The document discusses polymorphism and object-oriented programming concepts. It defines polymorphism as an object taking on many forms, and describes how it occurs through parent and child class relationships in Java. The key points are:
- Polymorphism allows a parent class reference to refer to a child class object.
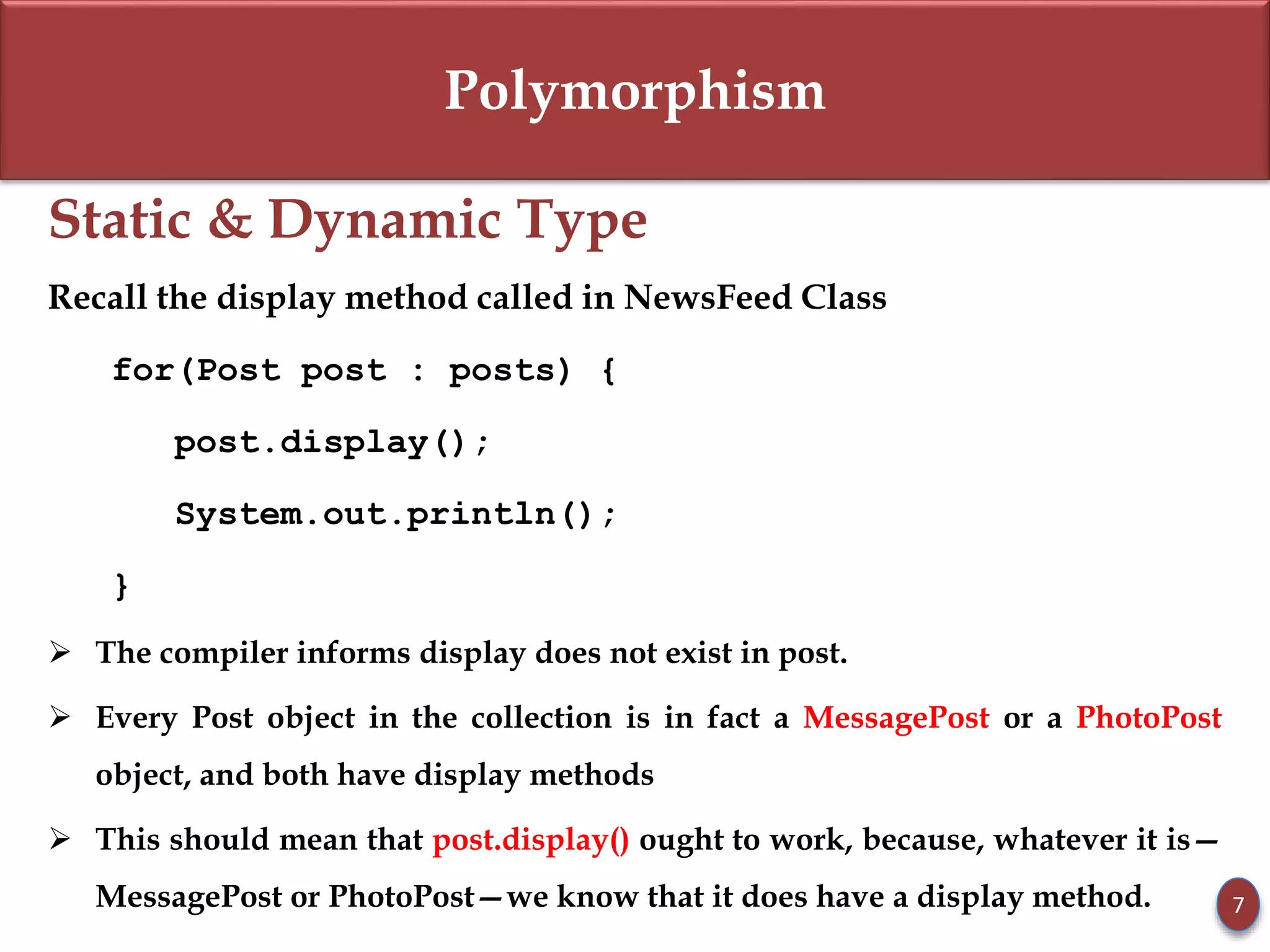
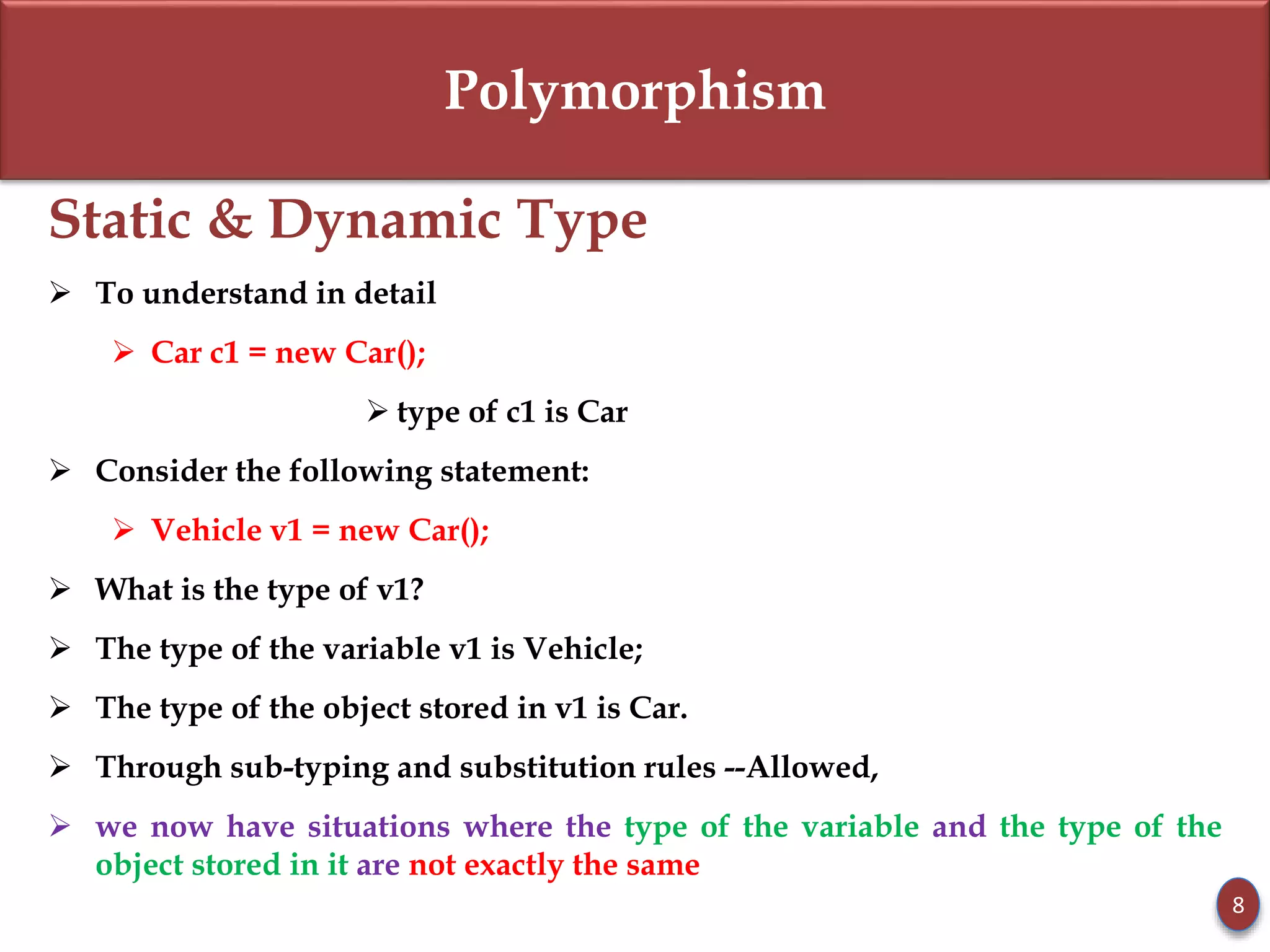
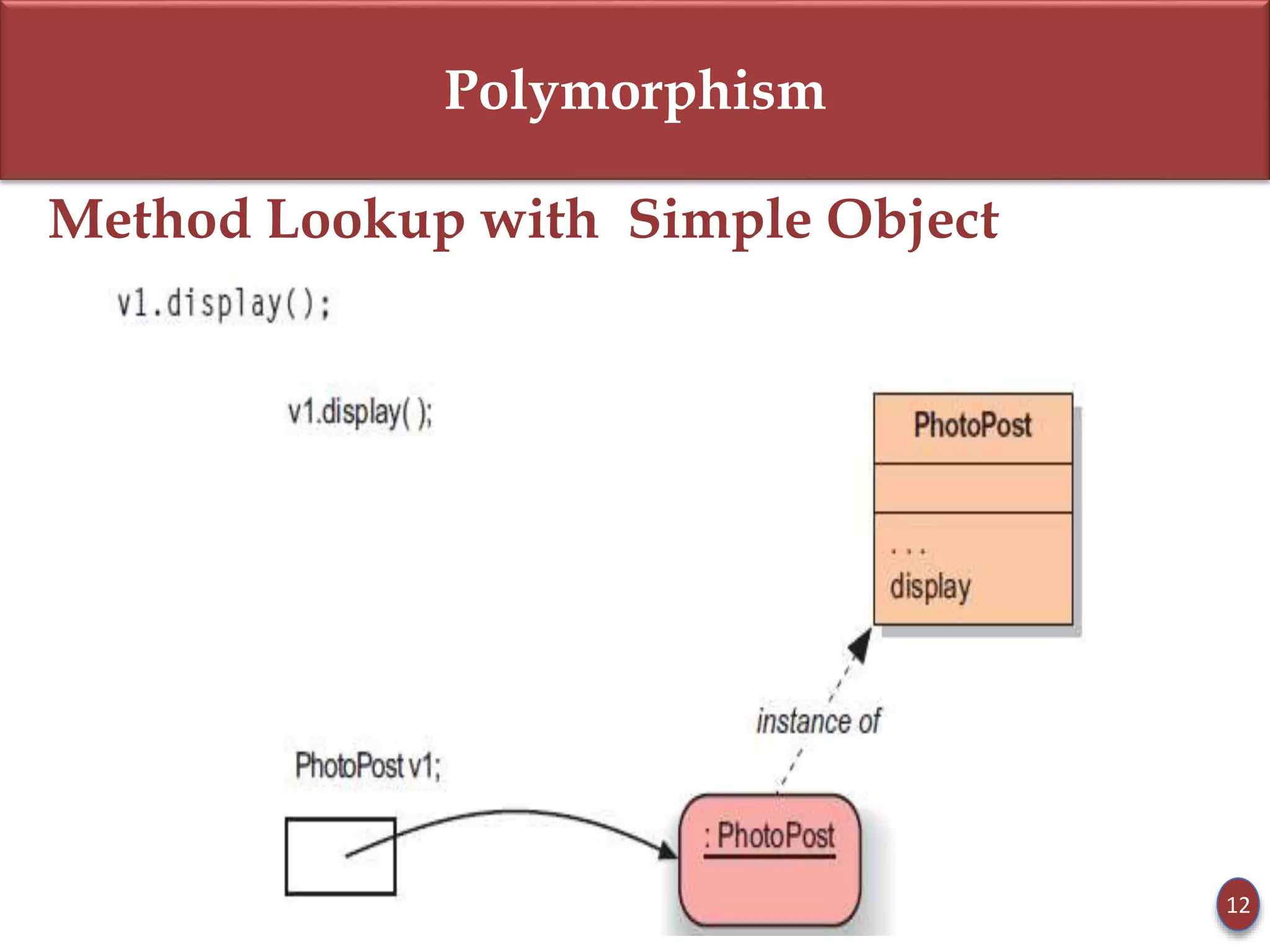
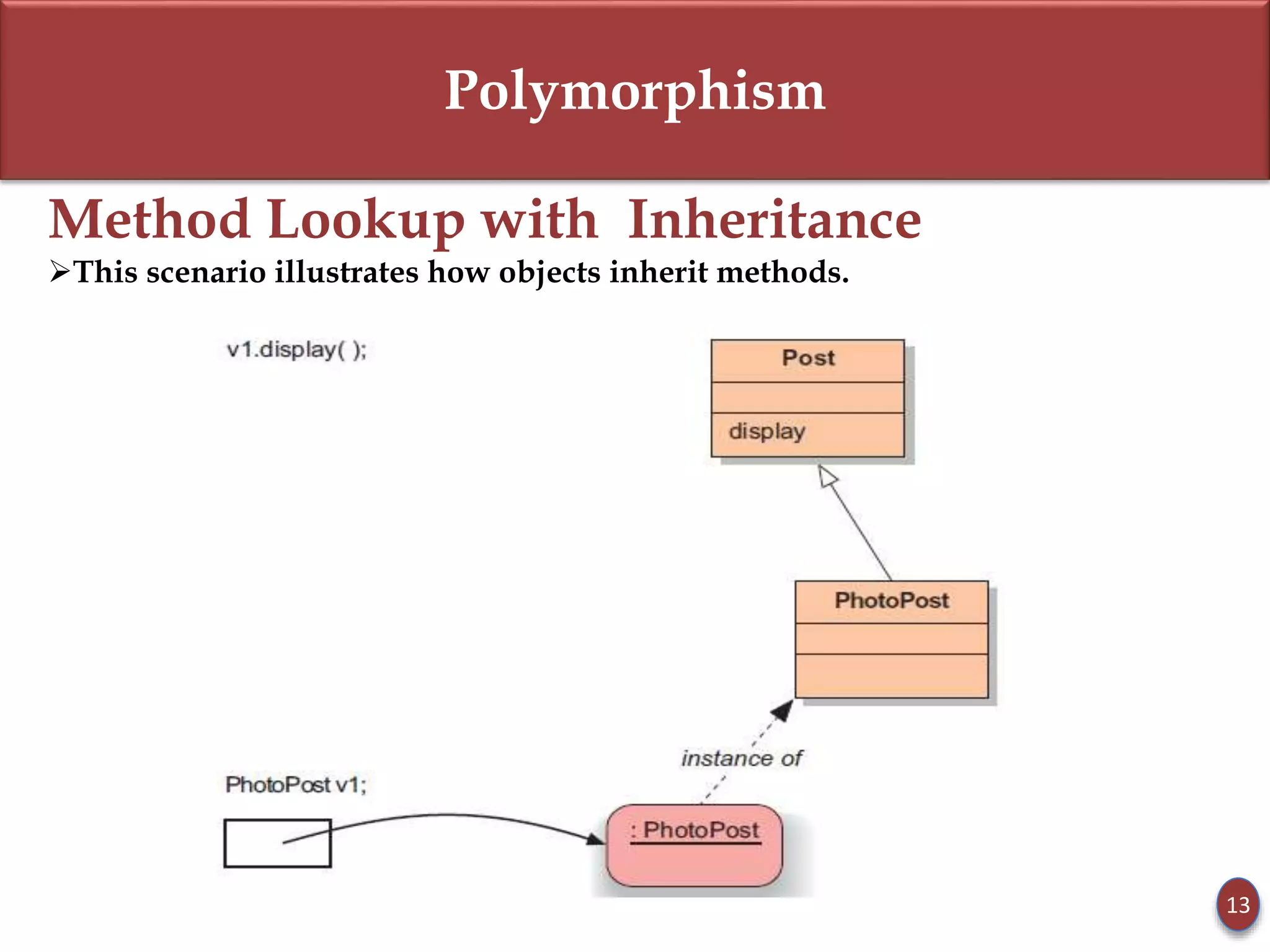
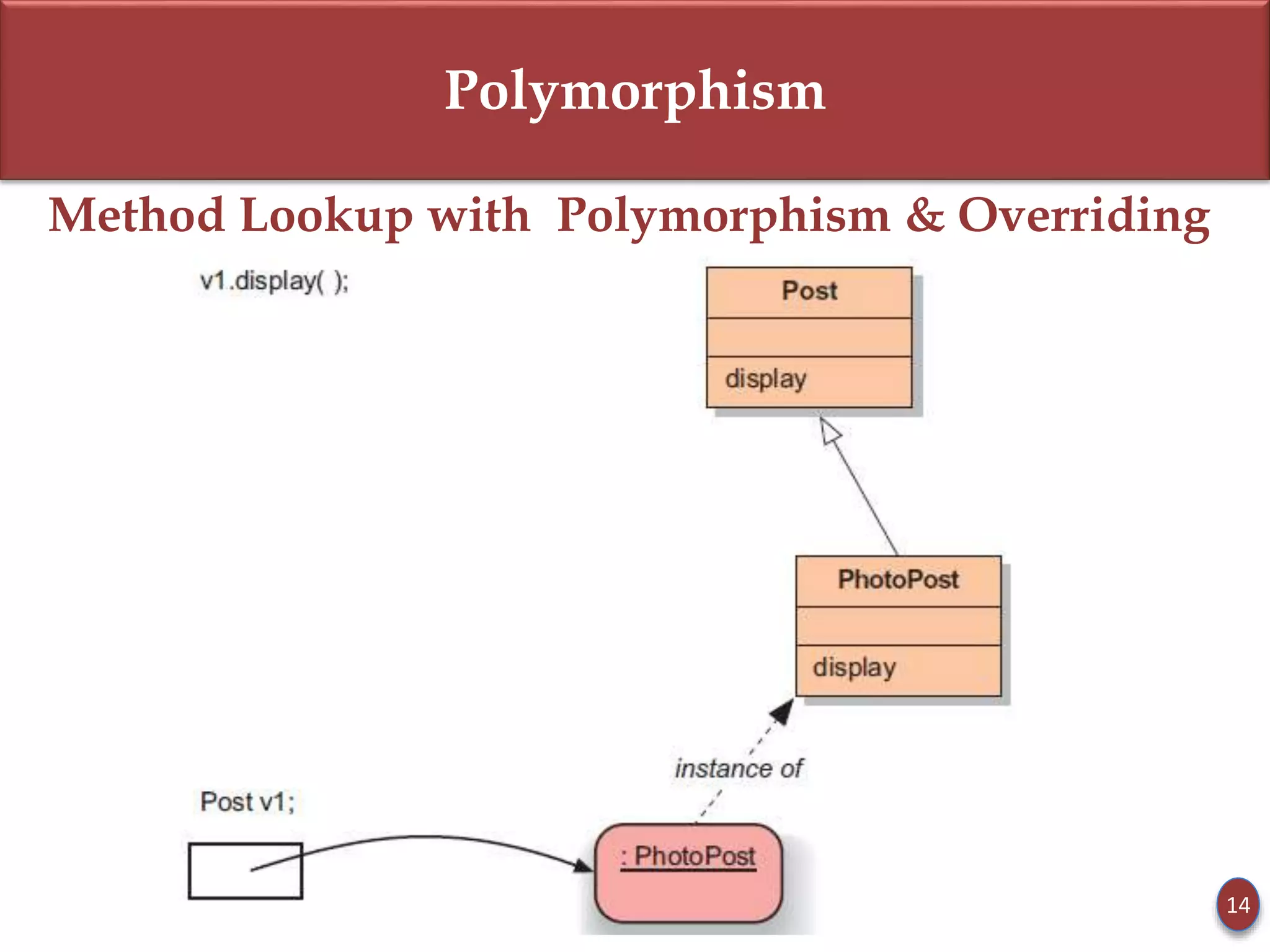
- Static type refers to a reference variable's type, while dynamic type refers to the actual object's type. Dynamic binding means the method called is based on the object's dynamic type.
- Subclasses can override methods to achieve polymorphic behavior like with the display() method.
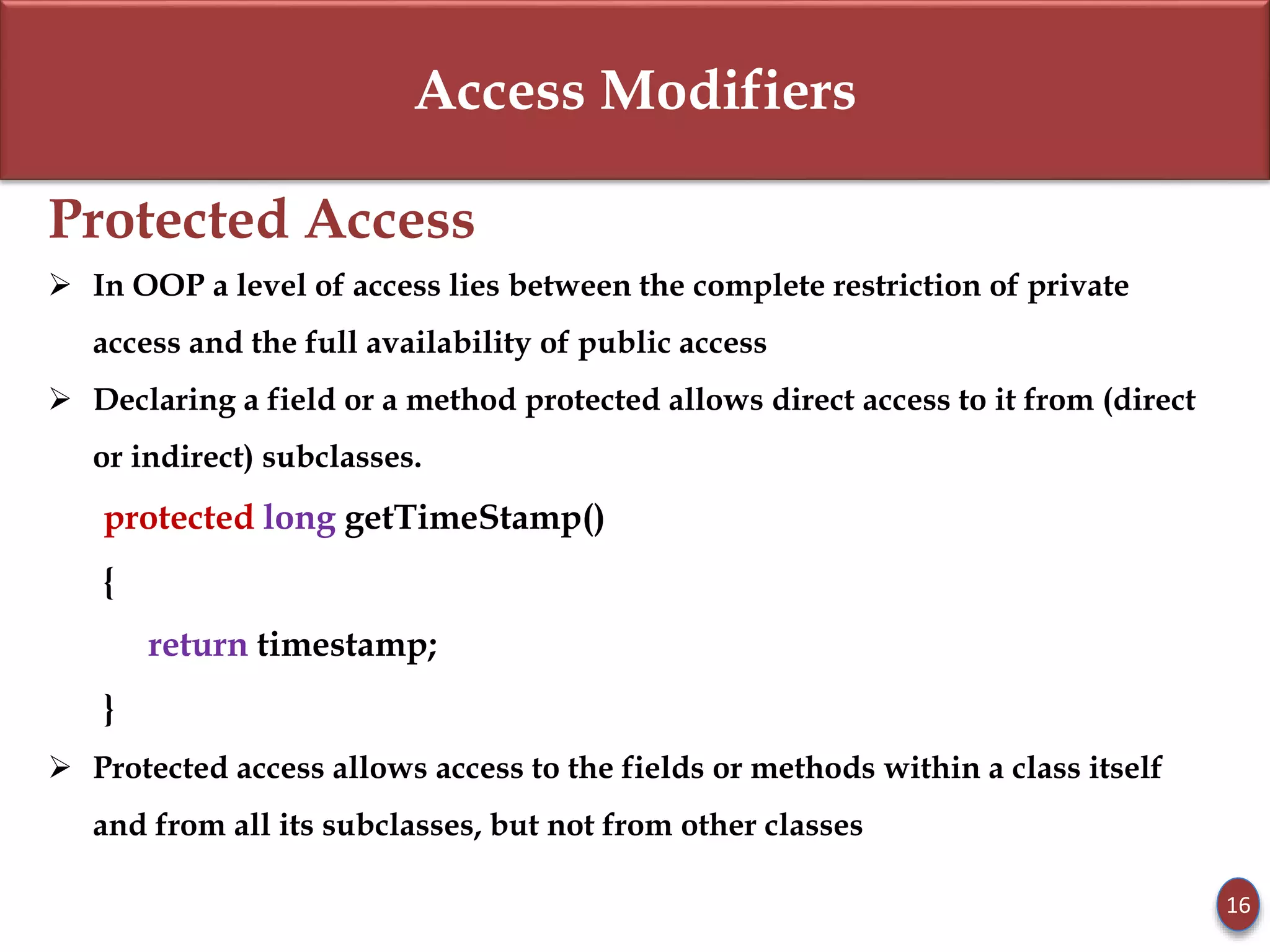
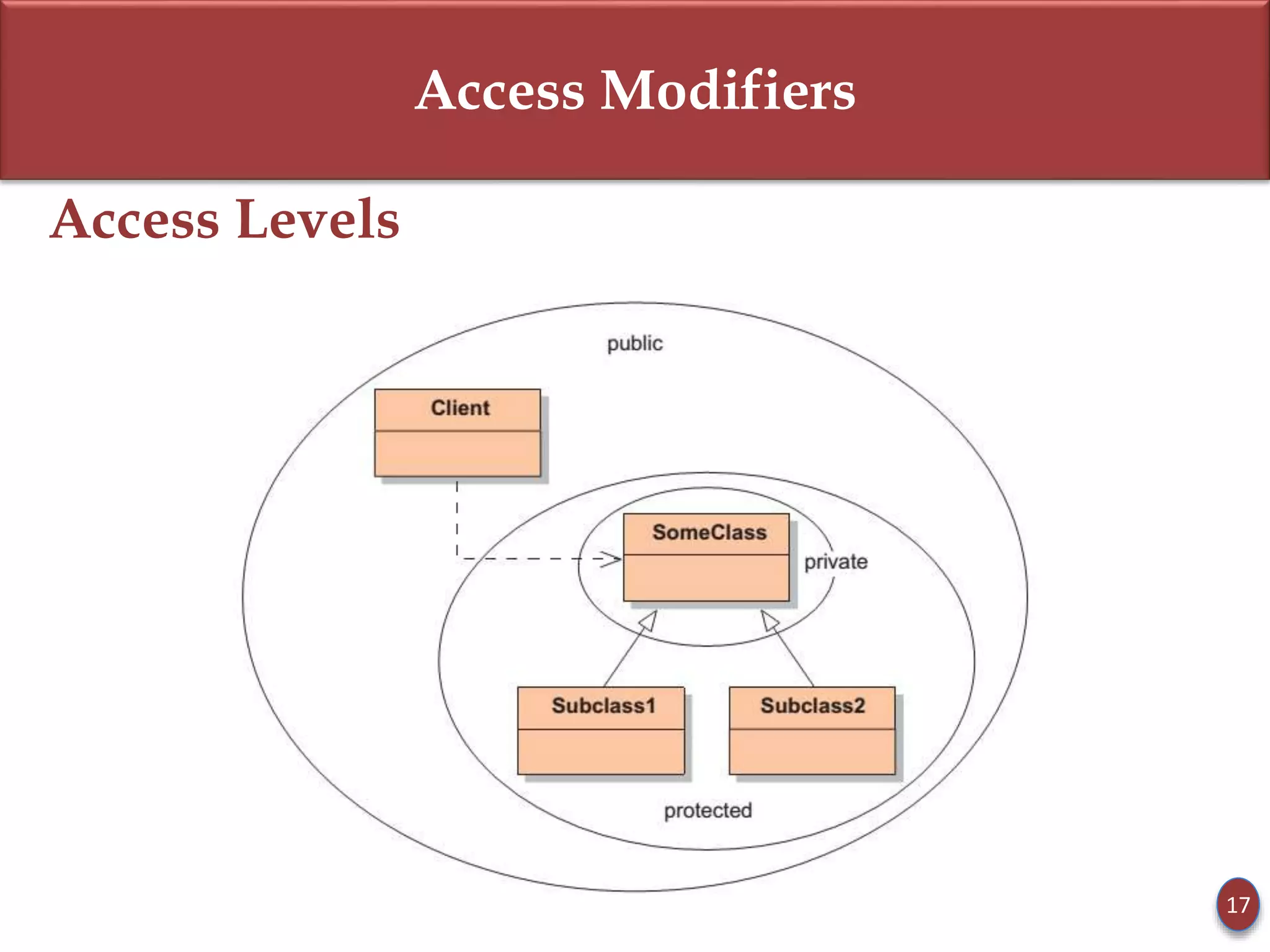
- Access modifiers like private, public, and protected determine method/field accessibility in subclasses.
- Final methods





![Polymorphism
Redefining Display Method
public void display()
{
super.display();
System.out.println(" ["+ filename + "]");
System.out.println(" "+ caption);
}
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-17-151112061242-lva1-app6892/75/Lecture-17-15-2048.jpg)



![Final Keyword
Final Keyword – Example Code
class Bike9{
final int speedlimit=90;//final variable
void run(){
speedlimit=400;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike9 obj=new Bike9();
obj.run();
}
}//end of class
Output – Compile time error
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture-17-151112061242-lva1-app6892/75/Lecture-17-21-2048.jpg)