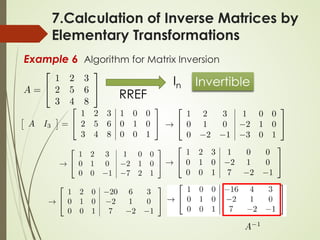
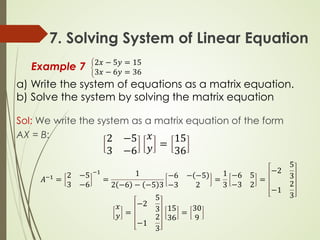
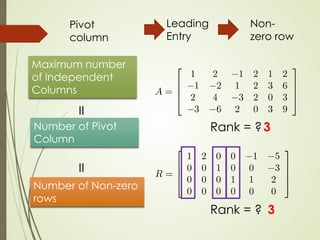
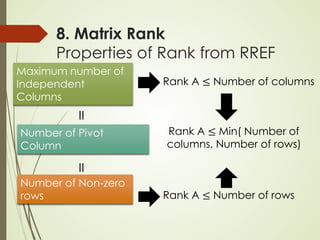
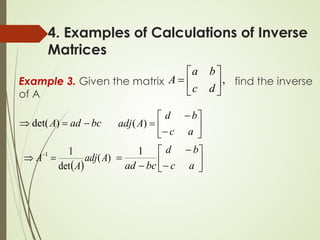
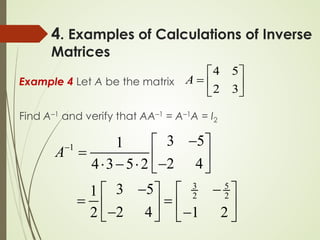
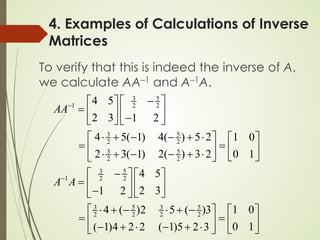
This lecture discusses inverse matrices and matrix rank. It defines an inverse matrix as a matrix A-1 such that A-1A = AA-1 = I, where I is the identity matrix. For a matrix to have an inverse, it must be square and have a non-zero determinant. The lecture provides examples of calculating inverse matrices and shows that the inverse can be found using the adjoint matrix and determinant. Properties of inverse matrices include the inverse of products and transposes. Inverse matrices can also be computed using Gaussian elimination to put the matrix in reduced row echelon form. Matrix rank is also introduced.





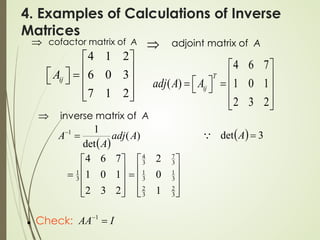
![3. Theorem of Inverse Matrix
If each element of a square matrix A is replaced by
its cofactor, then the transpose of the matrix
obtained is called the adjoint matrix of A:
Matrix of cofactors of A:
Adjoint matrix of A:
[ ]
11 12 1
21 22 2
1 2
n
n
ij
n n nn
A A A
A A A
A
A A A
=
11 21 1
12 22 2
1 2
( )
n
T n
ij
n n nn
A A A
A A A
adj A A
A A A
= =
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3inversematriceshotom-221115114328-0a23a39a/85/Lecture-3-Inverse-matrices-hotom-pdf-6-320.jpg)



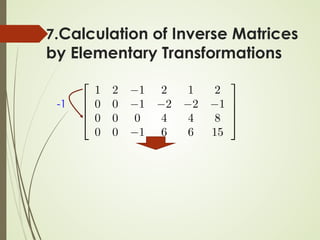
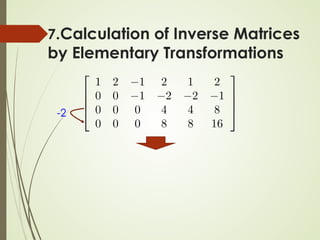
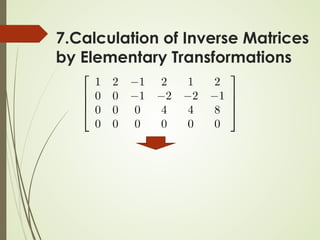
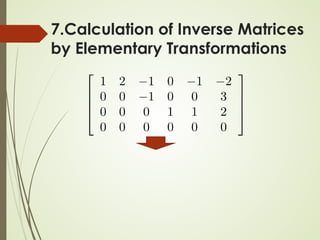



![Algorithm for Matrix Inversion
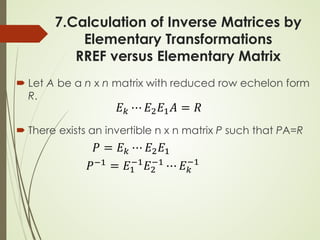
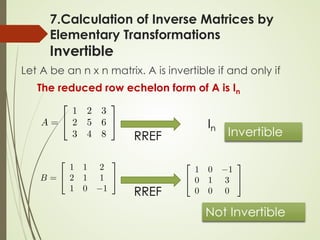
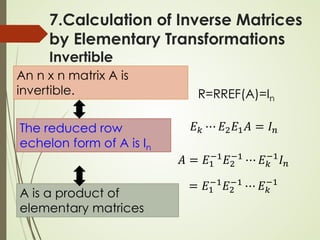
Let A be an n x n matrix. Transform [ A In ] into its RREF
[ R B ]
R is the RREF of A
B is a n x n matrix (not RREF)
If R = In, then A is invertible B = A-1
𝐸𝐸𝑘𝑘 ⋯ 𝐸𝐸2𝐸𝐸1 𝐴𝐴 𝐼𝐼𝑛𝑛 = 𝑅𝑅 𝐸𝐸𝑘𝑘 ⋯ 𝐸𝐸2𝐸𝐸1
𝐴𝐴−1
𝐼𝐼𝑛𝑛
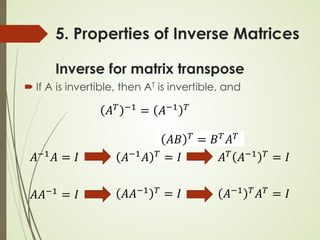
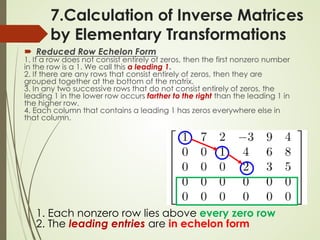
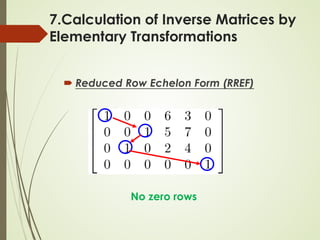
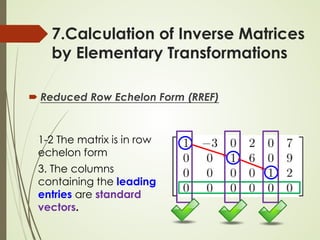
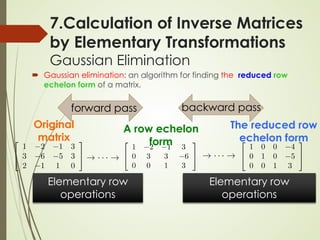
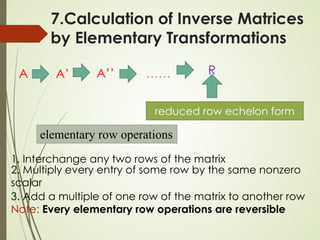
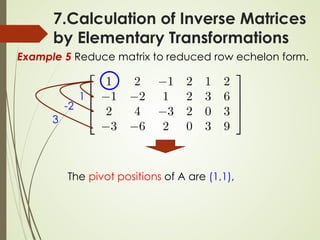
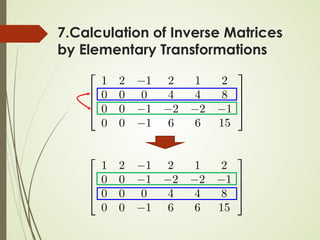
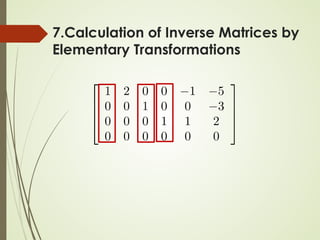
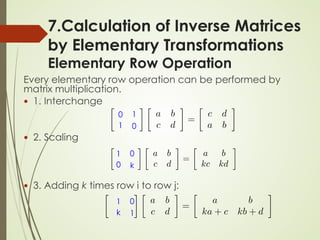
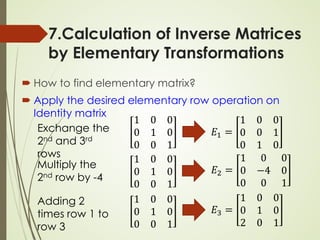
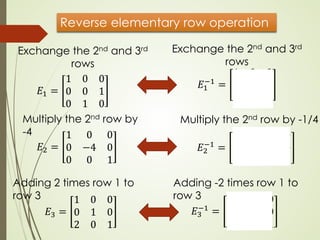
7.Calculation of Inverse Matrices
by Elementary Transformations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3inversematriceshotom-221115114328-0a23a39a/85/Lecture-3-Inverse-matrices-hotom-pdf-36-320.jpg)