This lecture covered object-oriented programming concepts of inheritance and polymorphism:
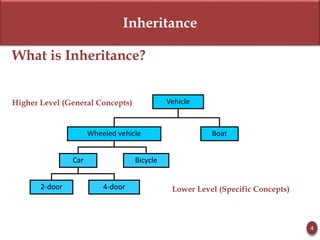
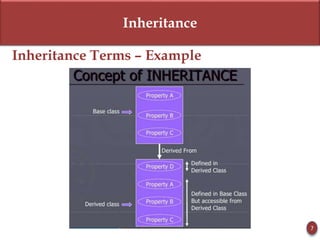
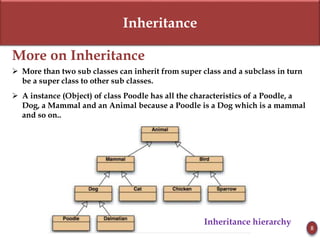
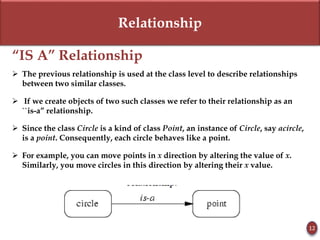
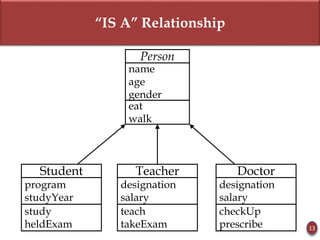
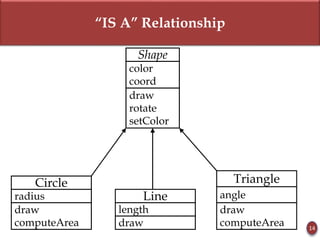
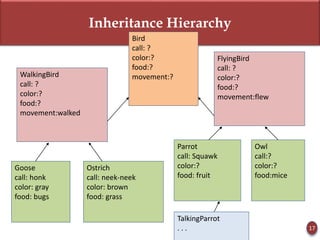
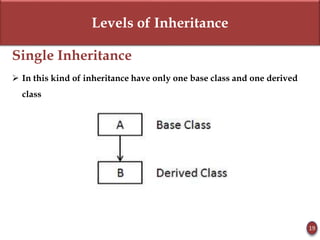
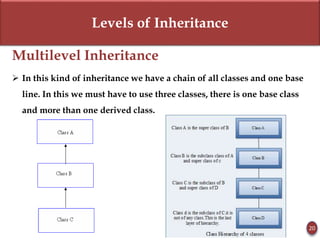
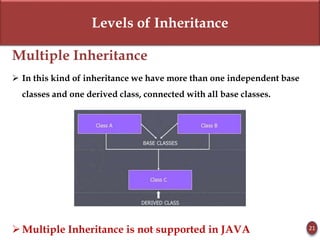
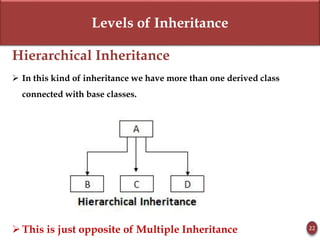
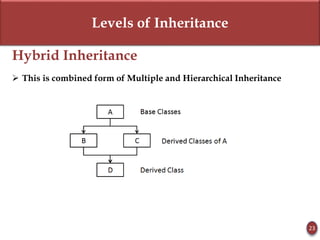
Inheritance allows new objects to take on properties of existing objects in a hierarchy. It was defined and real-world examples like mobile phones and vehicles were provided. Key inheritance terms like superclass, subclass, and relationships like "is-a-kind-of" and "is-a" were explained.
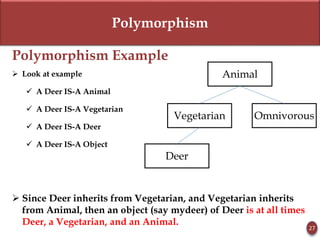
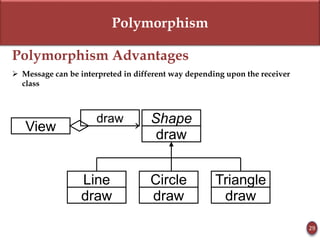
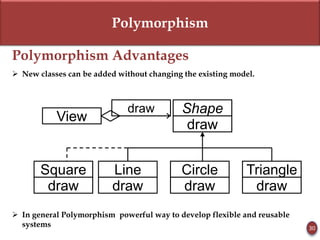
Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on many forms. It allows sending the same message to objects of different classes and having the objects respond differently. Advantages are flexibility and reusability.