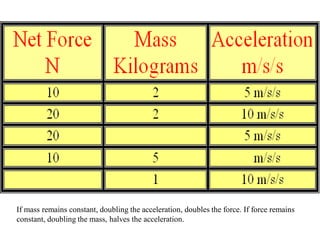
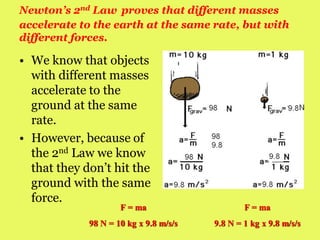
Newton's laws of motion consist of three principles: the first law states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force; the second law defines force as mass times acceleration (F=ma); and the third law asserts that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. These laws explain how objects behave under various forces and the concept of inertia, as well as applications in real-world scenarios such as vehicle motion and bird flight. Understanding these laws is essential for grasping the fundamentals of physics and mechanics.