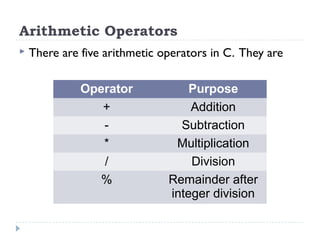
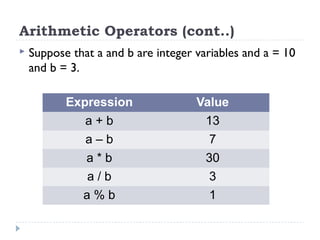
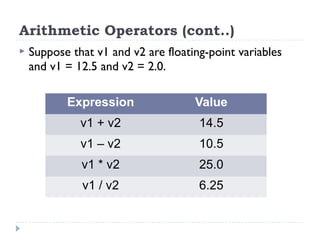
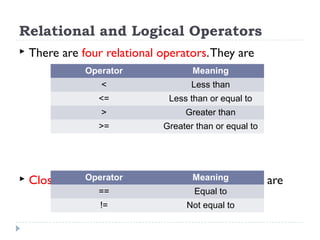
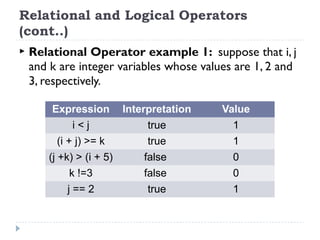
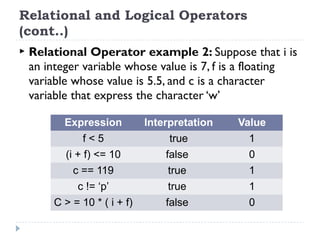
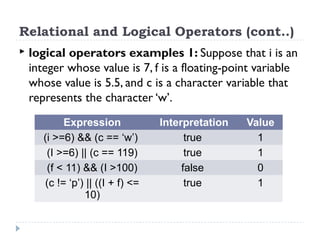
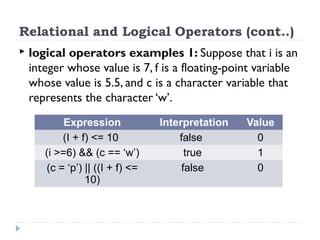
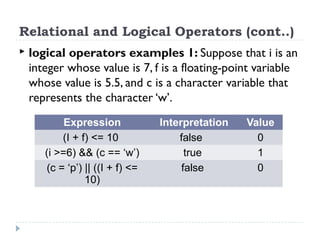
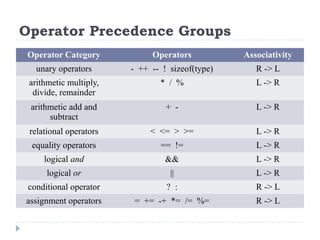
The document provides an overview of various operators and expressions in C programming, detailing operands, arithmetic operators, unary operators, relational and logical operators, assignment and conditional operators. It explains operator usage with examples and discusses operator precedence and associativity. The document serves as a foundational guide to understanding how different operators function in C programming.