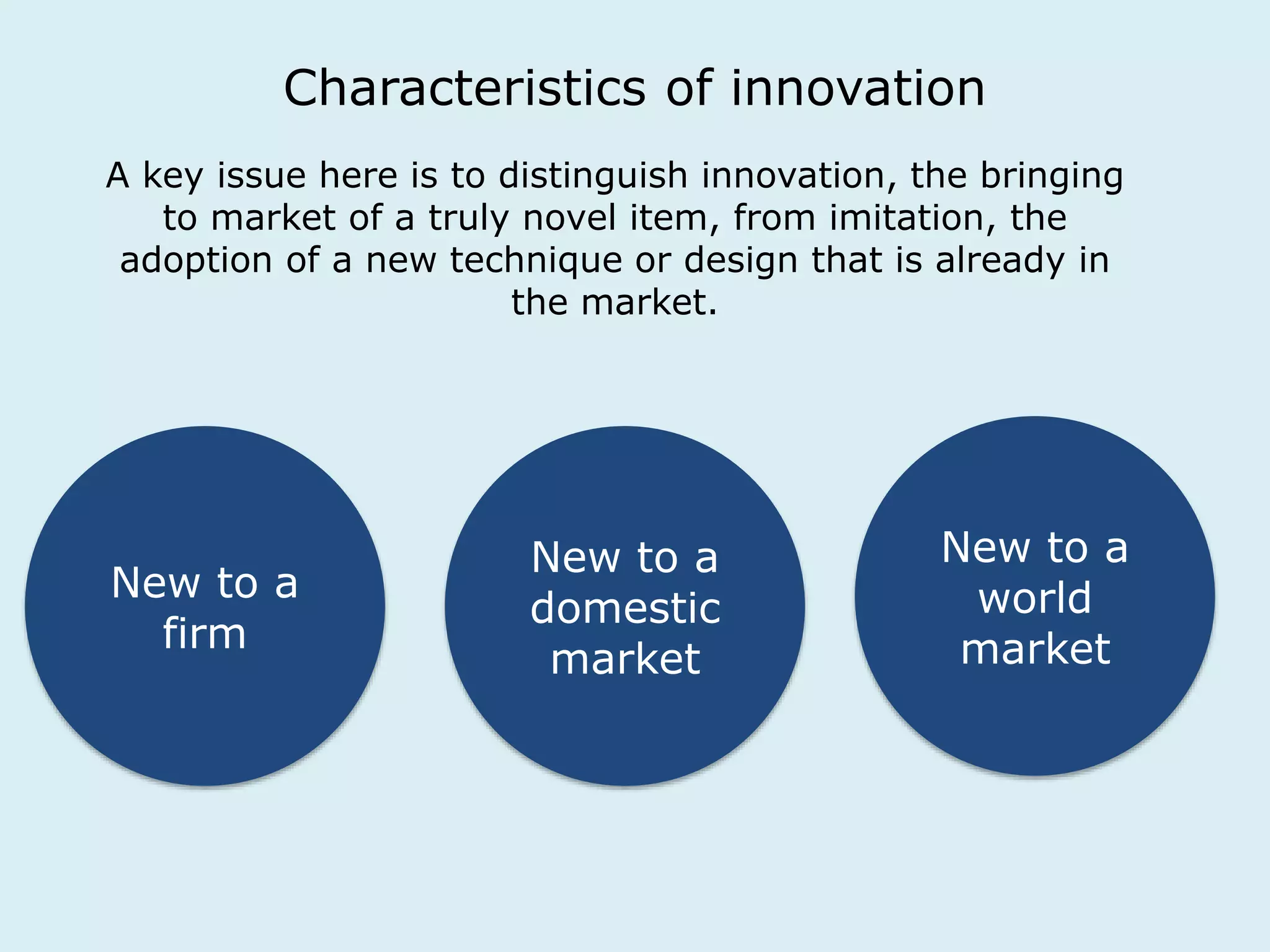
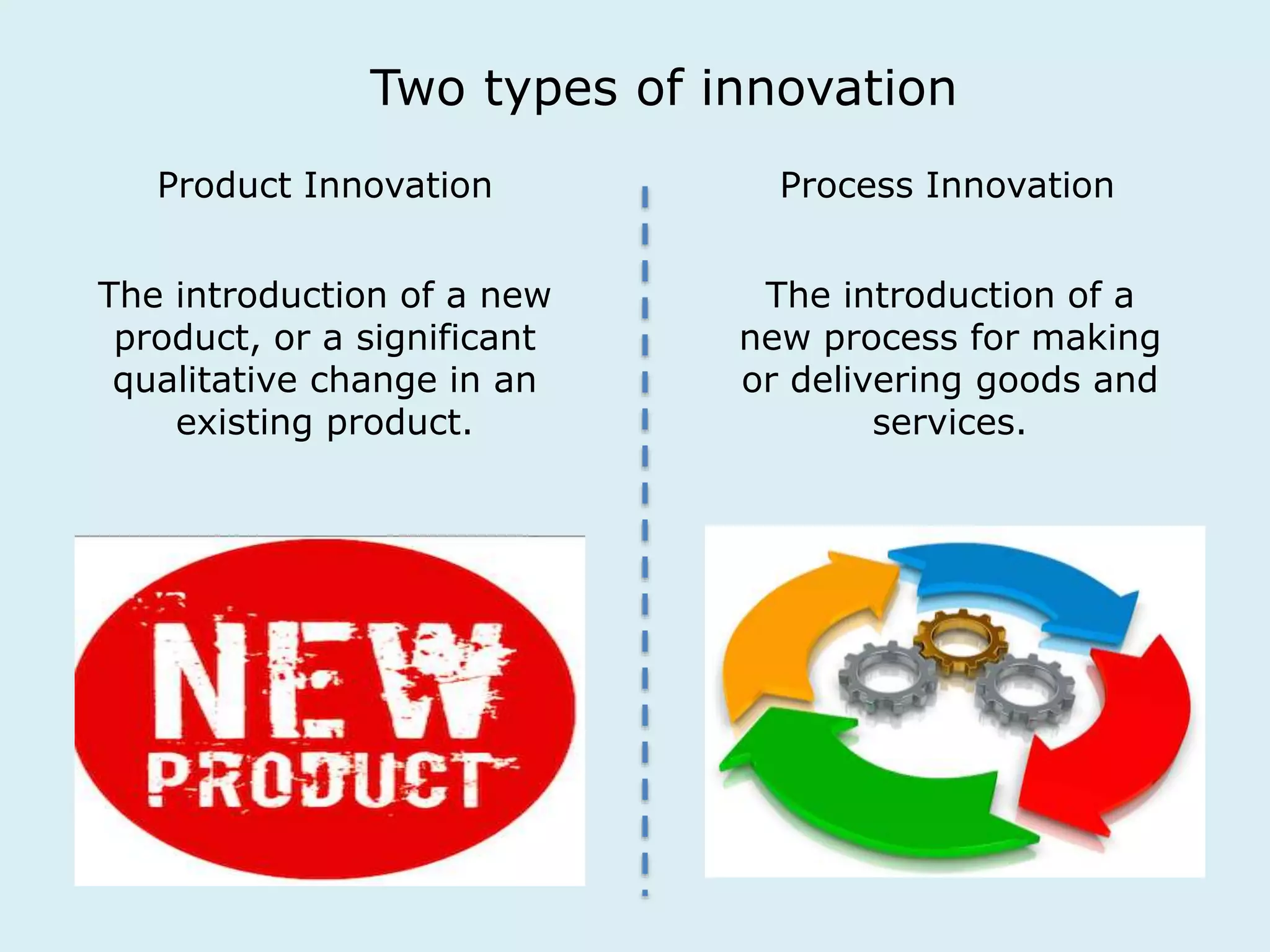
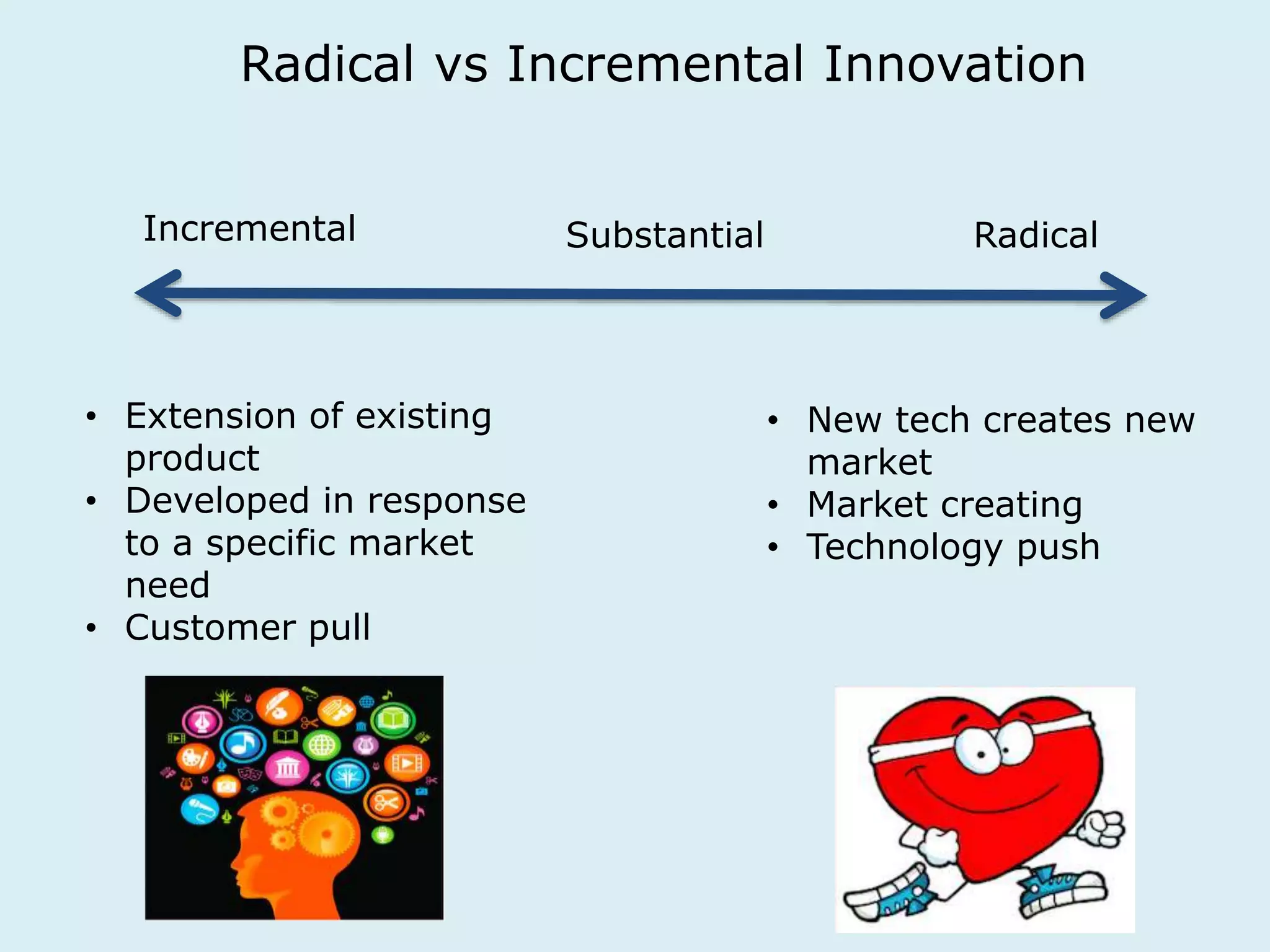
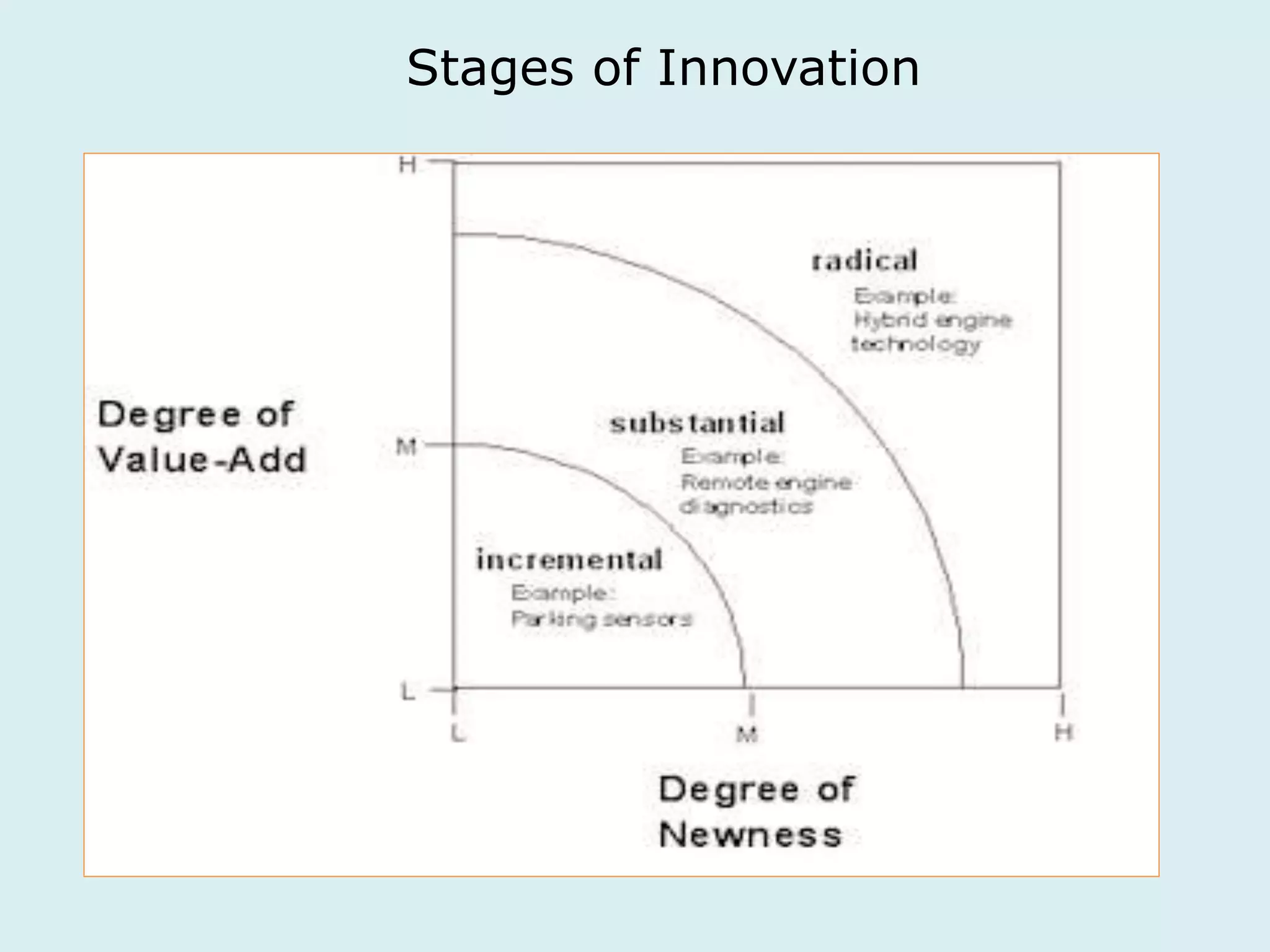
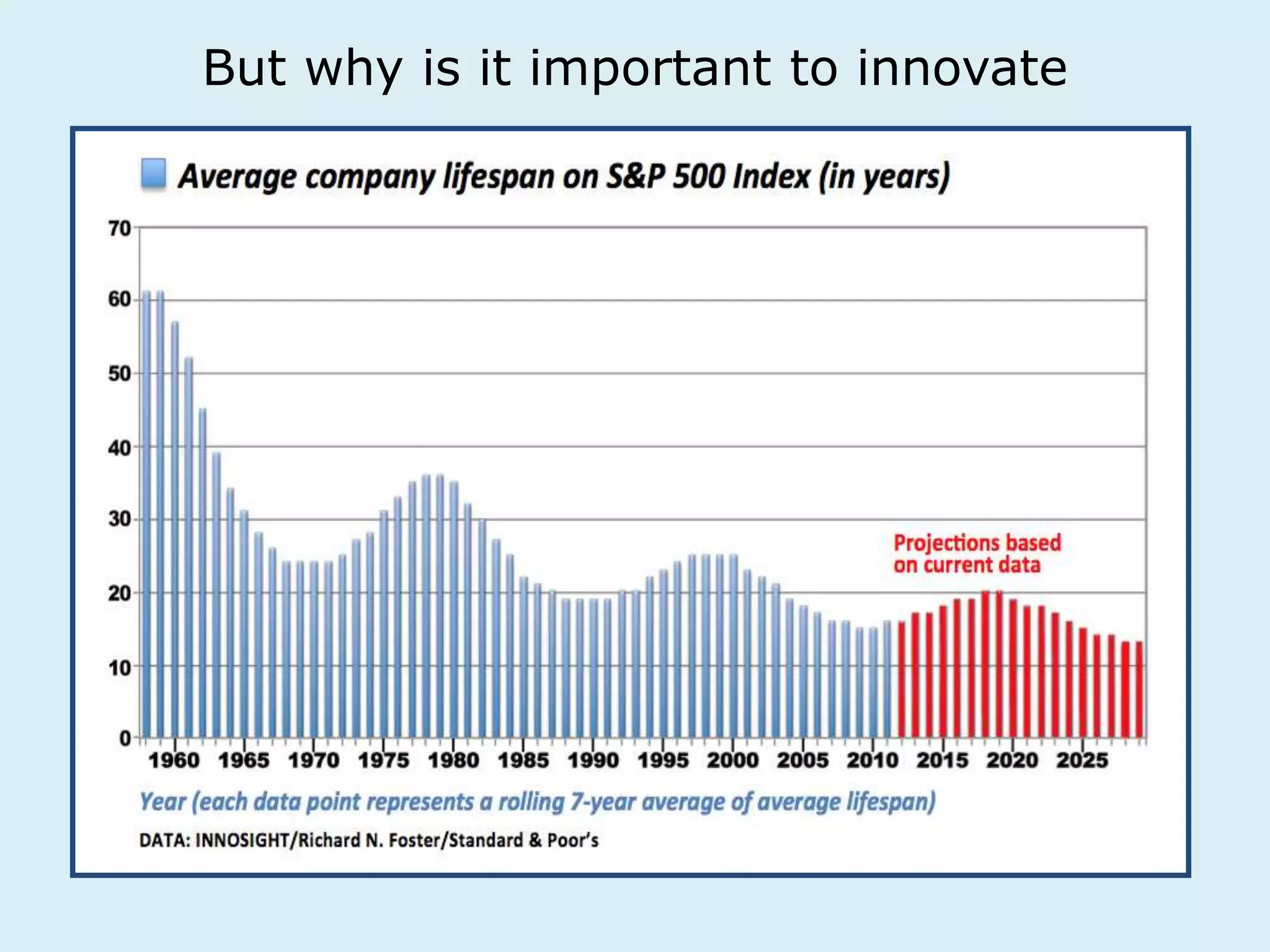
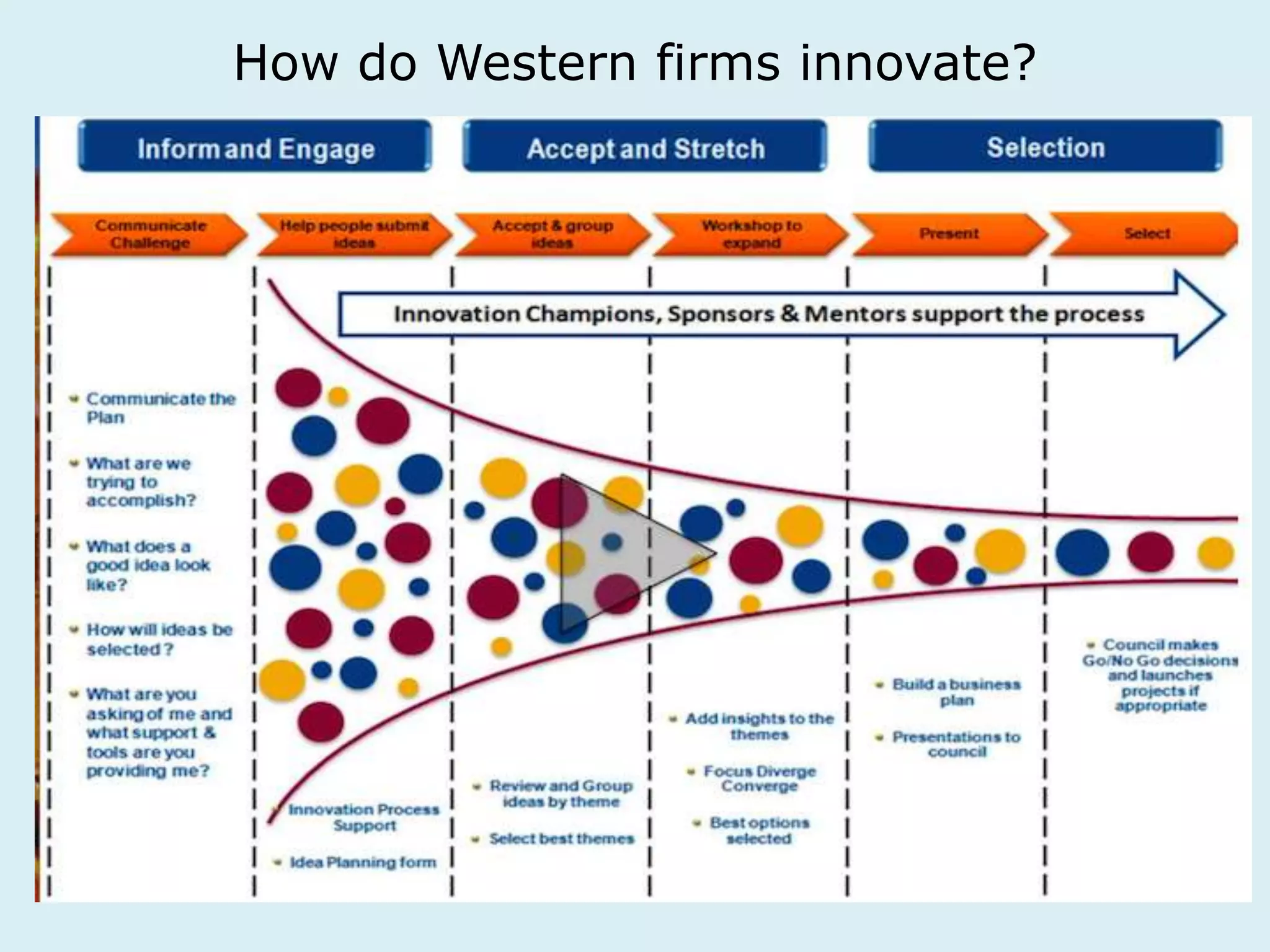
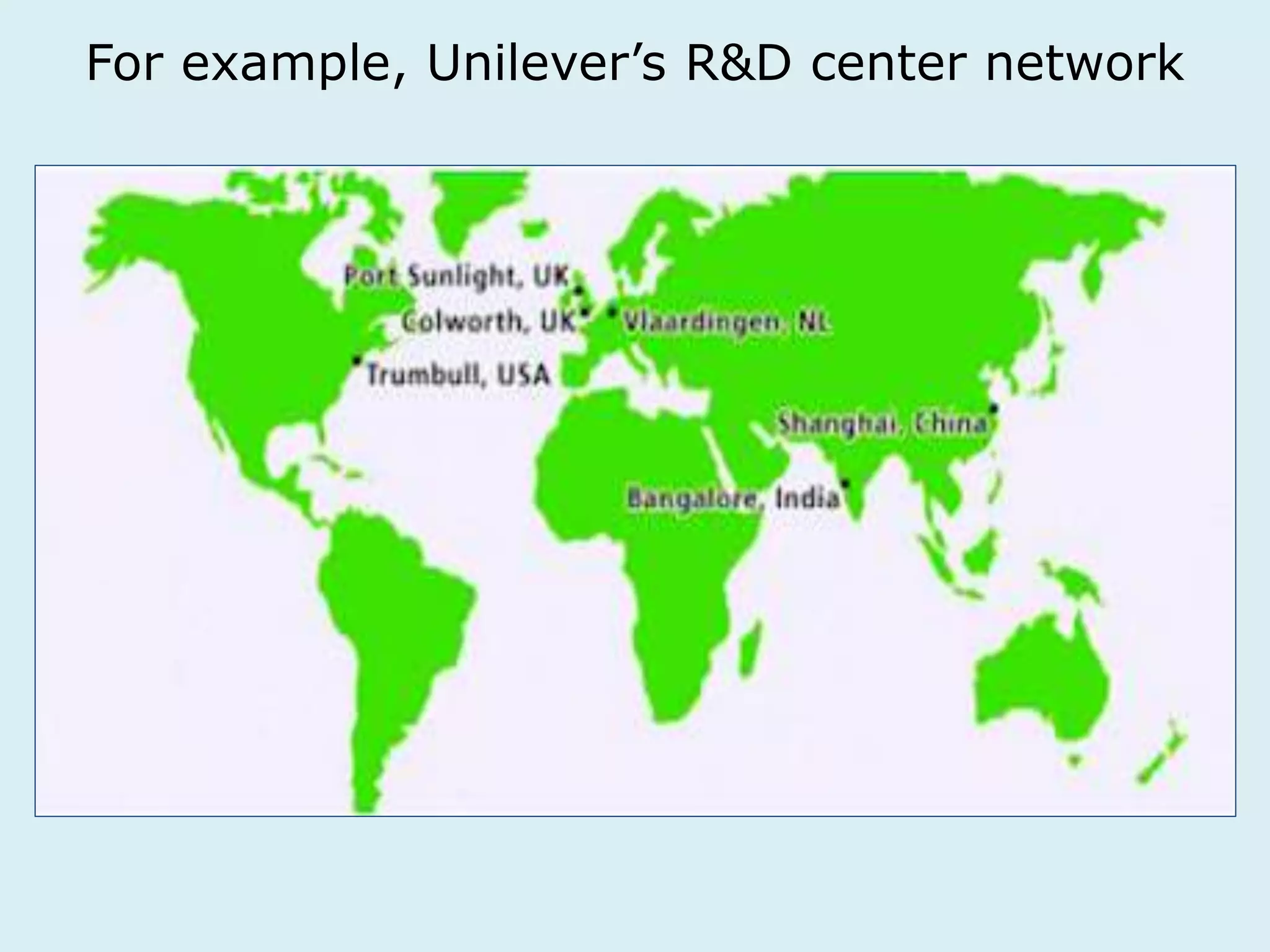
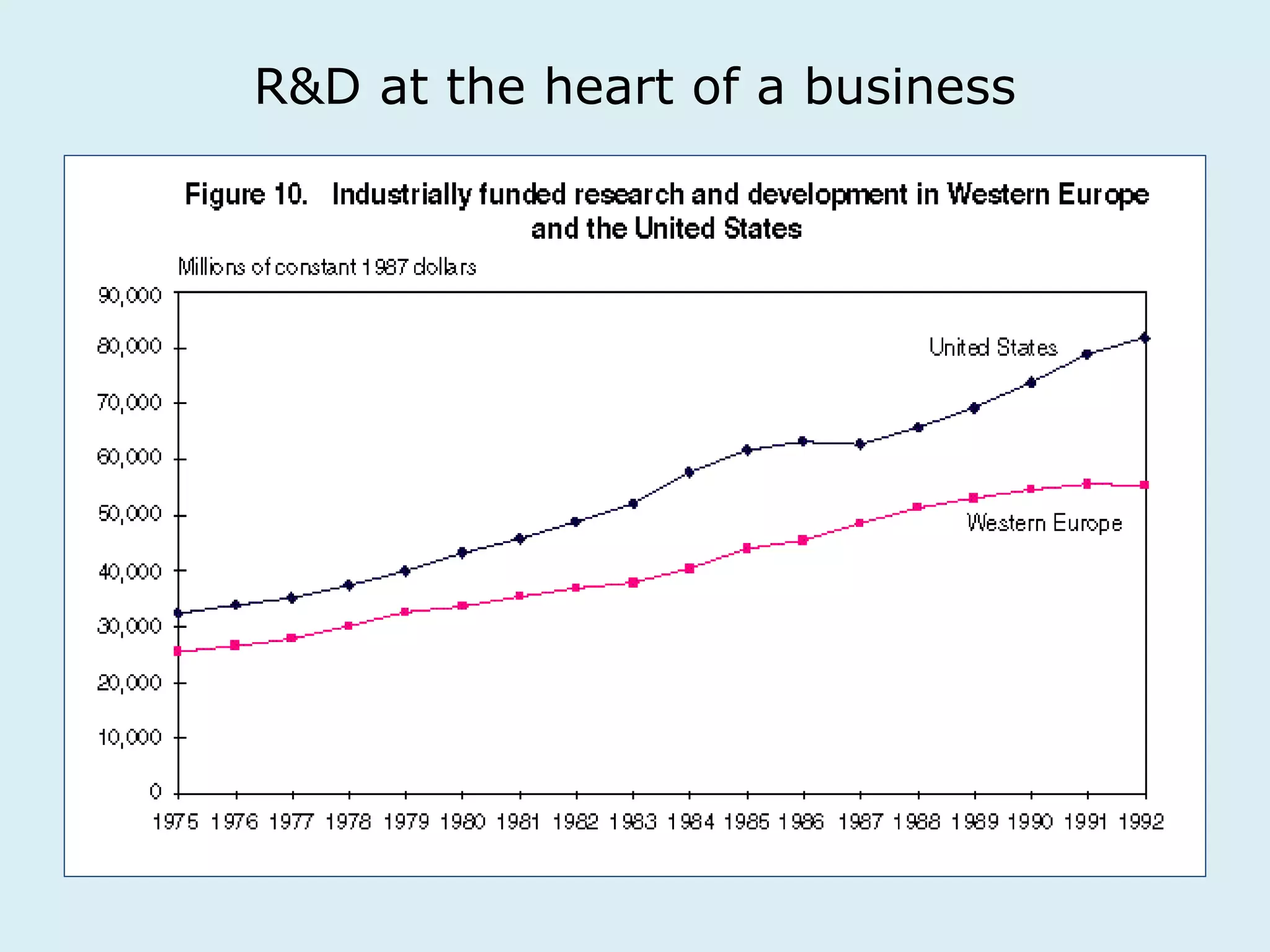
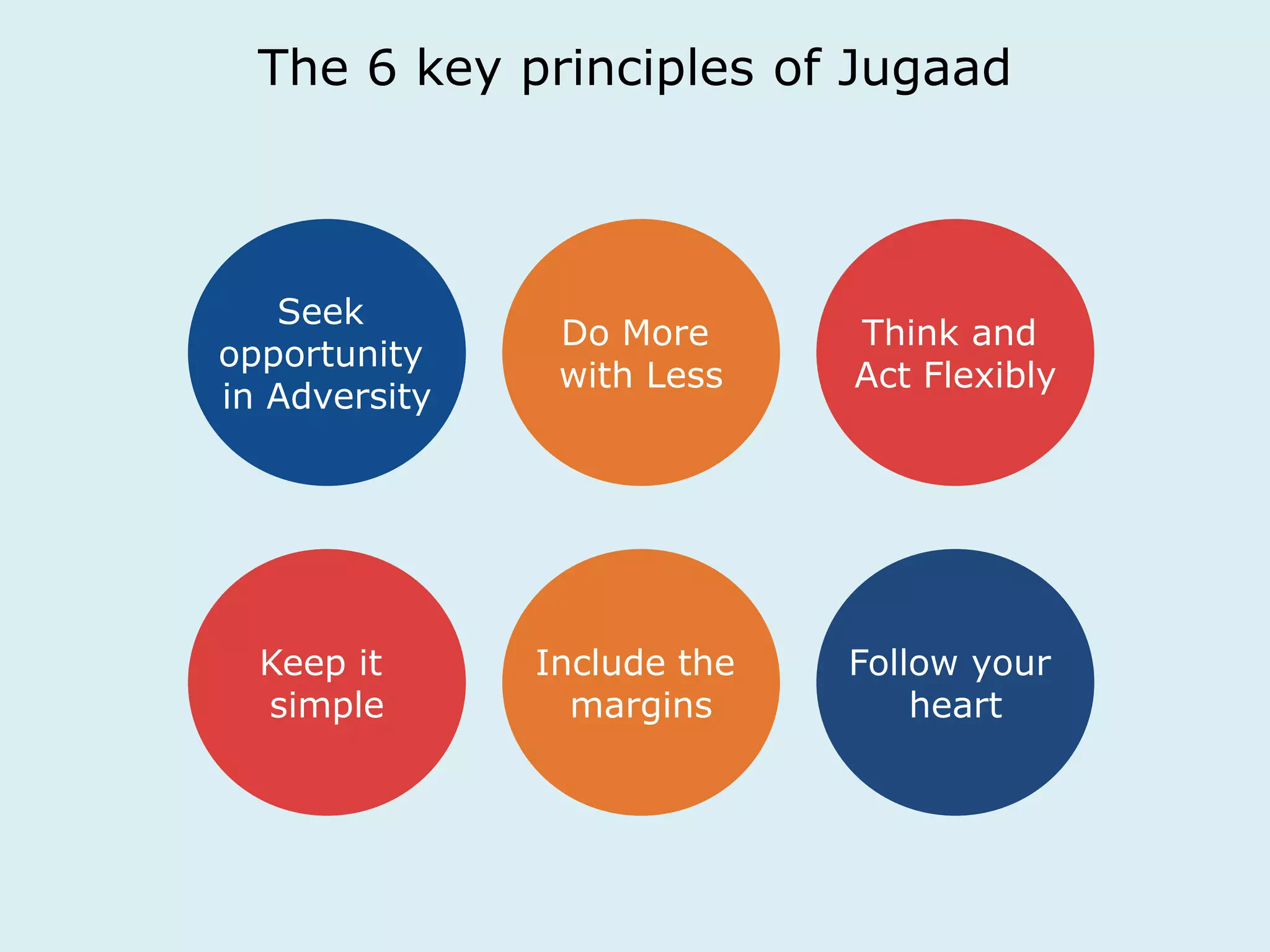
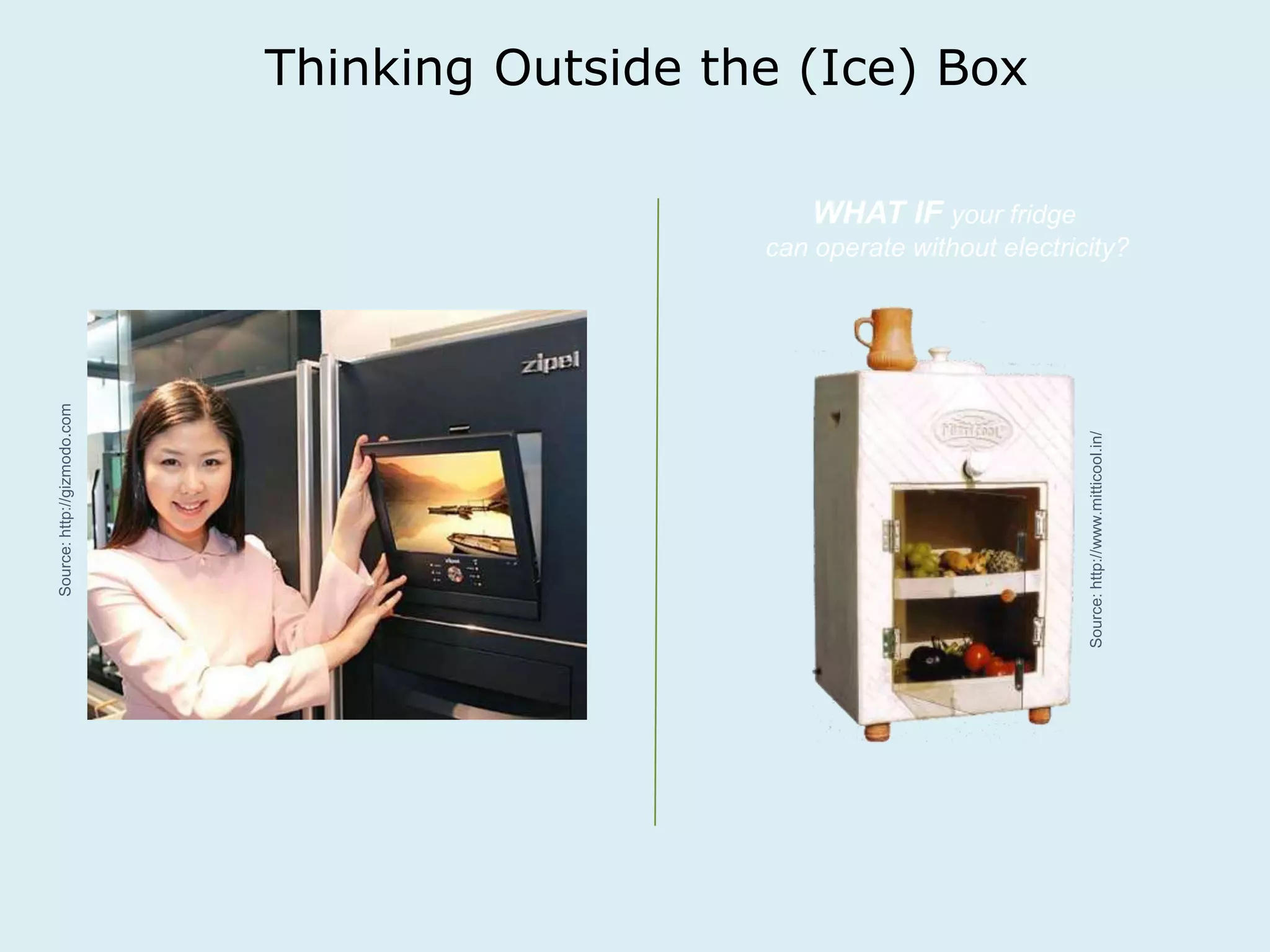
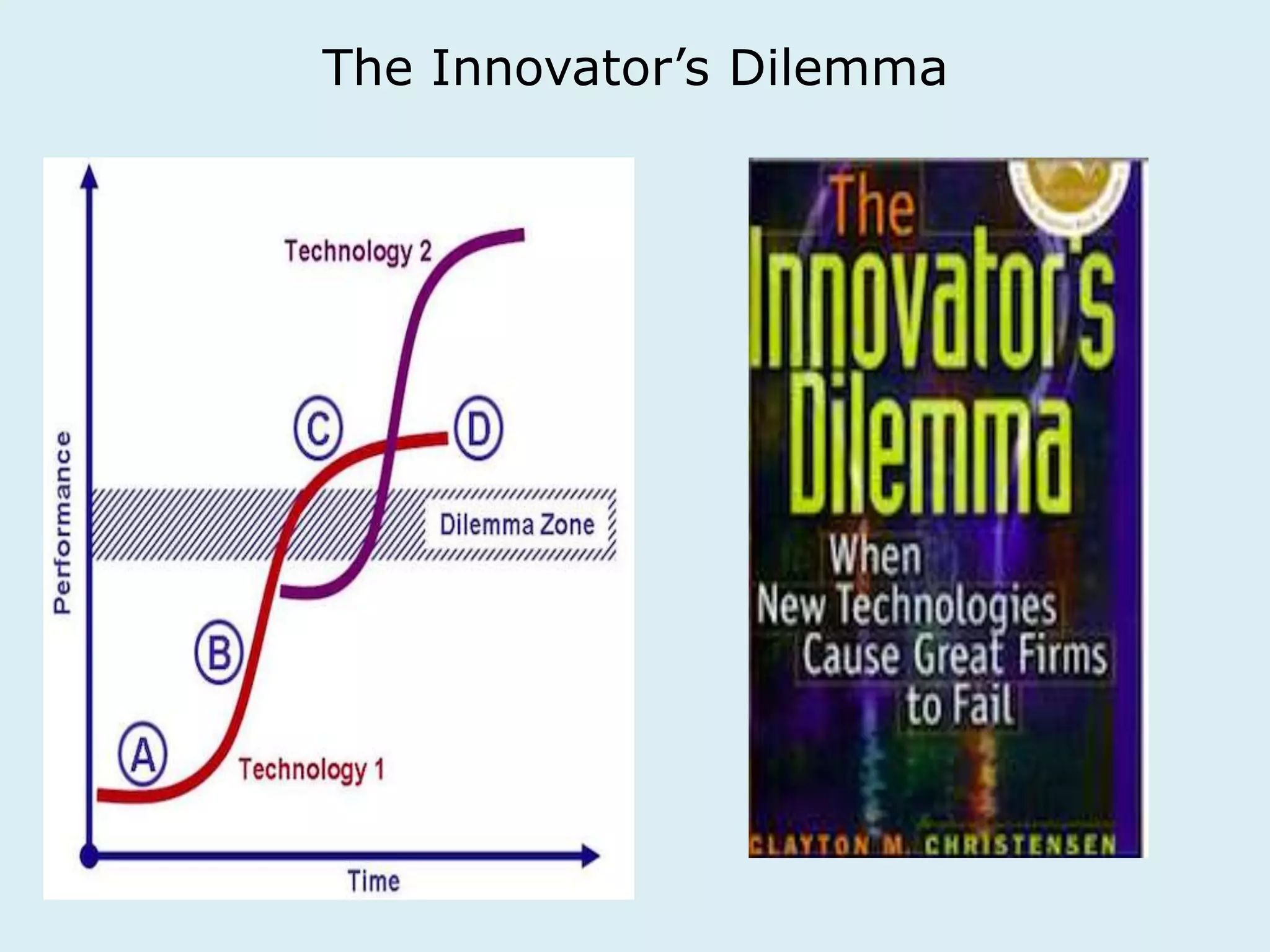
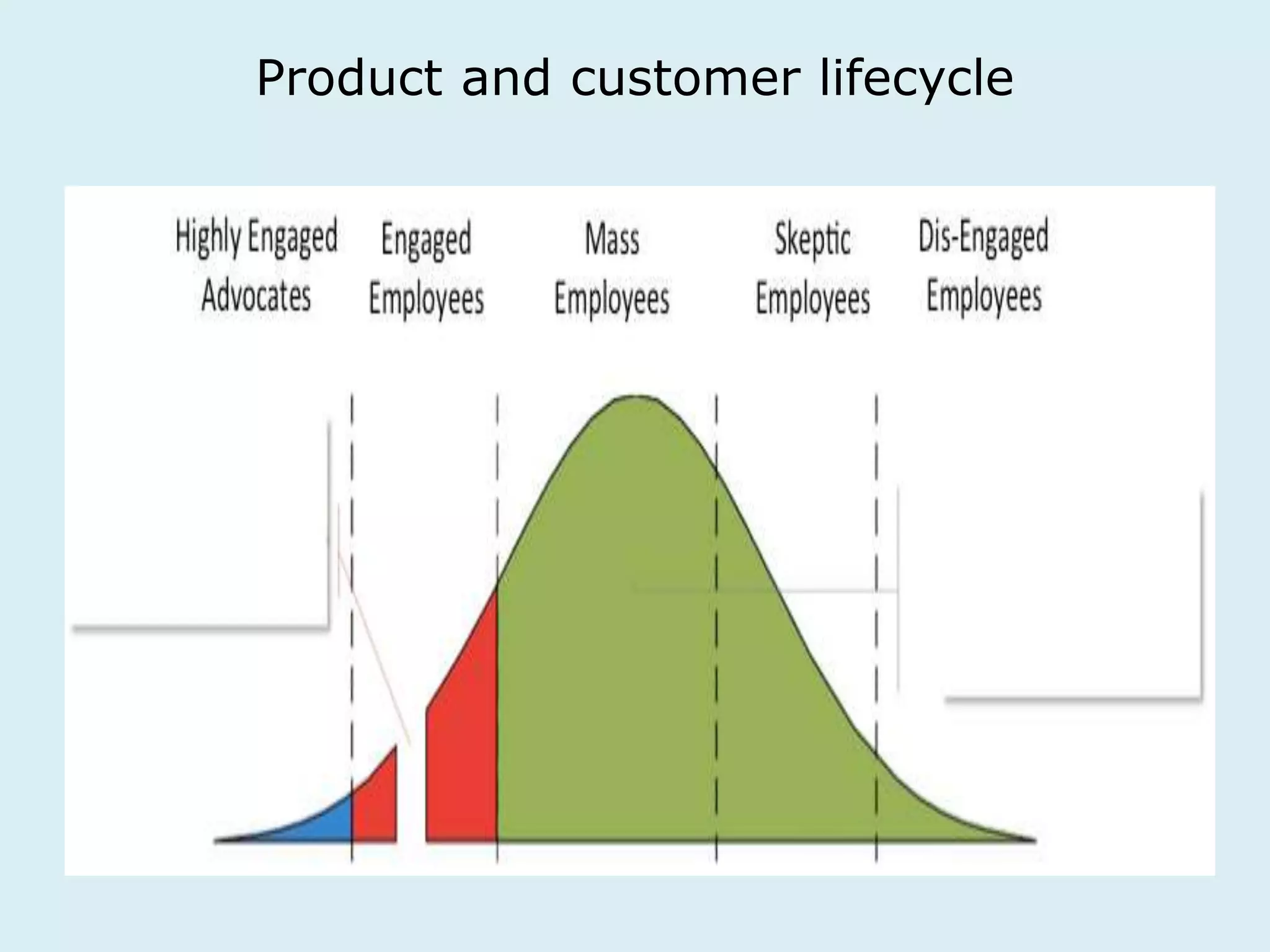
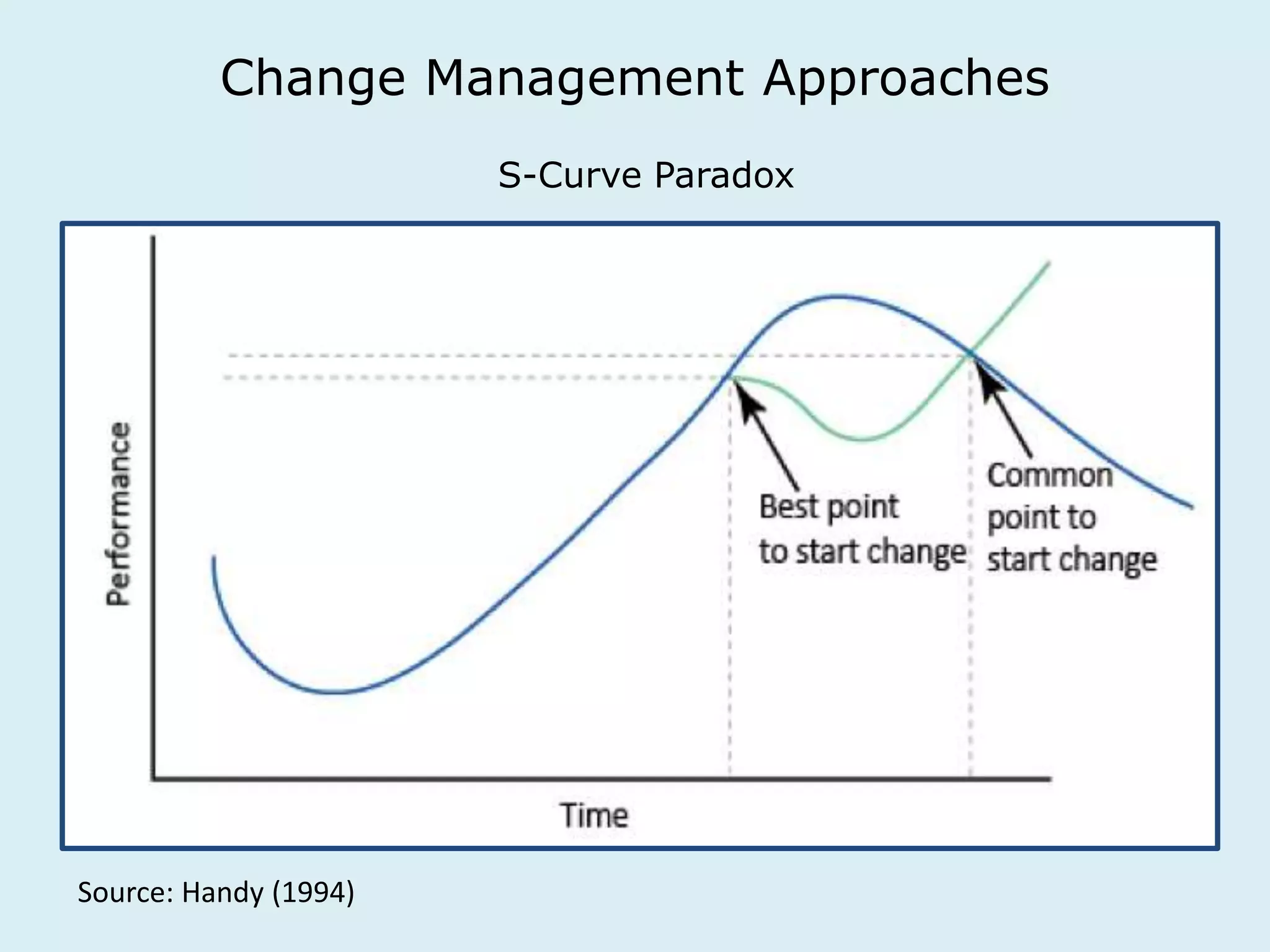
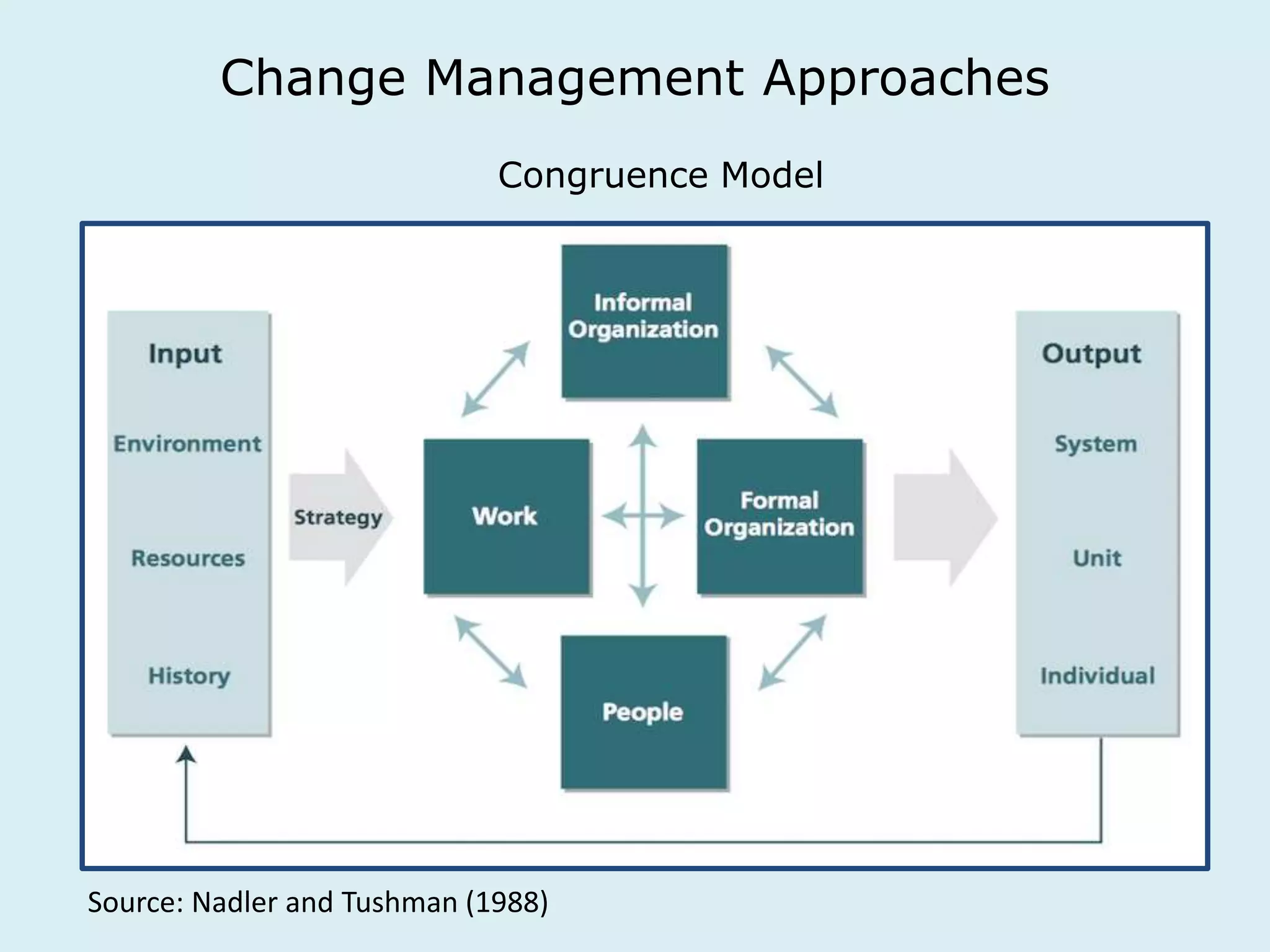
This document provides an overview of a lecture on innovation and change in the consumer goods industry. It will examine what innovation is, different types of innovation, challenges to innovation, and approaches to managing change. The learning outcomes are to understand models of innovation, discuss challenges and evaluate models for creating organizational change. The lecture will look at innovation in firms, disruptive innovation, and examples of innovation approaches used in Western firms compared to emerging markets.