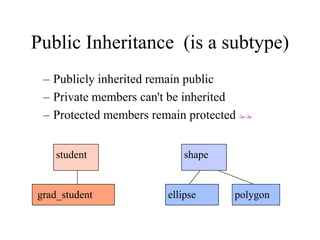
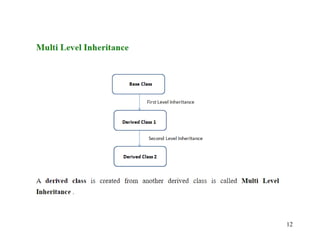
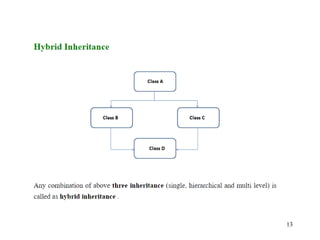
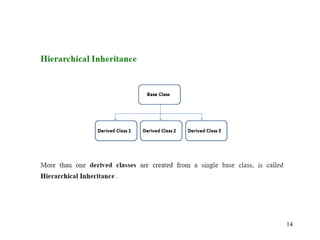
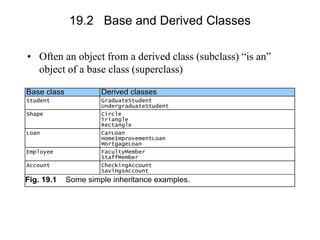
The document discusses inheritance in object-oriented programming. It defines inheritance as a process where an object of one class acquires properties of another class. The class that inherits properties is called the derived class, while the class being inherited from is called the base class. Inheritance allows for code reuse and modeling real-world is-a relationships between classes, and provides polymorphism. The key benefits are reusability of code and reflecting relationships between classes. Various types of inheritance like single, multi-level, hierarchical and multiple inheritance are also covered.