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improvedTDI score at week 24 compared with mono-components (0.42 units [p<0.005] and 0.36 units
[p<0.05] vs olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved SGRQ
total score compared with olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5
mcg qd (1.7 units [p<0.01] and 1.2 units [p<0.05], respectively)
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd reduced the weekly mean daily (24 h) rescue medication use vs the mono-components throughout the 52 week
treatment, but no values or statistical analysis has been reported
63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-63-320.jpg)
![Results
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved both primary end points and 24 weeks compared with mono-components
(FEV1= 85 and 60 mL for olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively [all p<0.001]
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improvedTDI score at week 24 compared with mono-components (0.42 units
[p<0.005] and 0.36 units [p<0.05] vs olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5 mcg qd, respectively
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd significantly improved SGRQ total score compared with olodaterol 5 mcg qd and tiotropium 5
mcg qd (1.7 units [p<0.01] and 1.2 [p<0.05], respectively)
• tiotropium/olodaterol 5/5 mcg qd reduced the weekly mean daily
(24 h) rescue medication use vs the mono-components
throughout the 52 week treatment, but no values or statistical
analysis has been reported
64](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7eb26538-ef79-46fc-af45-116d5580d5cf-161028192256/85/lecture-new-COPD-meds-64-320.jpg)








