1) The document discusses change, conflict, and crisis related to the environment and development. It explores definitions of key concepts like the environment, development, and sustainable development.
2) In the 1970s, the relationship between development and environmental damage began receiving more recognition, as issues like acid rain emerged. However, defining solutions remains difficult due to disagreement among experts and communities.
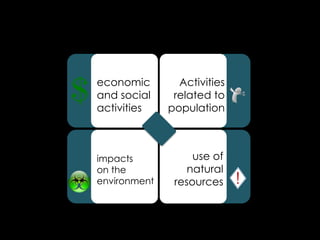
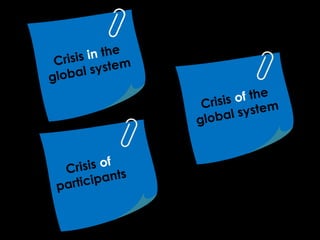
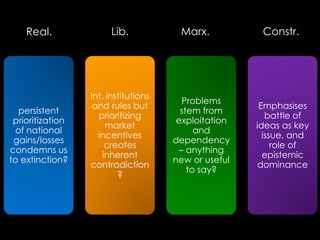
3) Current crises related to issues like climate change, resource scarcity, and biodiversity loss are creating tensions among states, industries, experts, and citizens over causes and solutions. There is no consensus on how to balance development and environmental sustainability.