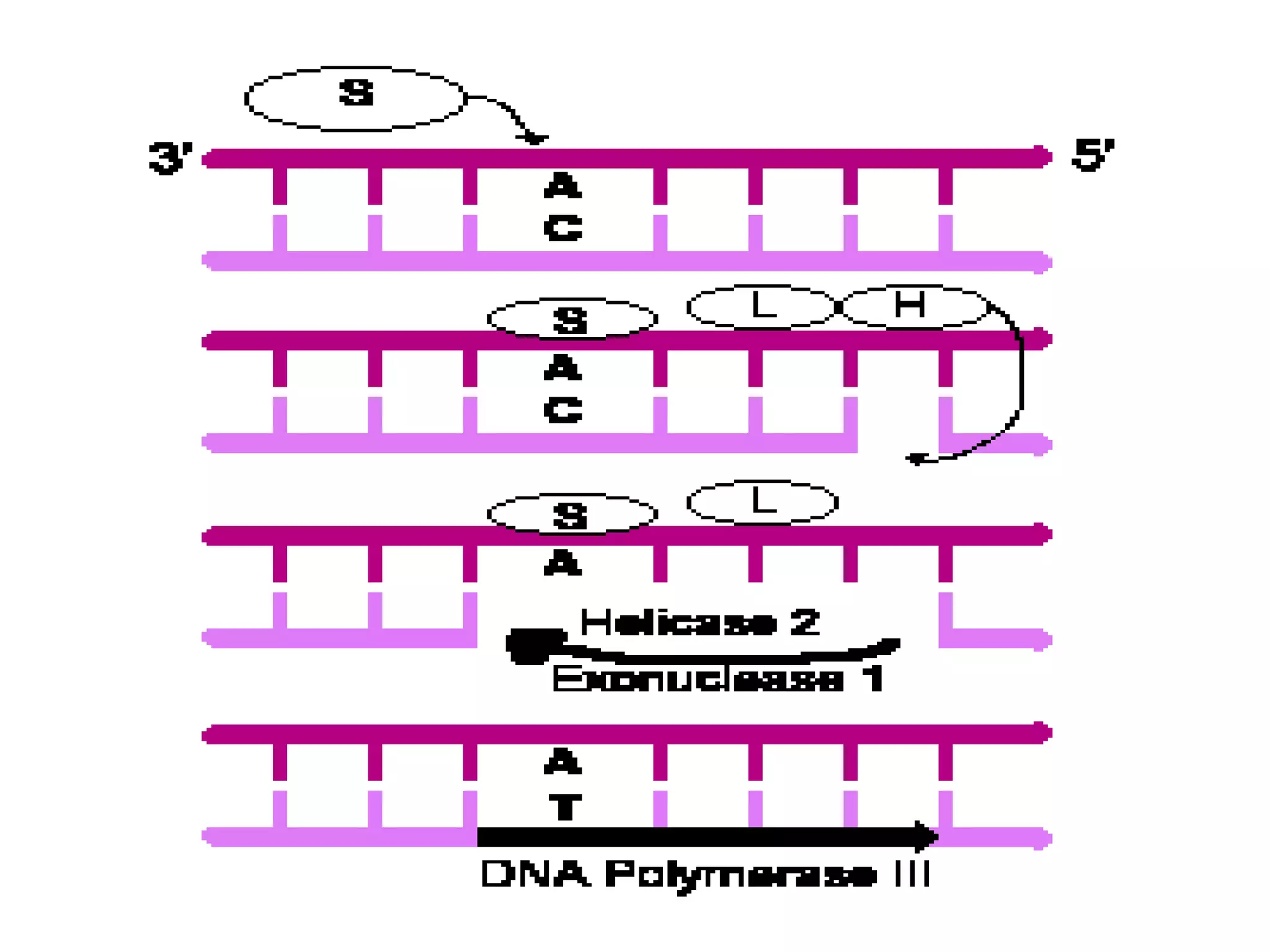
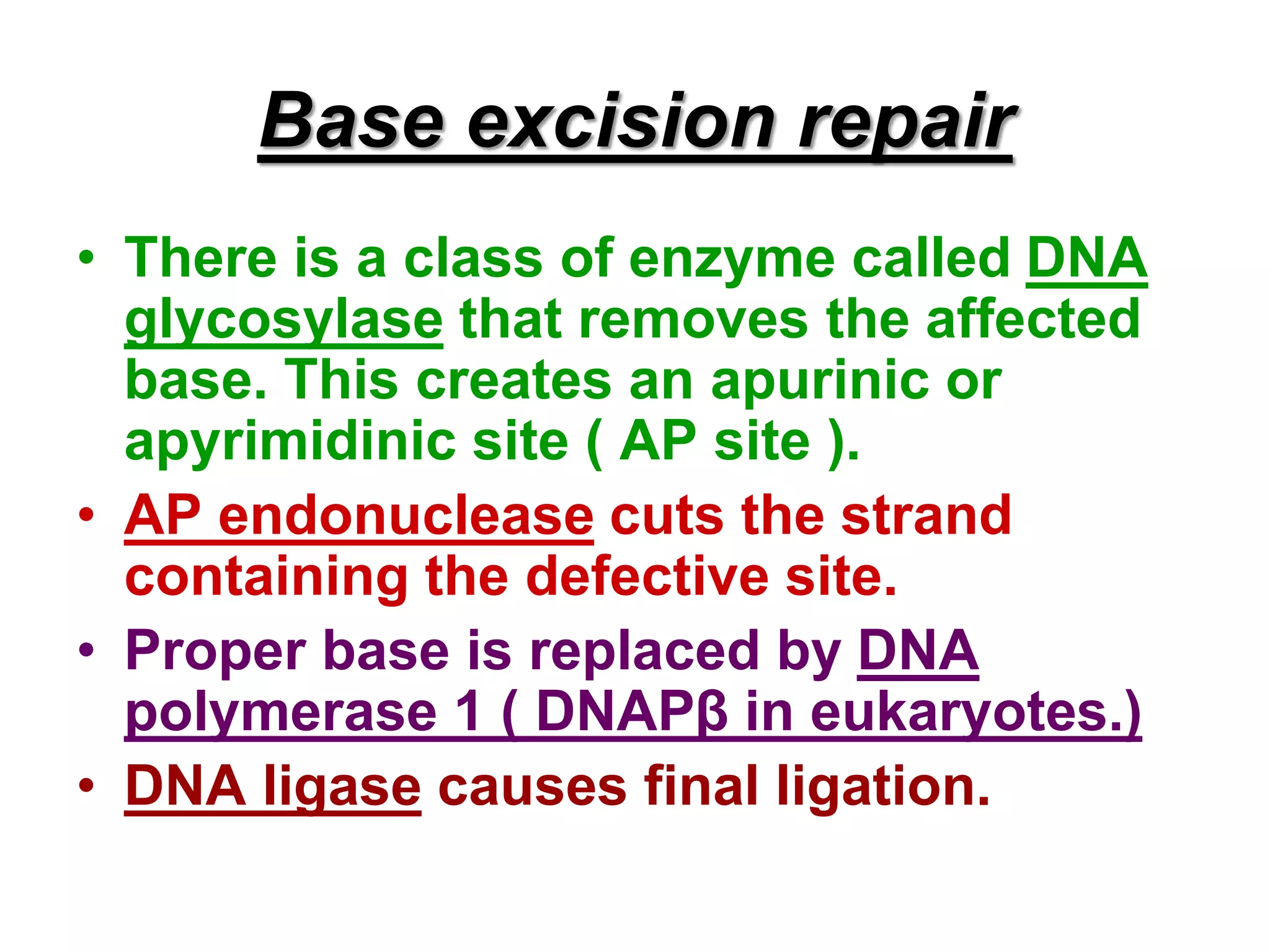
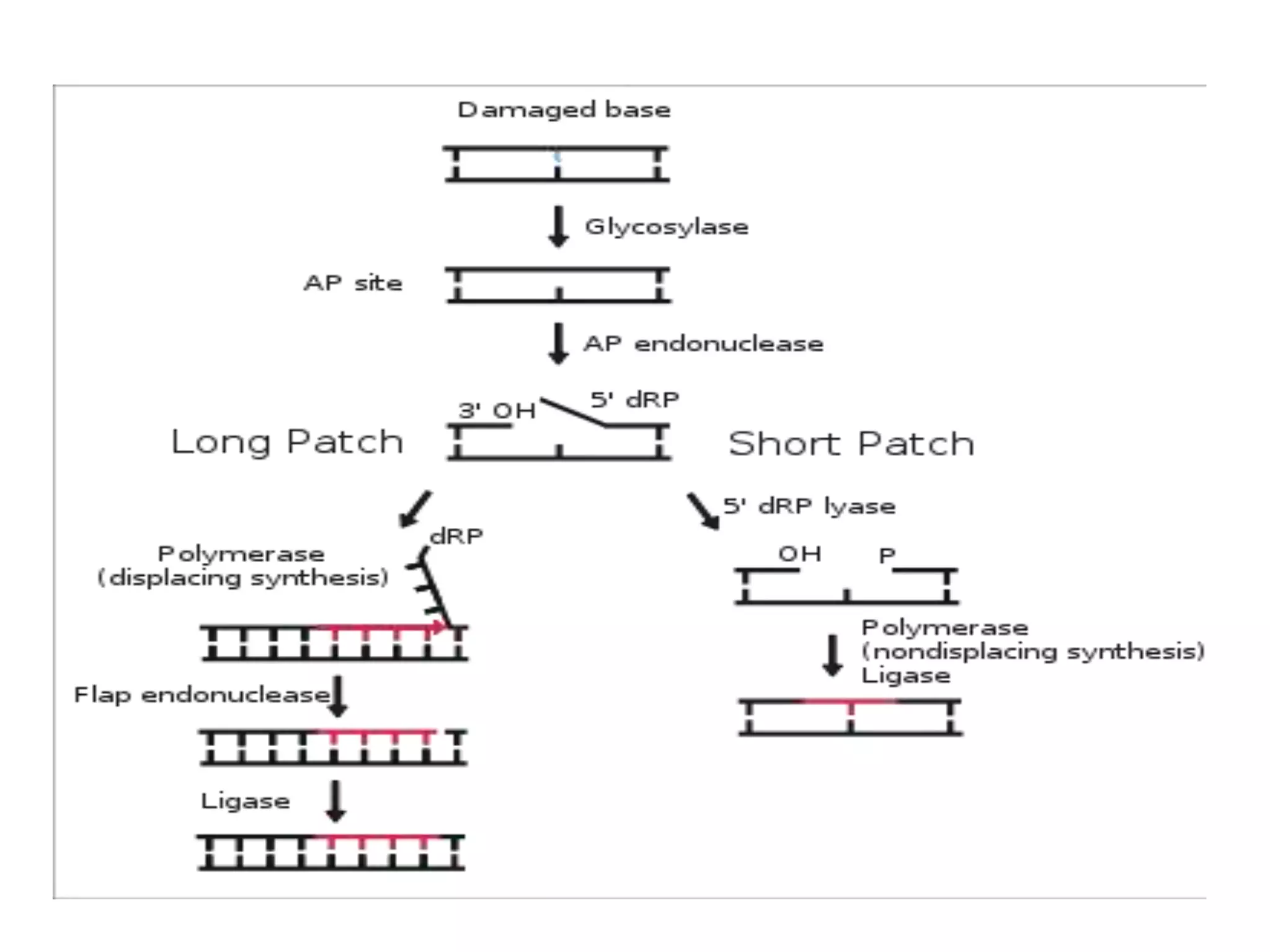
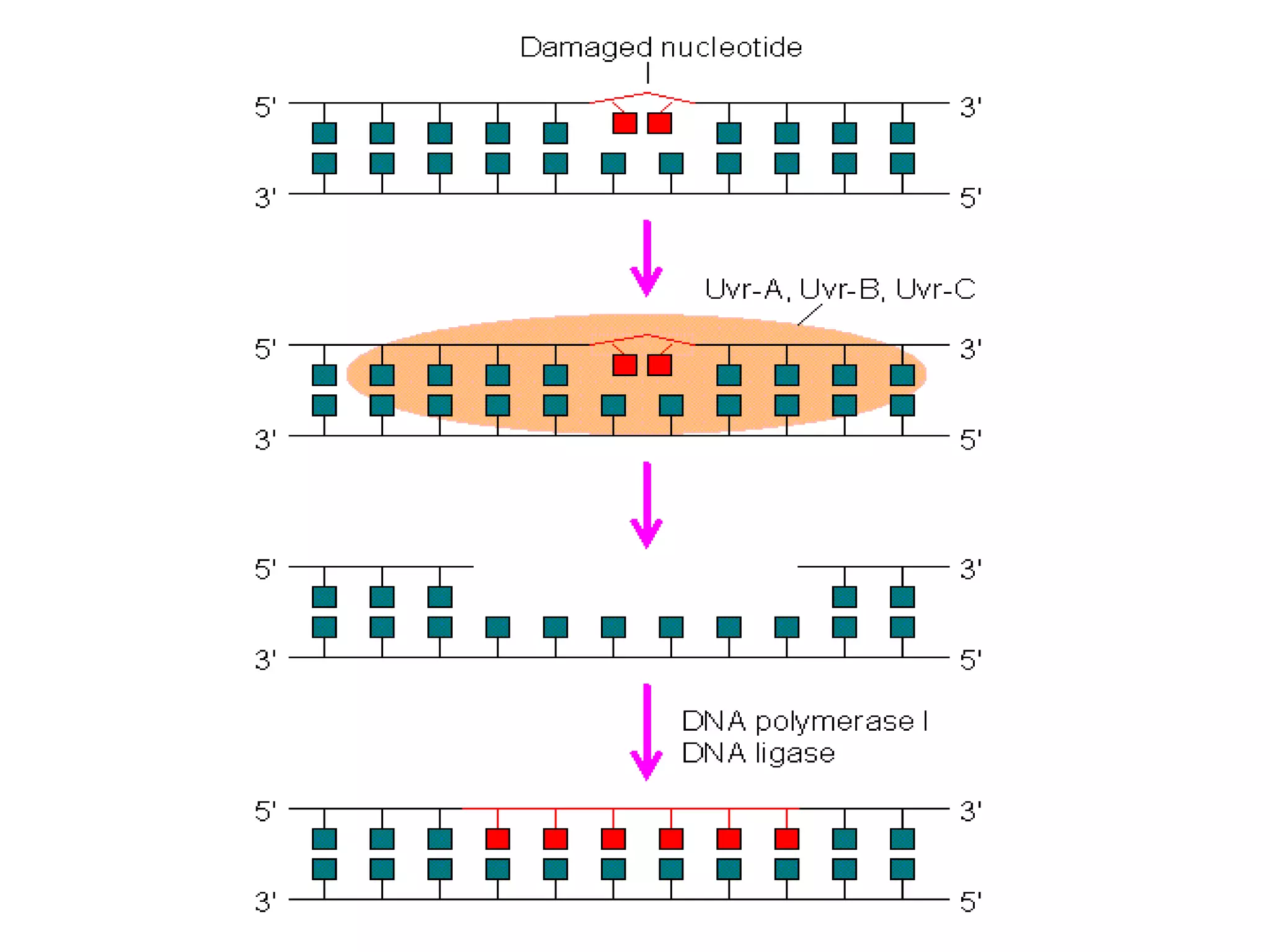
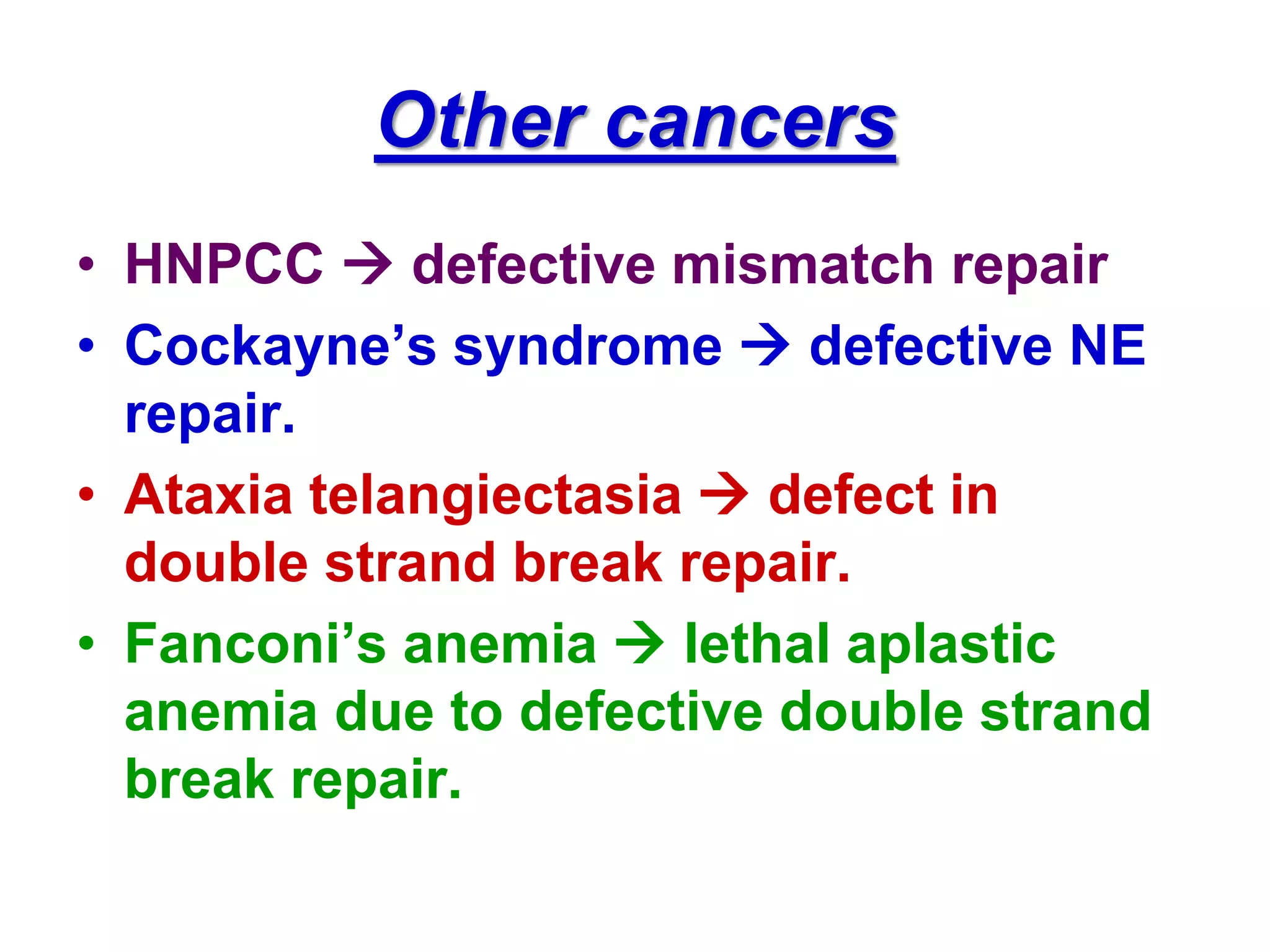
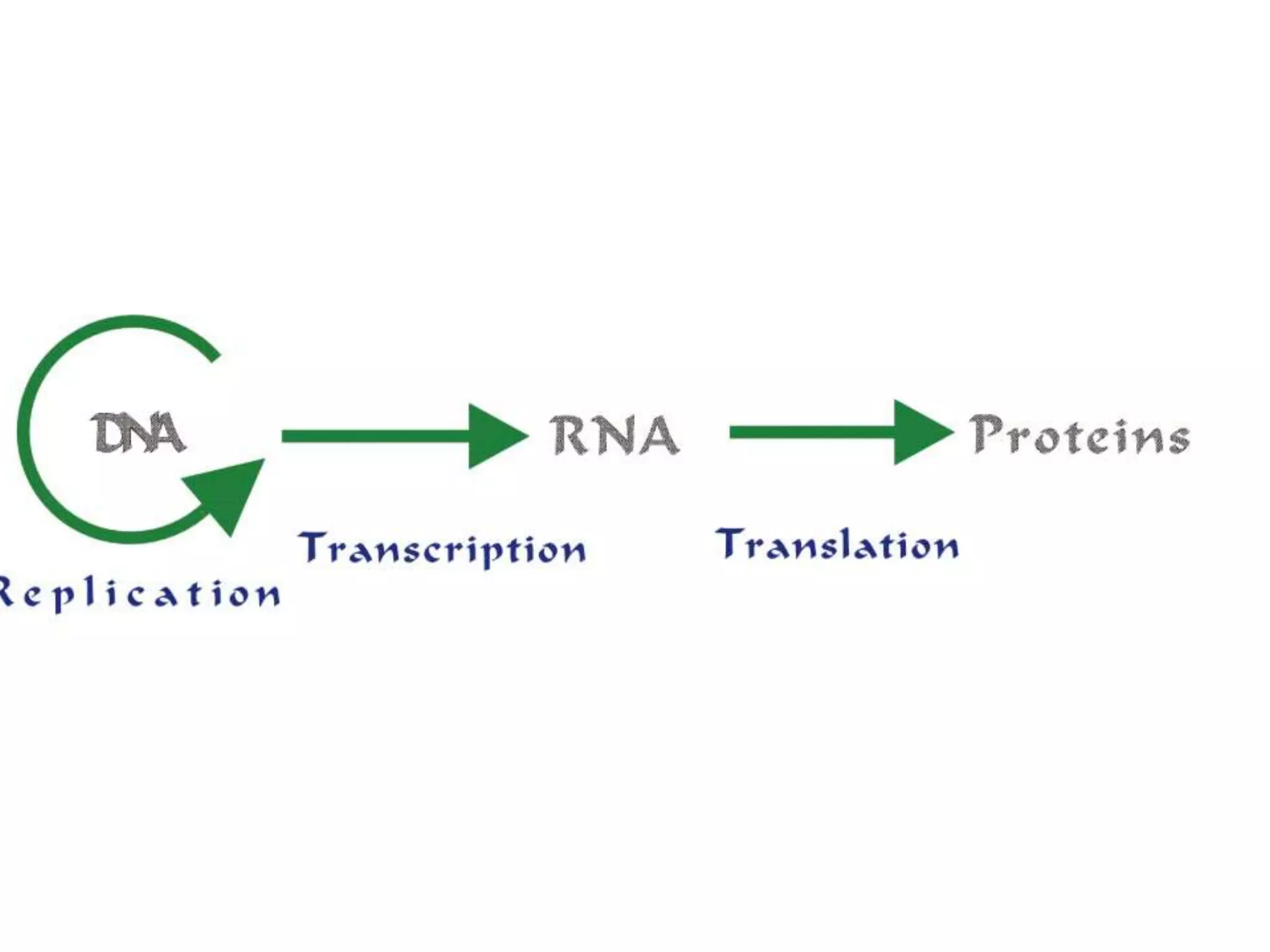
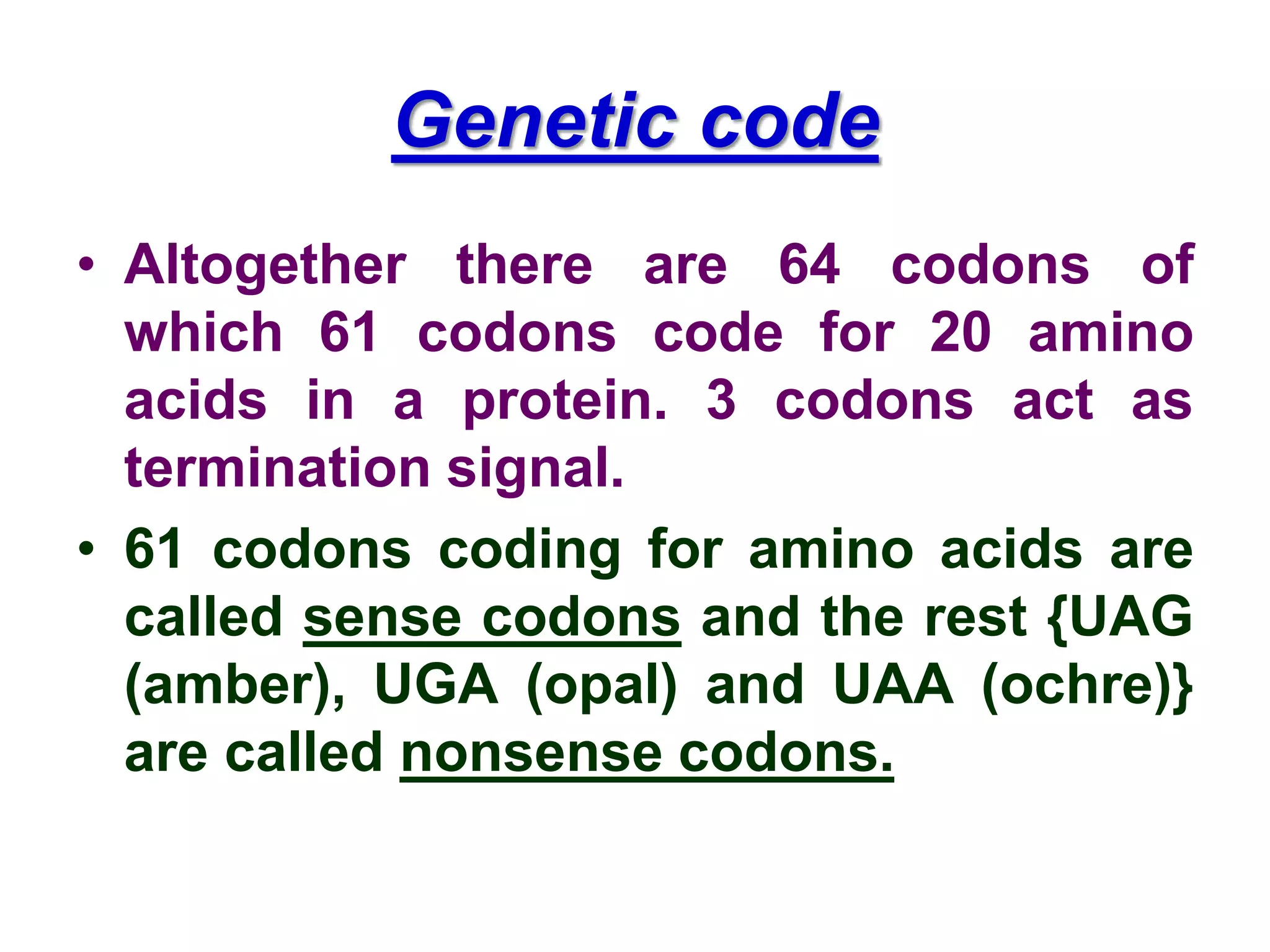
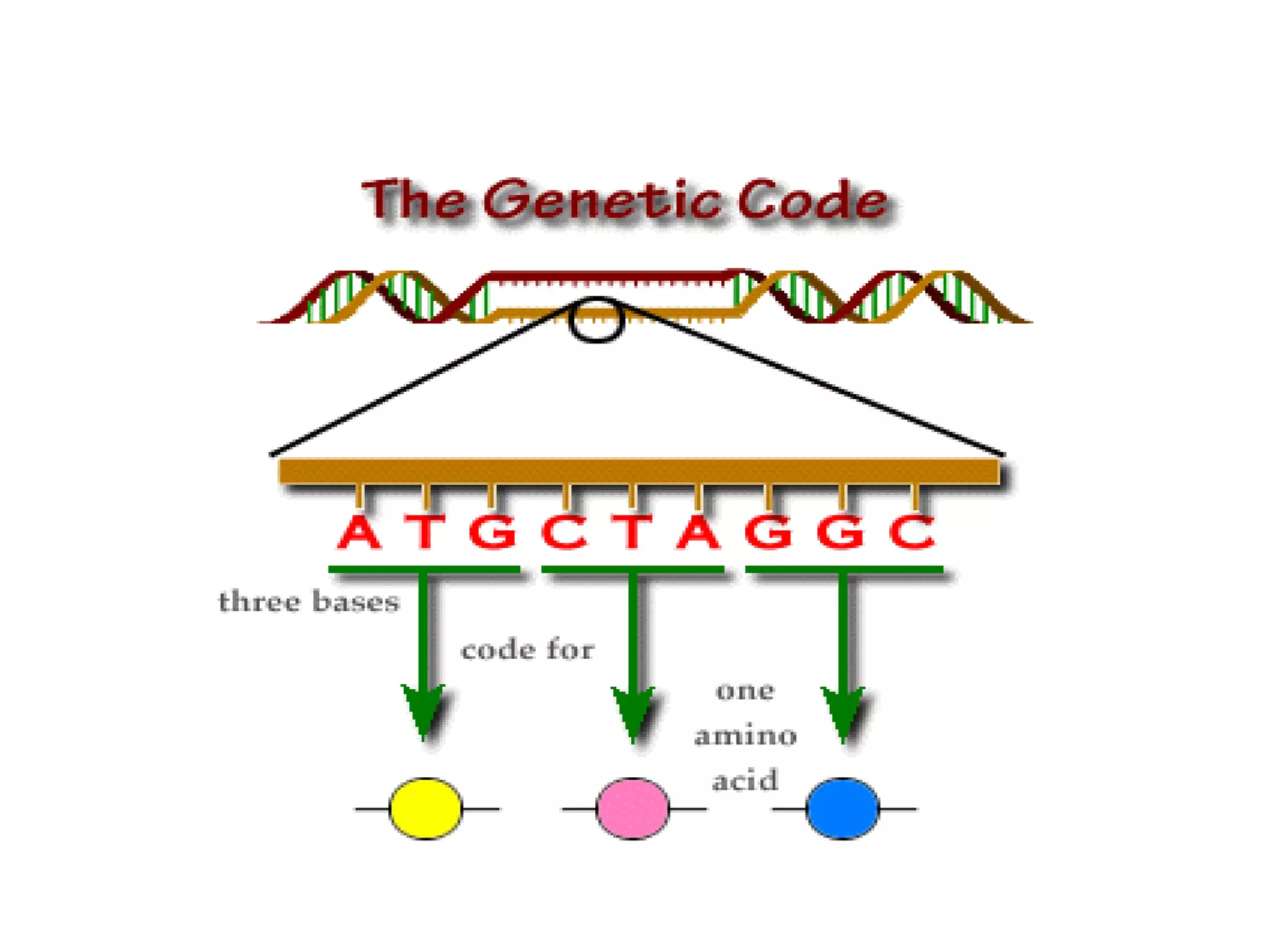
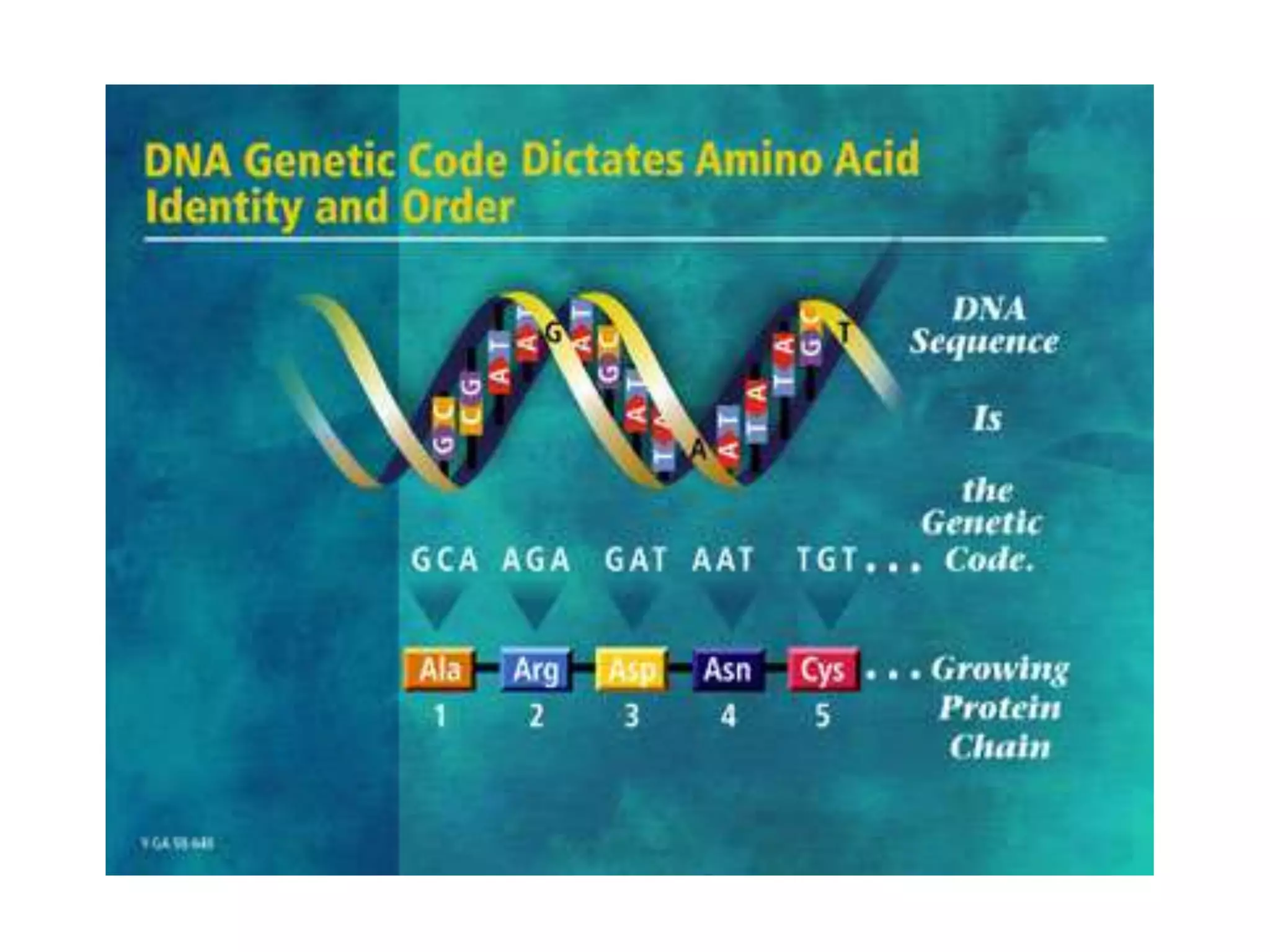
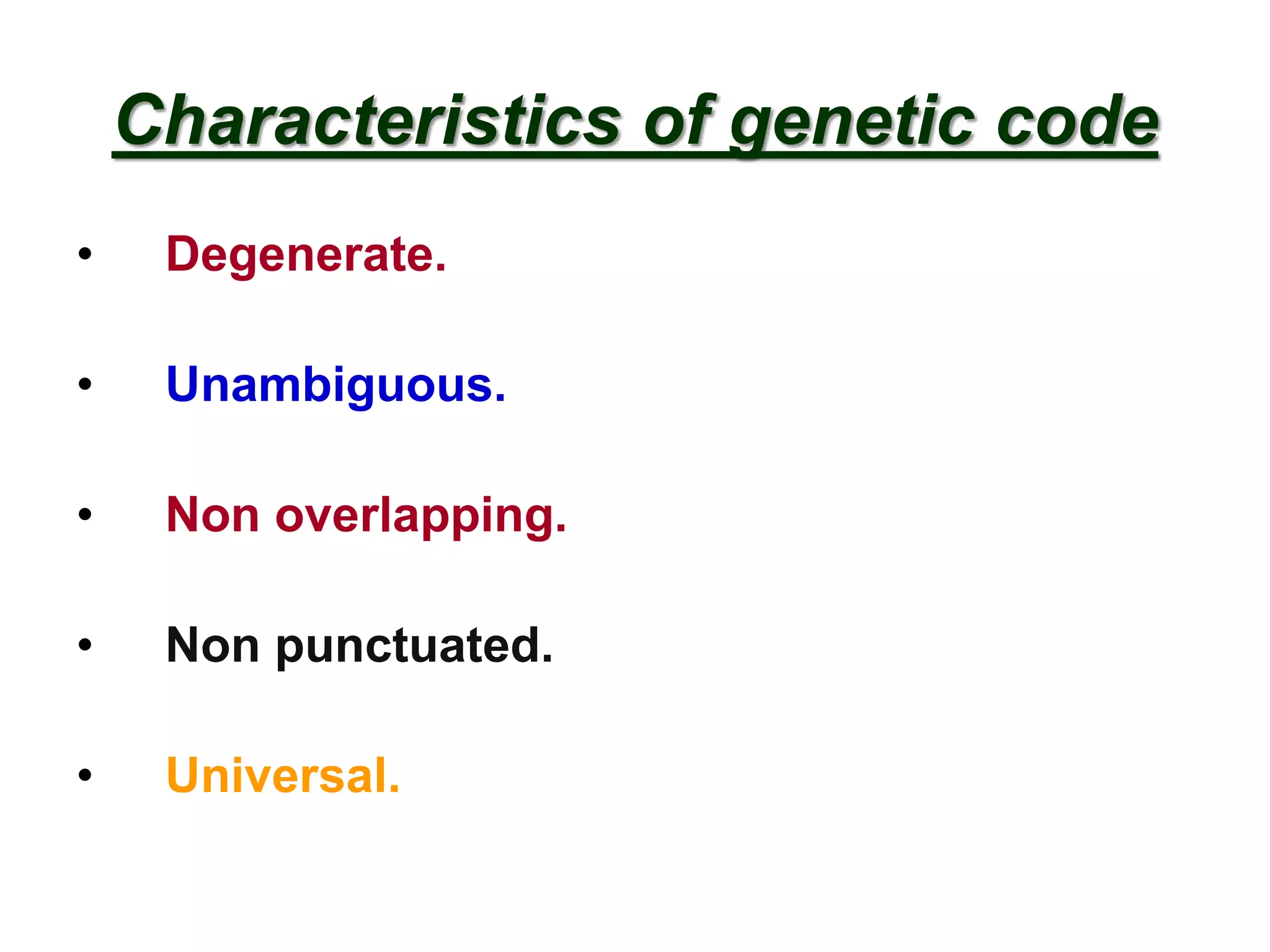
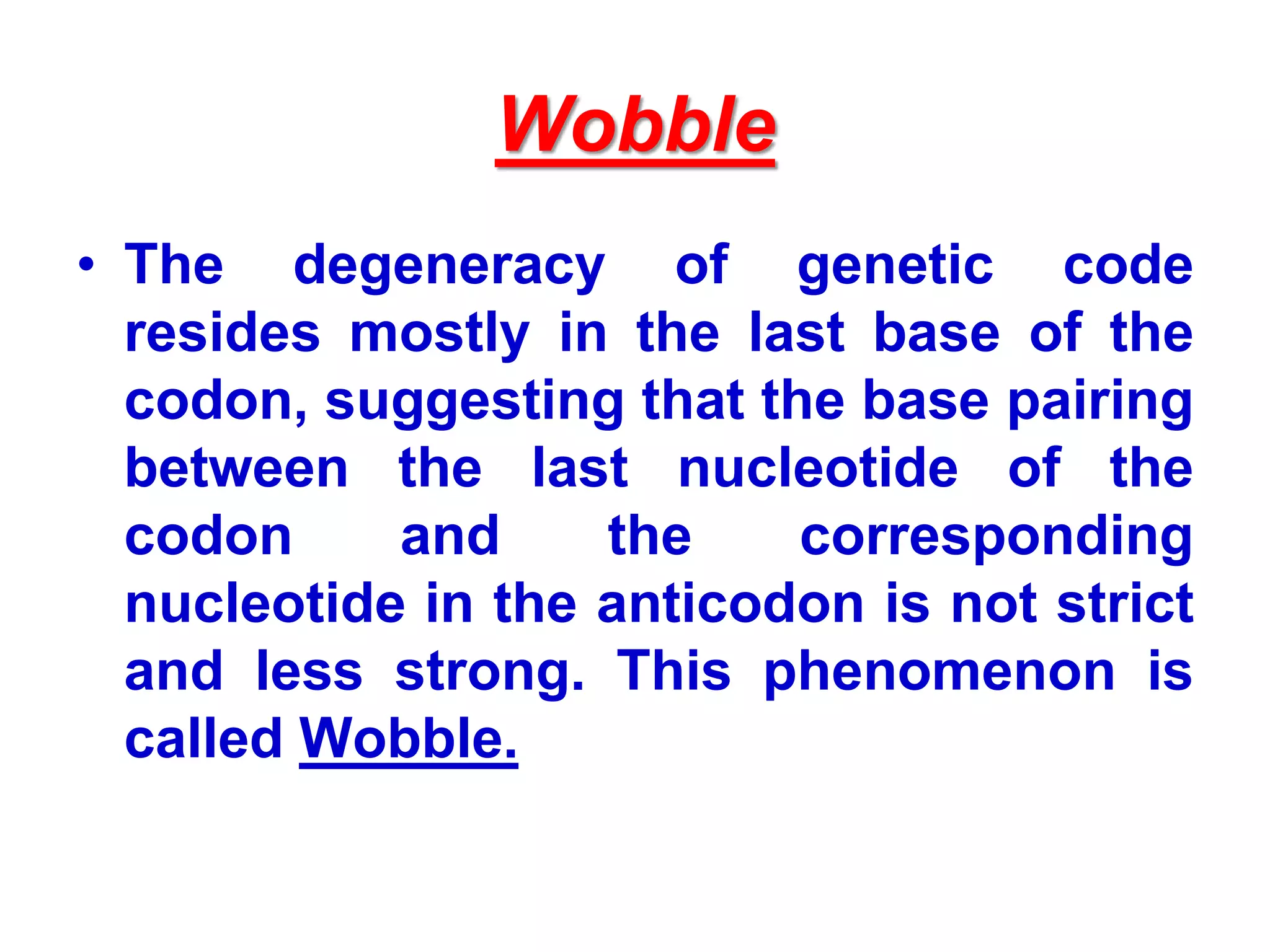
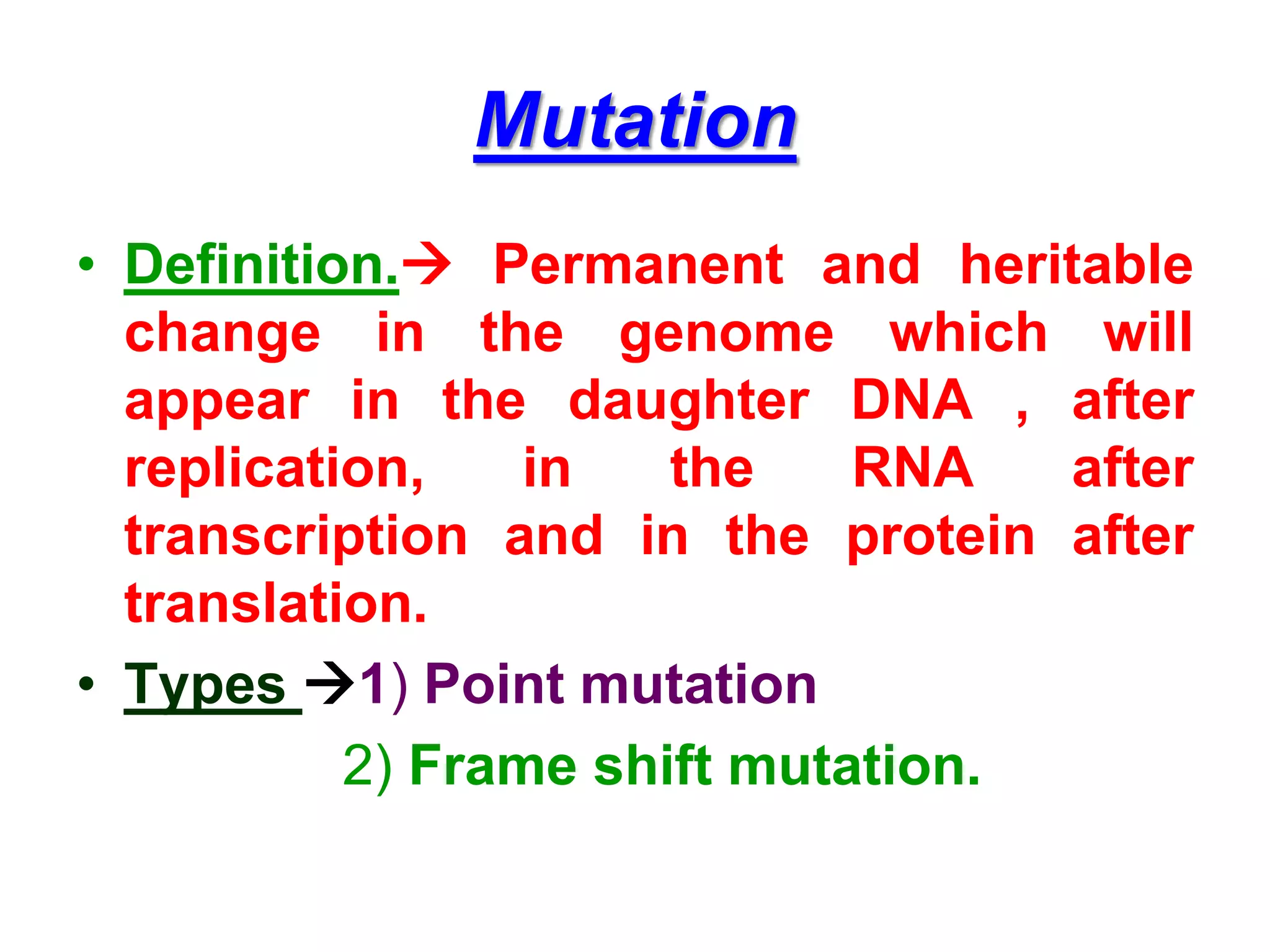
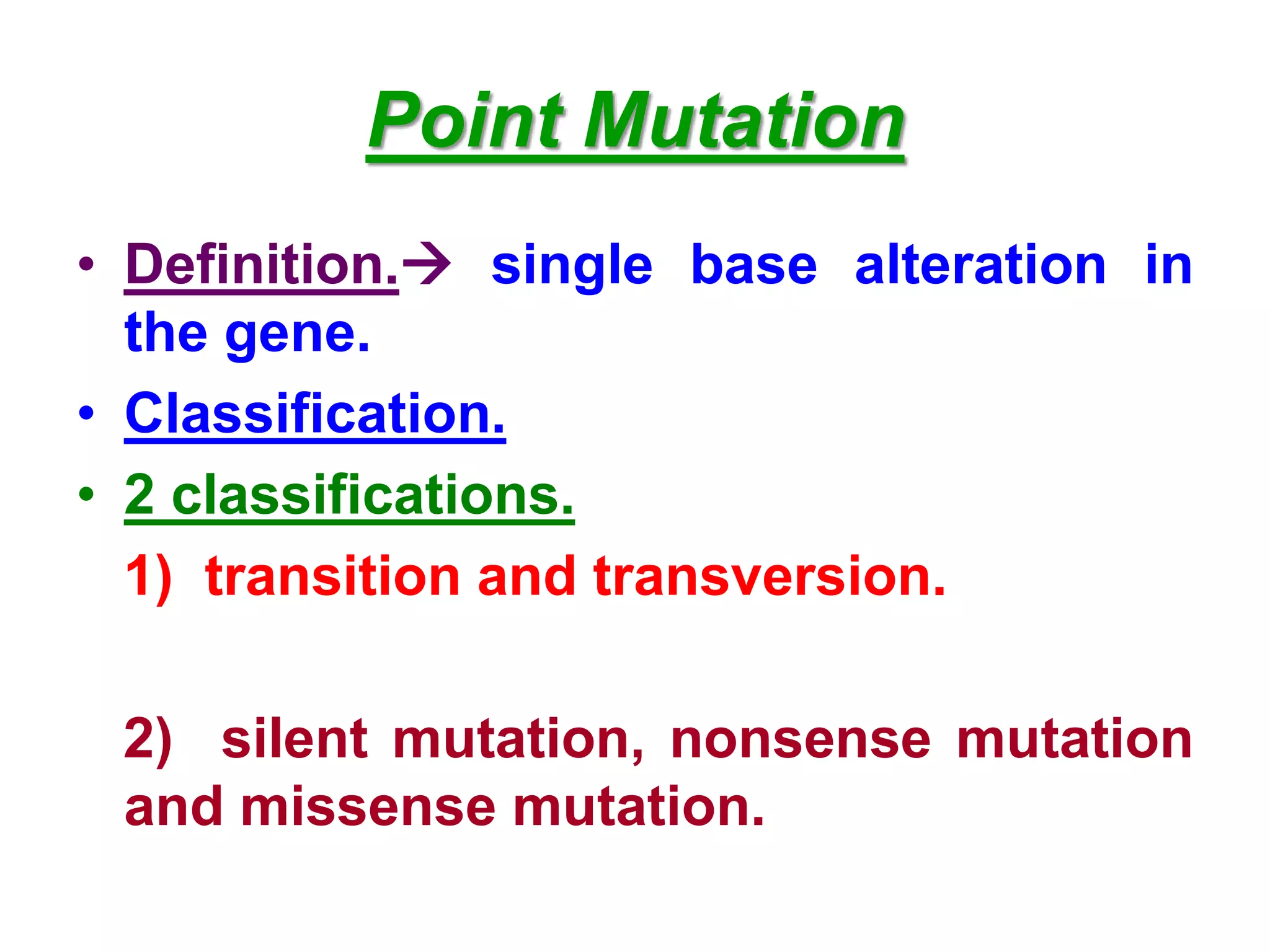
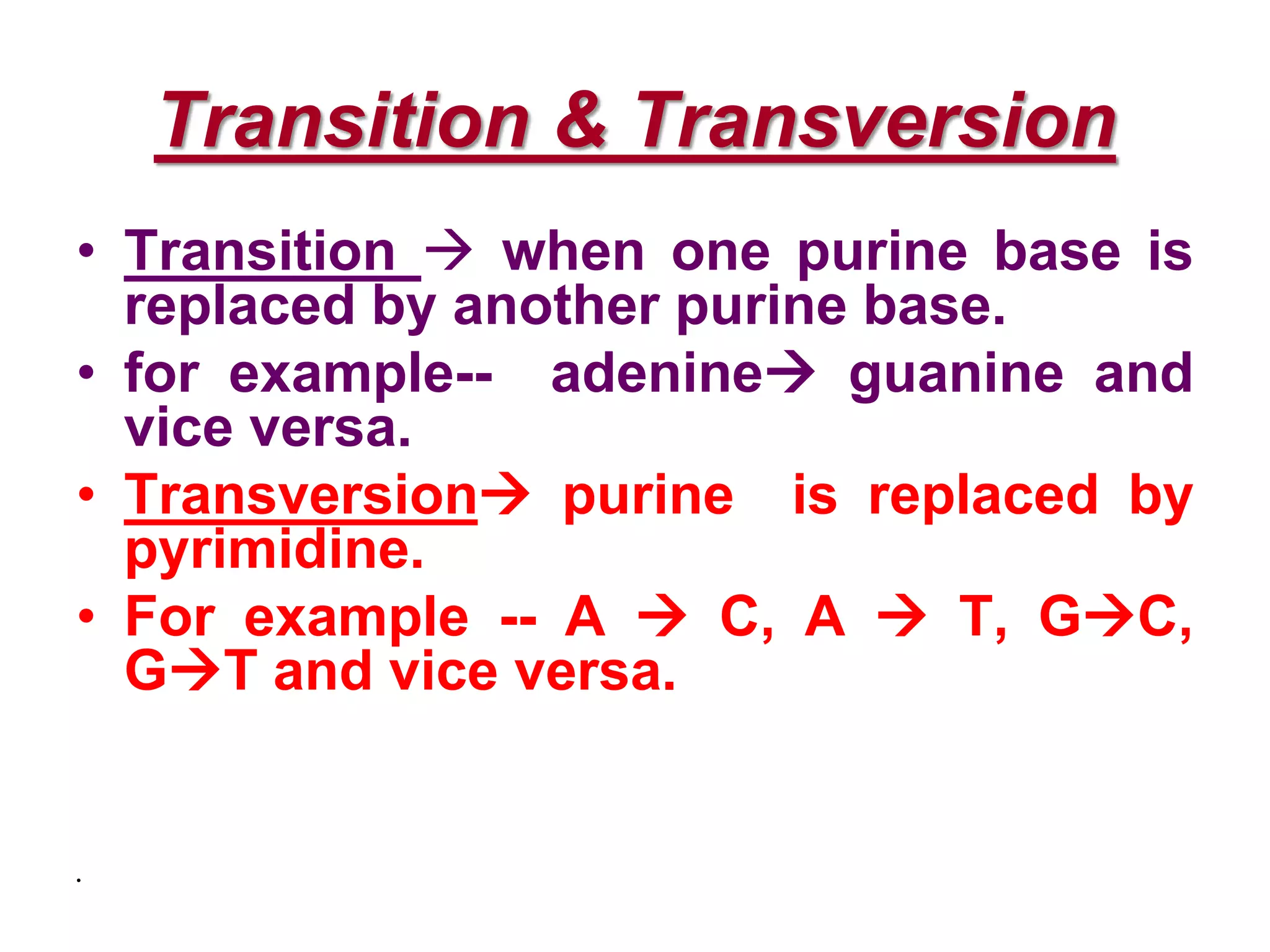
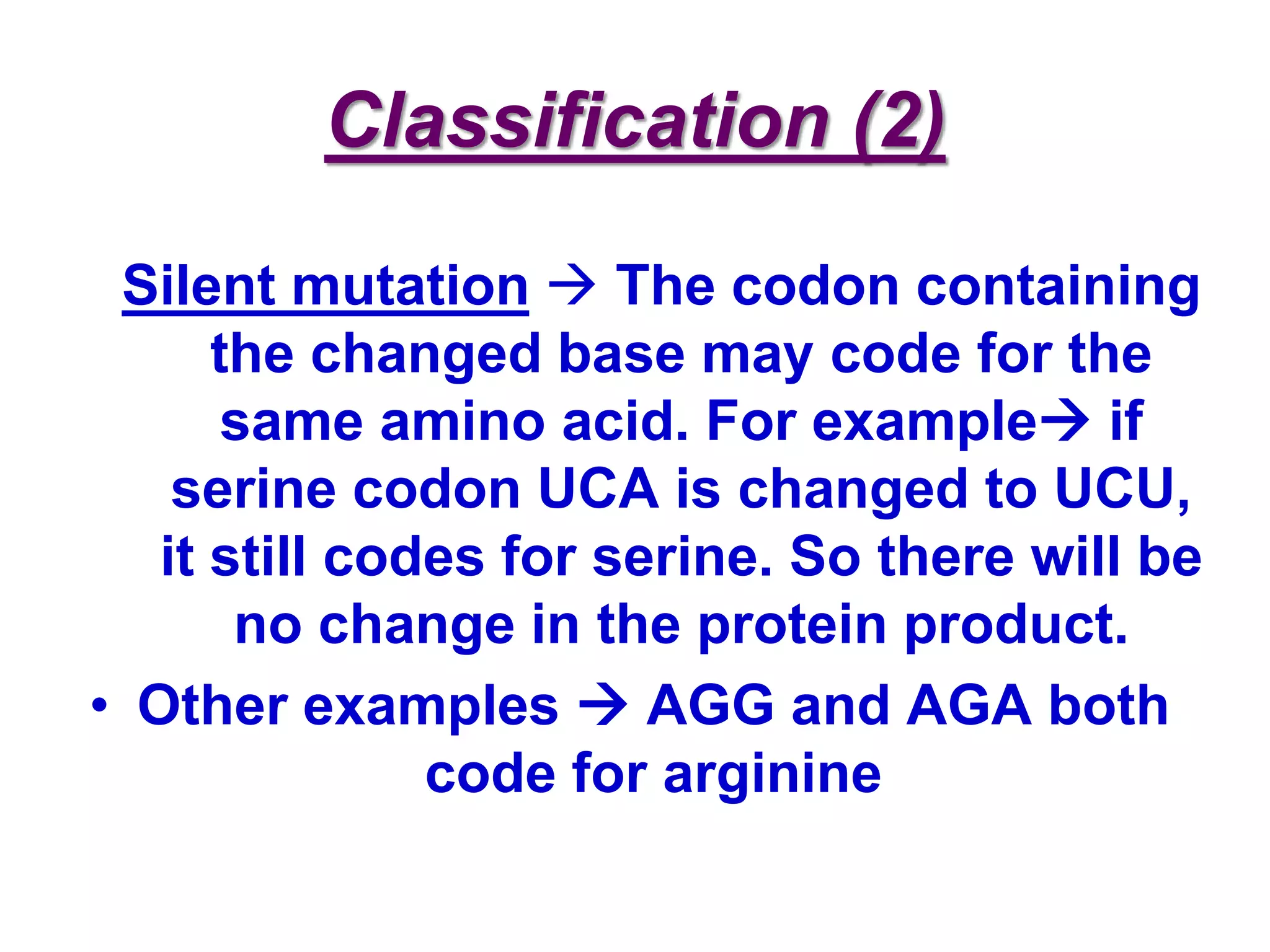
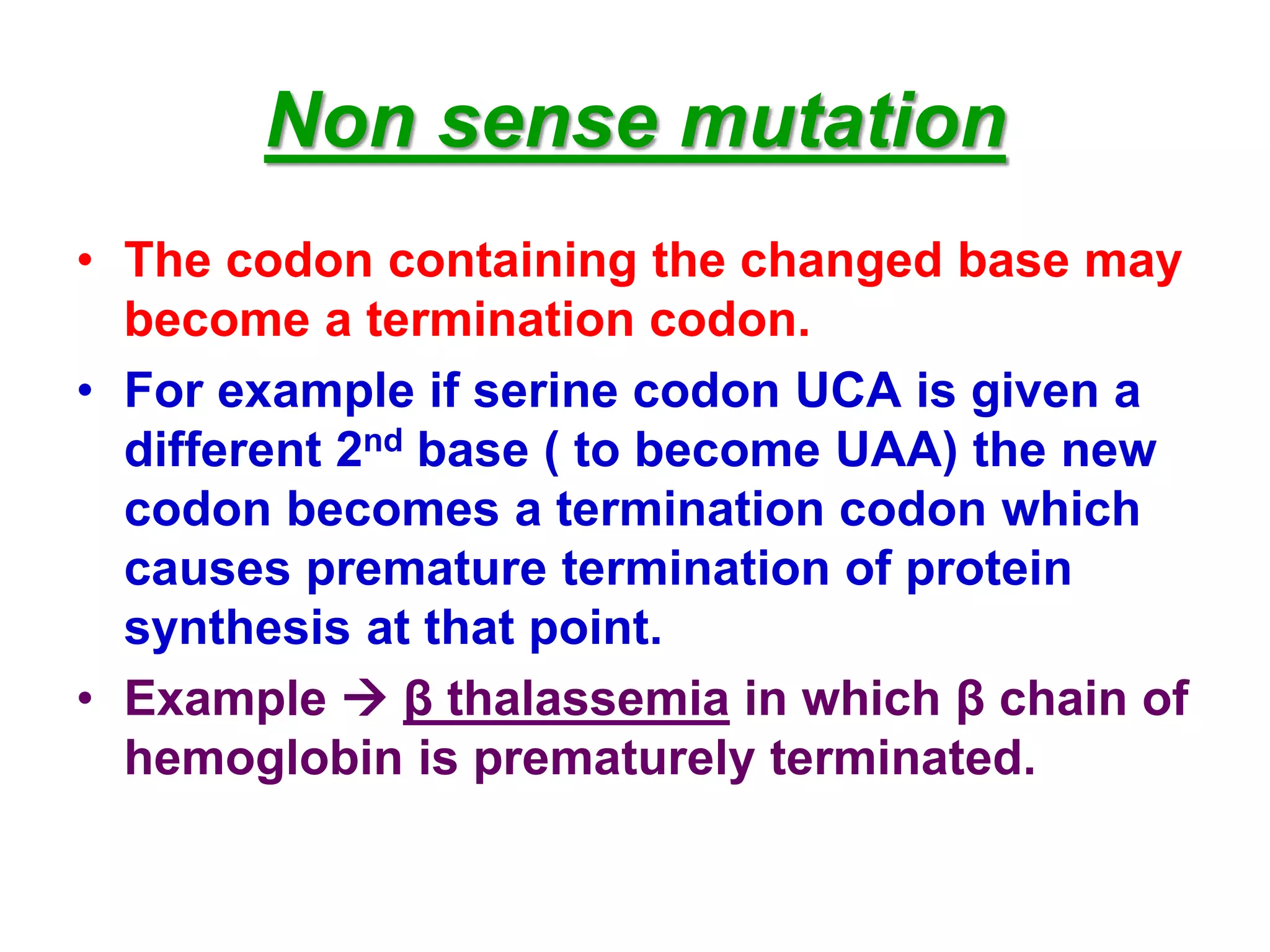
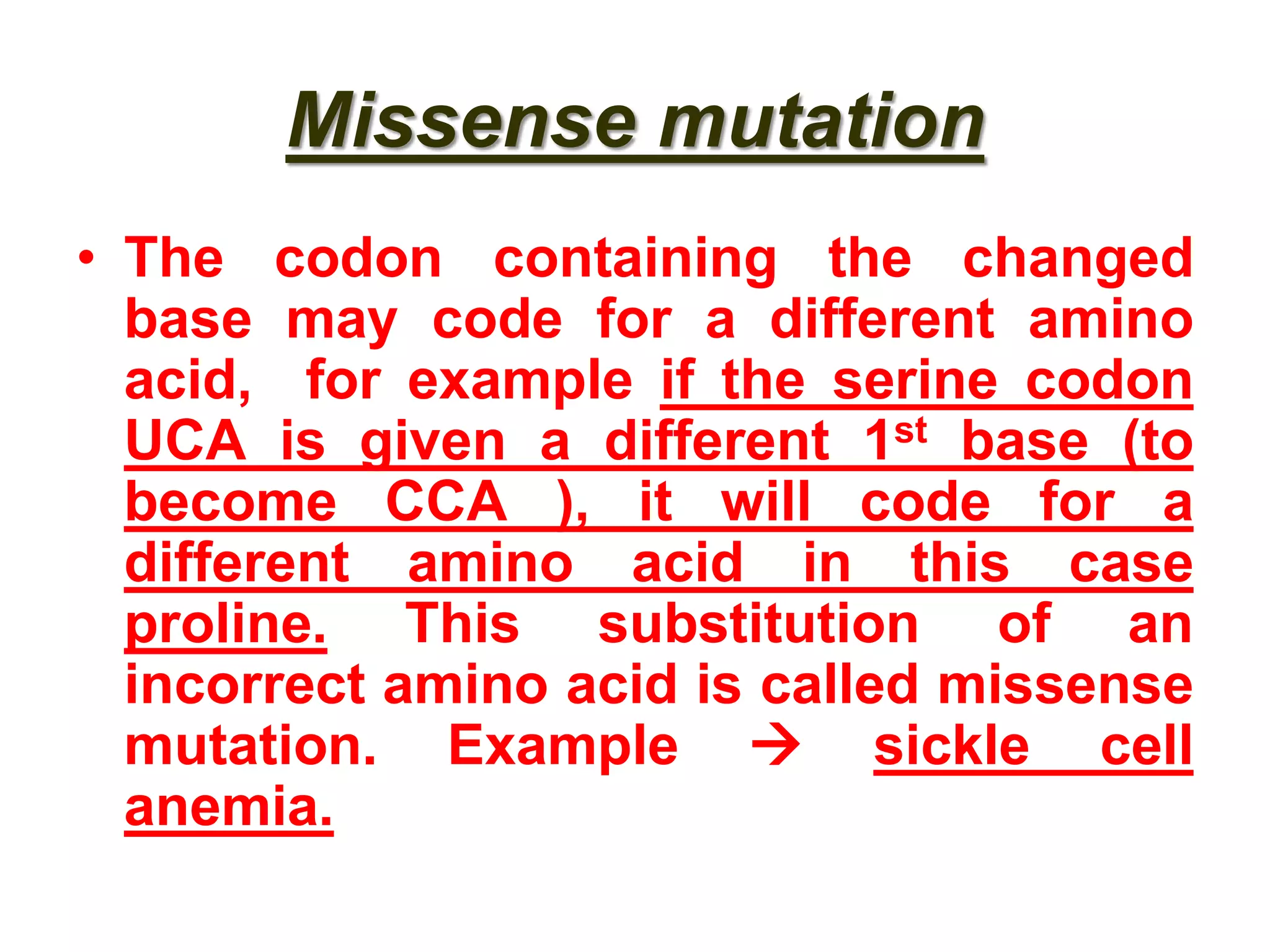
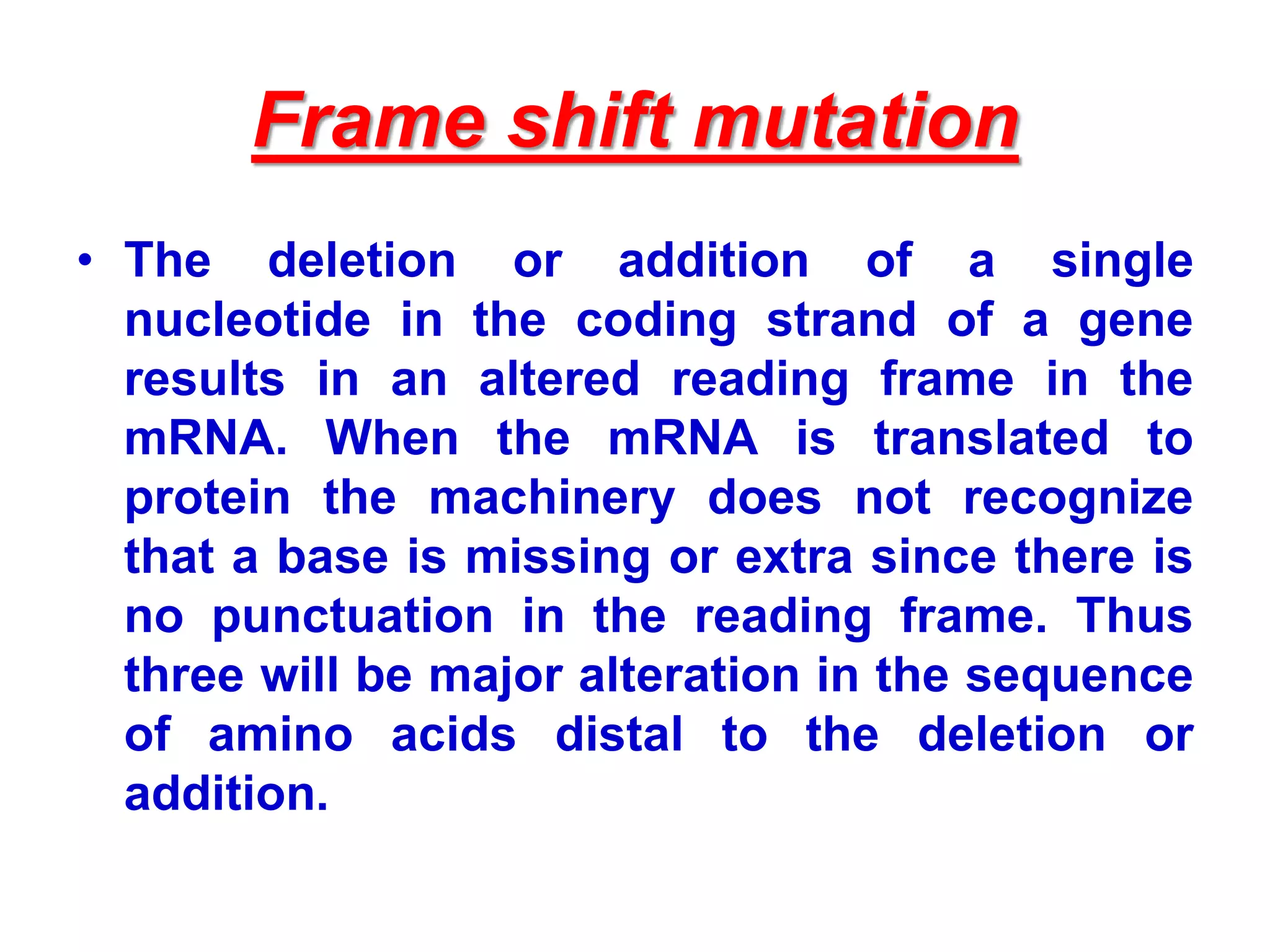
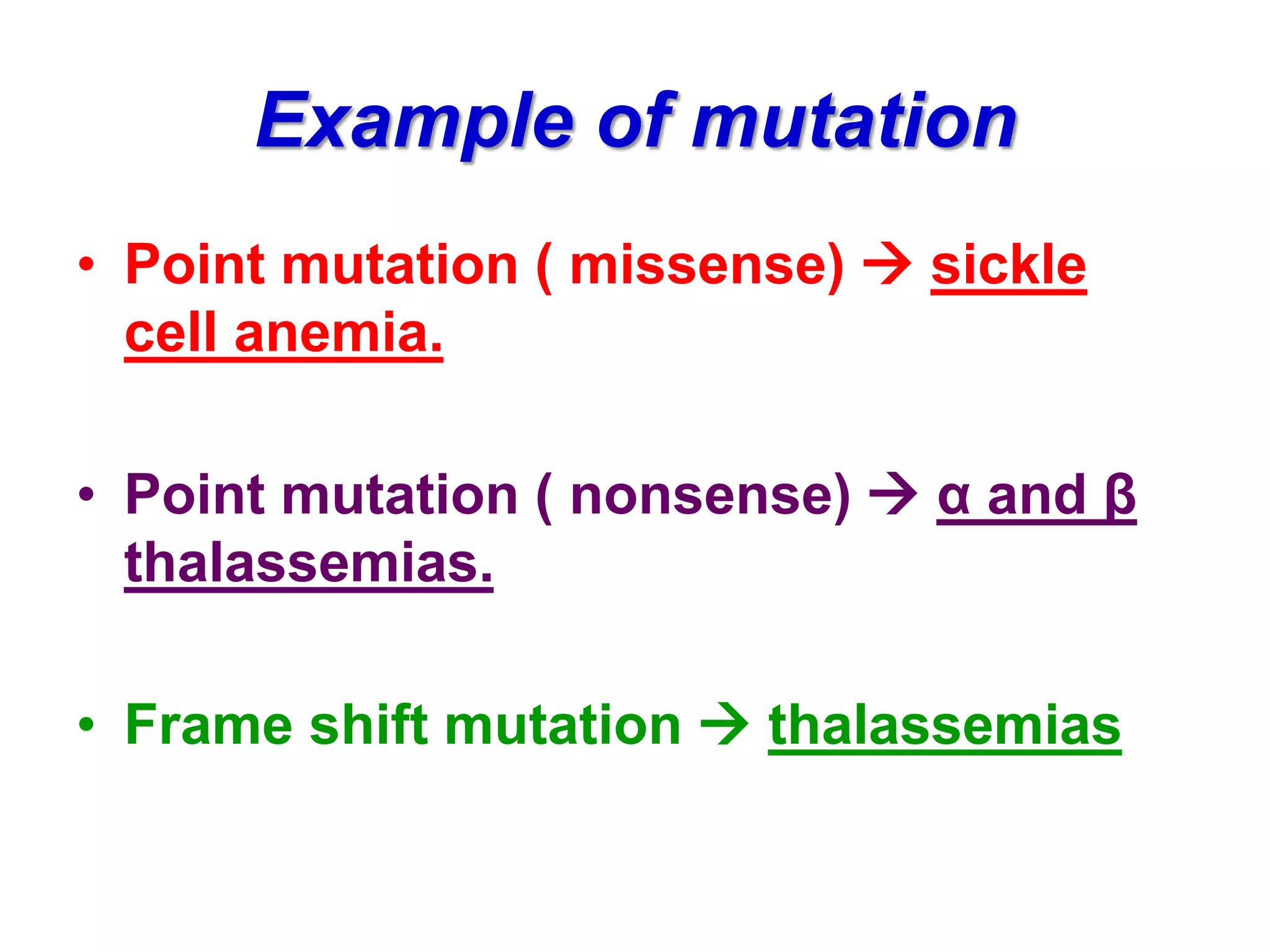
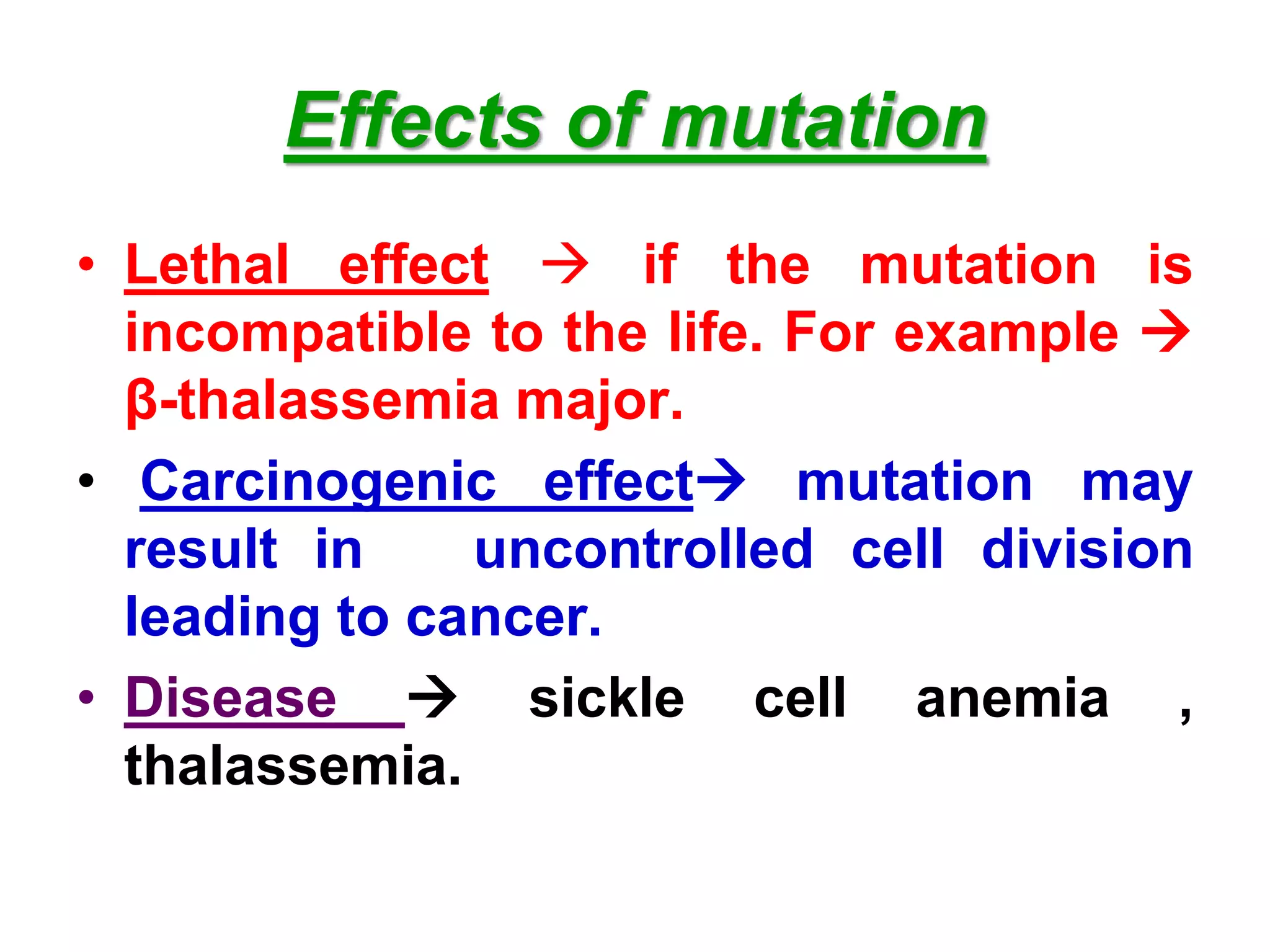
DNA repair systems fix damage to DNA to prevent mutations. The main repair pathways are mismatch repair, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and double strand break repair. Defects in repair genes can lead to cancers like xeroderma pigmentosa. The genetic code translates DNA into protein via mRNA. It is degenerate, unambiguous, and universal, with some variation between organisms. Mutations are changes to DNA that can be point mutations or frameshift mutations, and can have effects like causing disease or cancer.