This document provides an overview of nucleic acid chemistry concepts including:
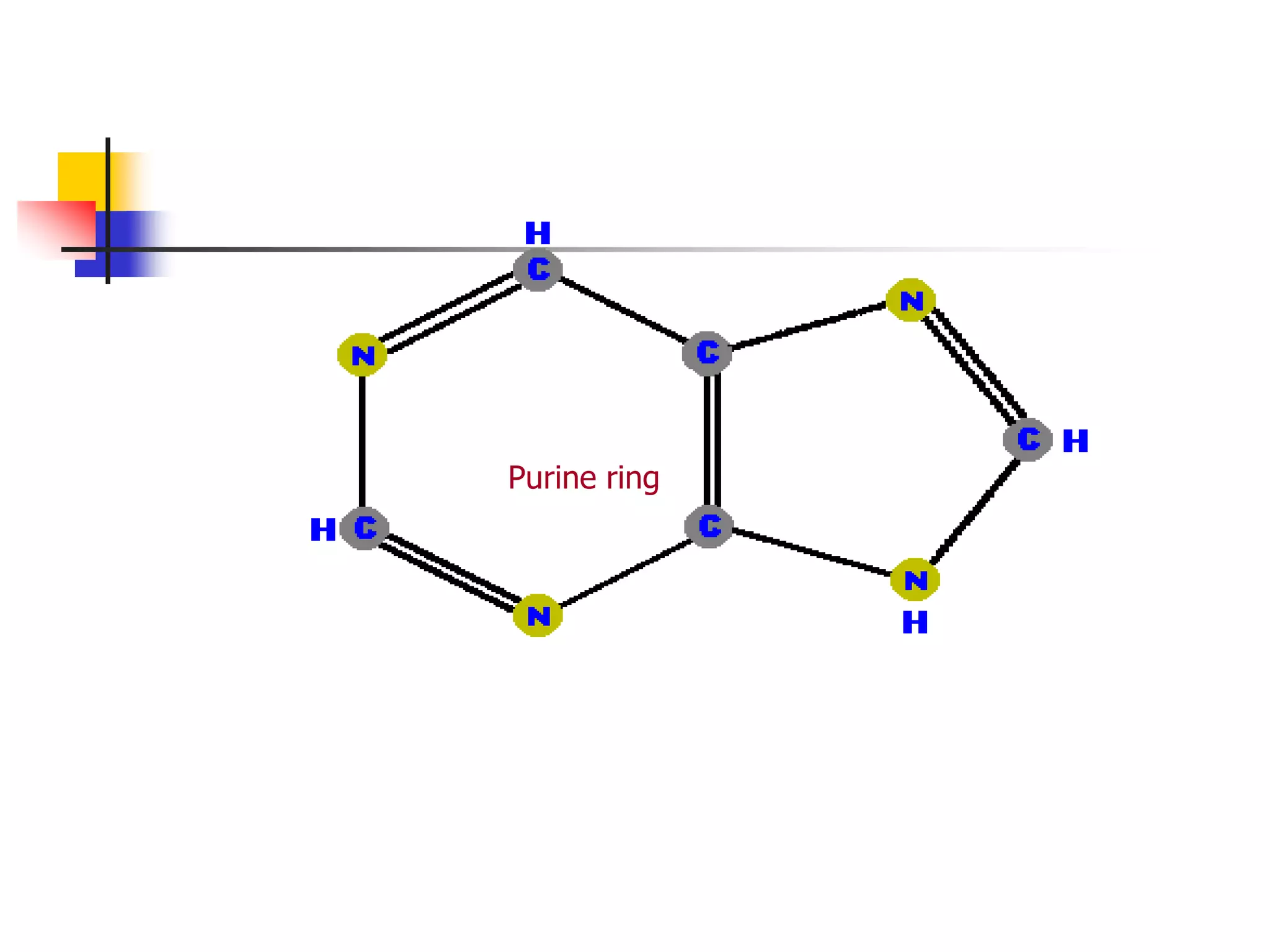
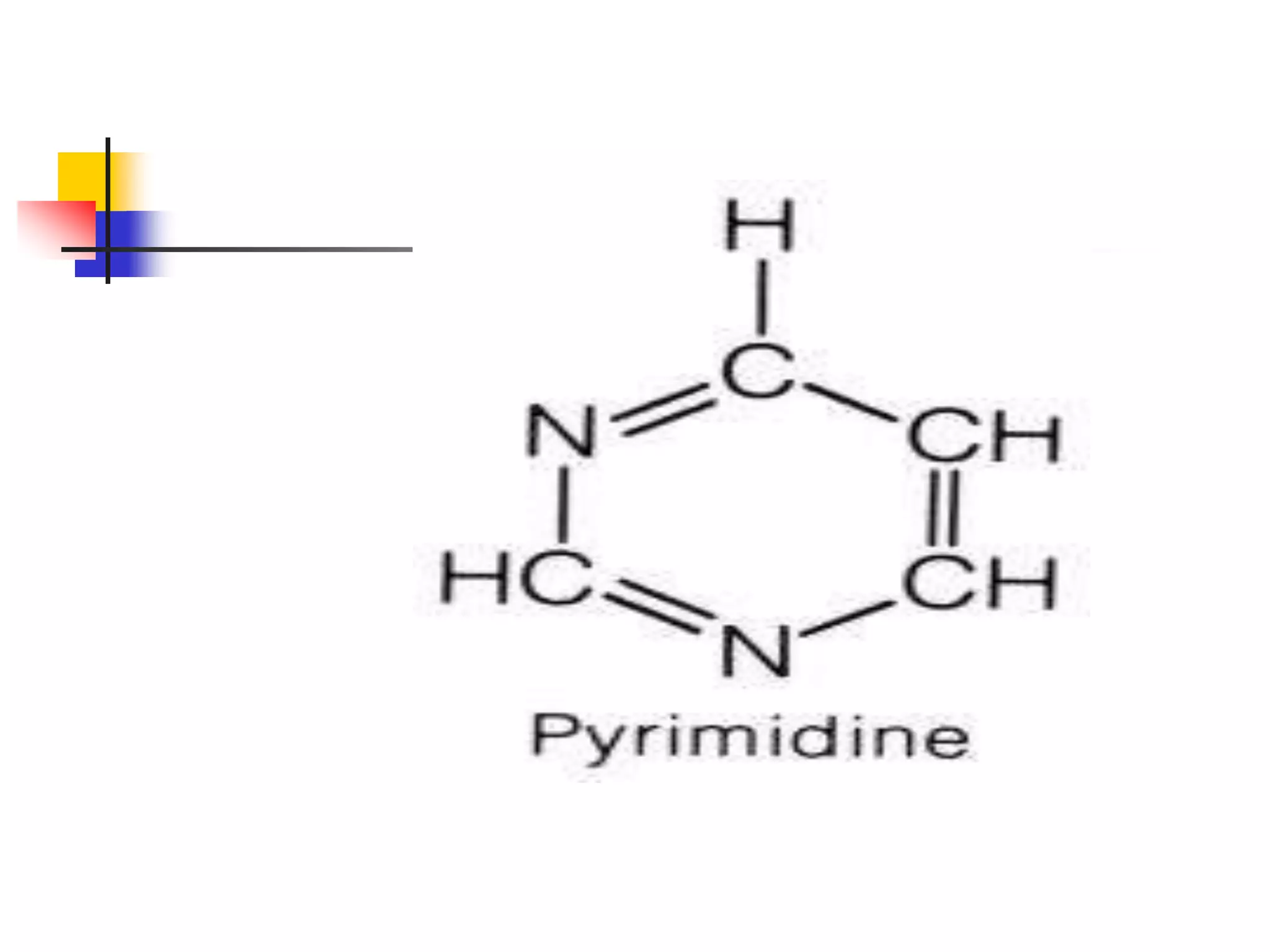
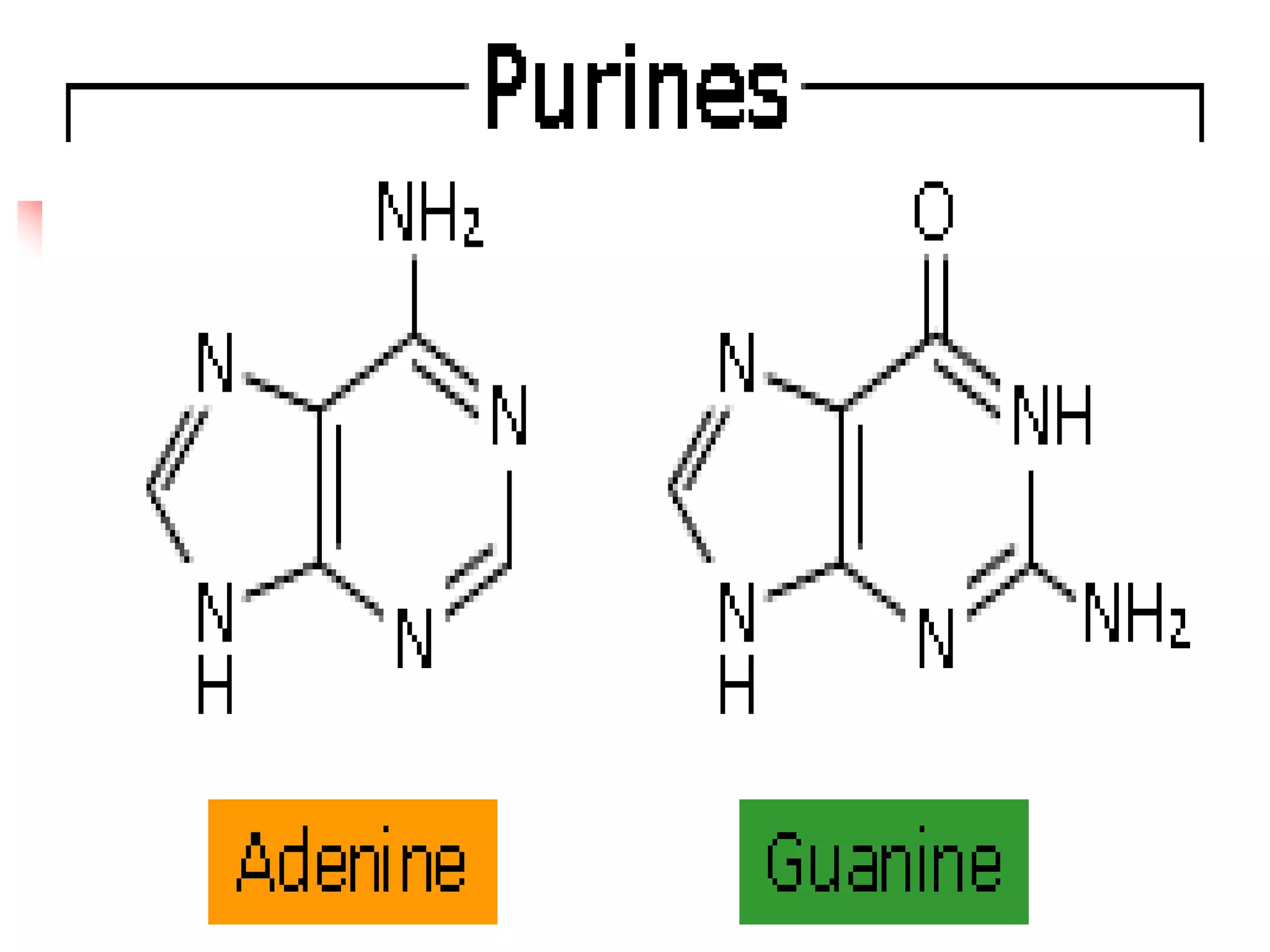
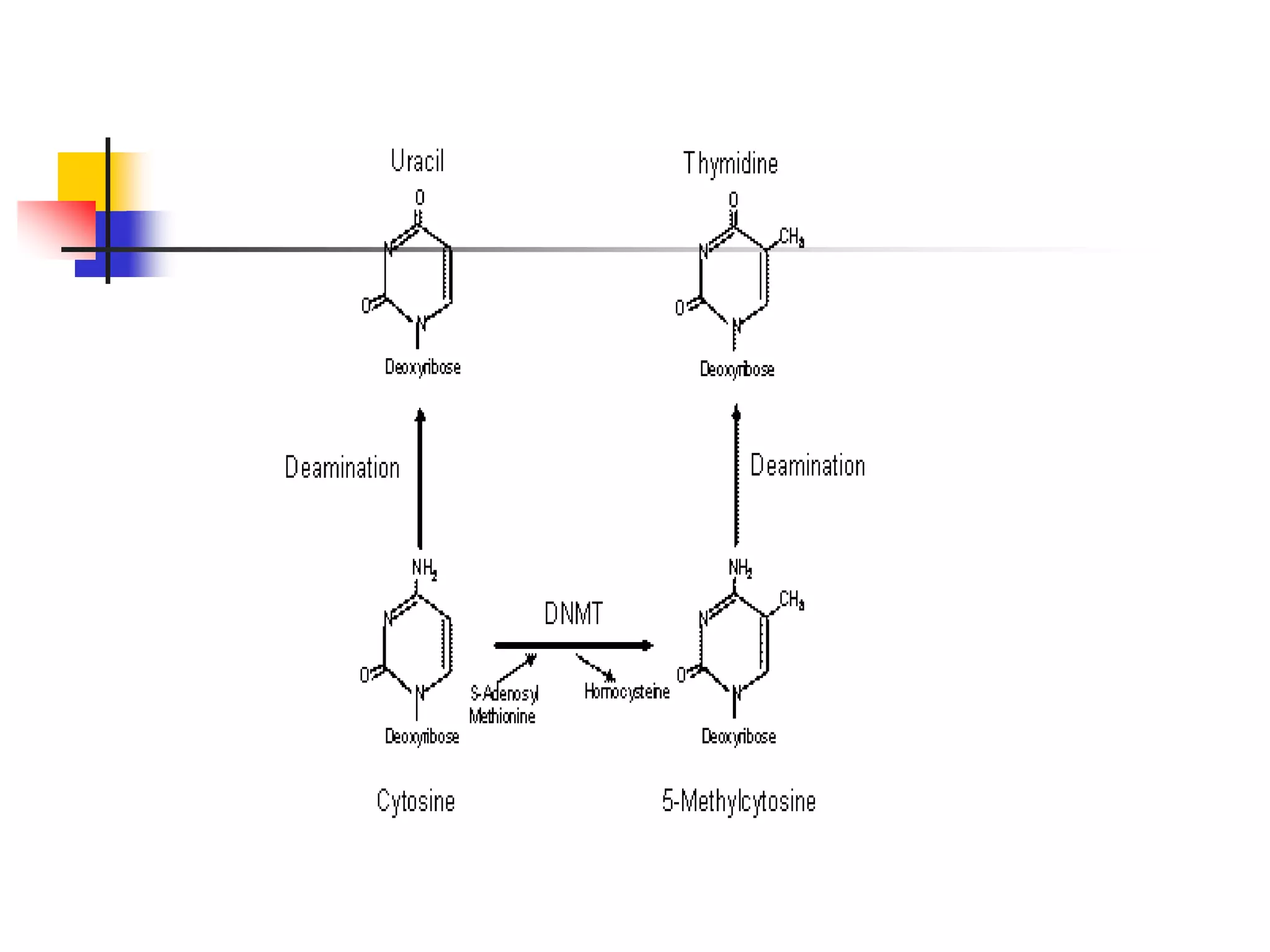
1) Purines and pyrimidines are the basic structures that make up nucleotides and nucleic acids. Major purines include adenine and guanine, while major pyrimidines include cytosine, uracil, and thymine.
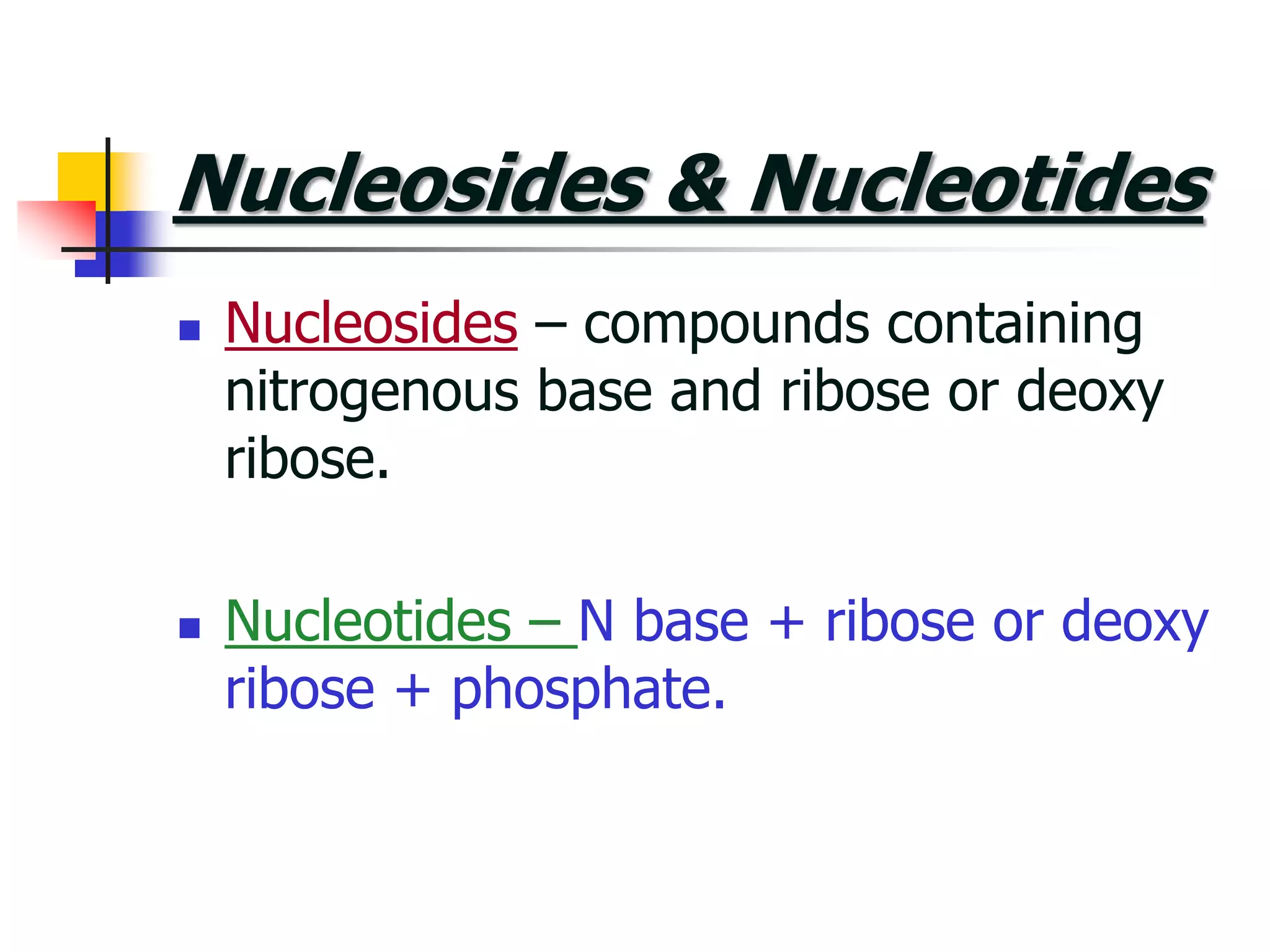
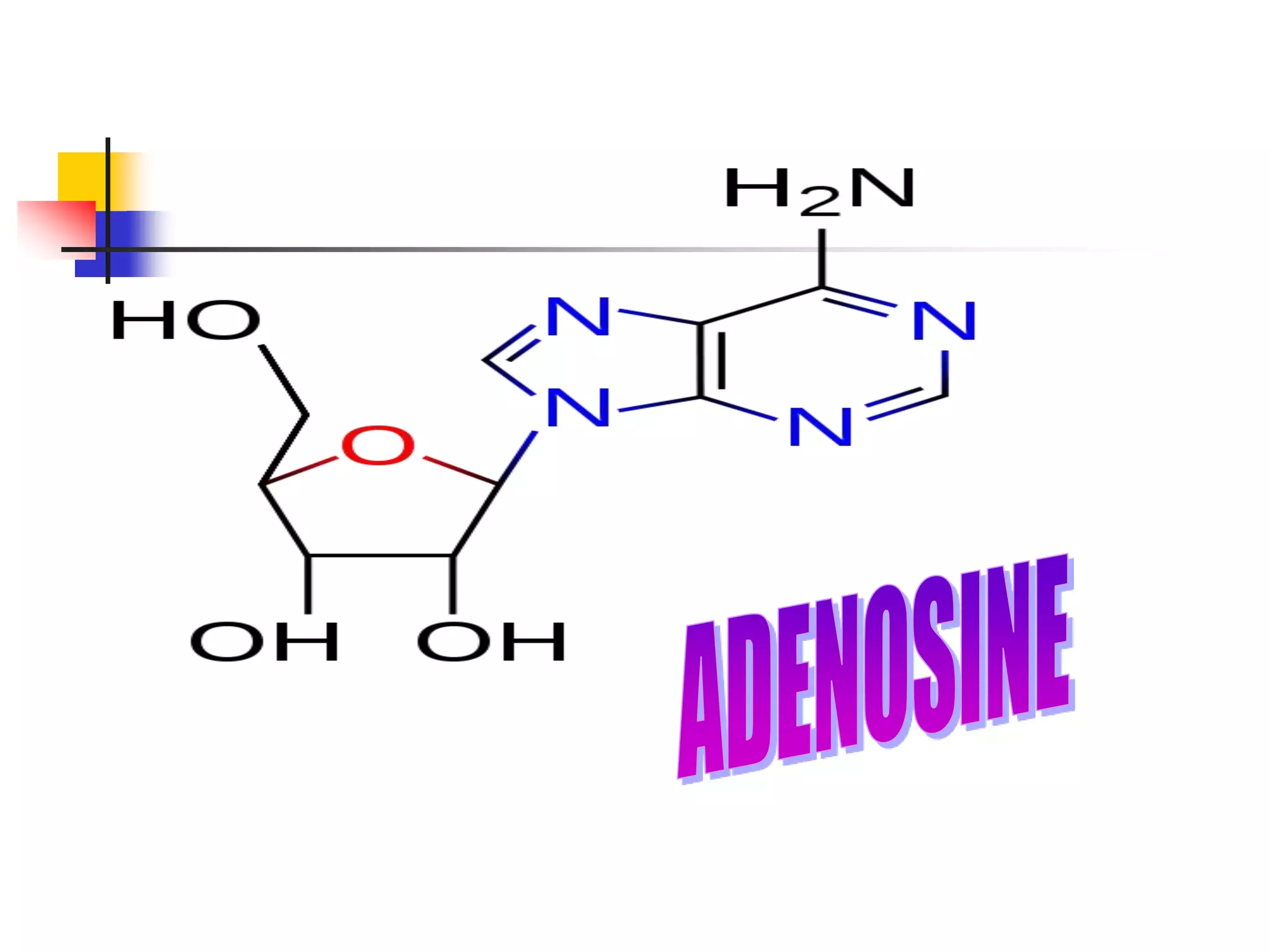
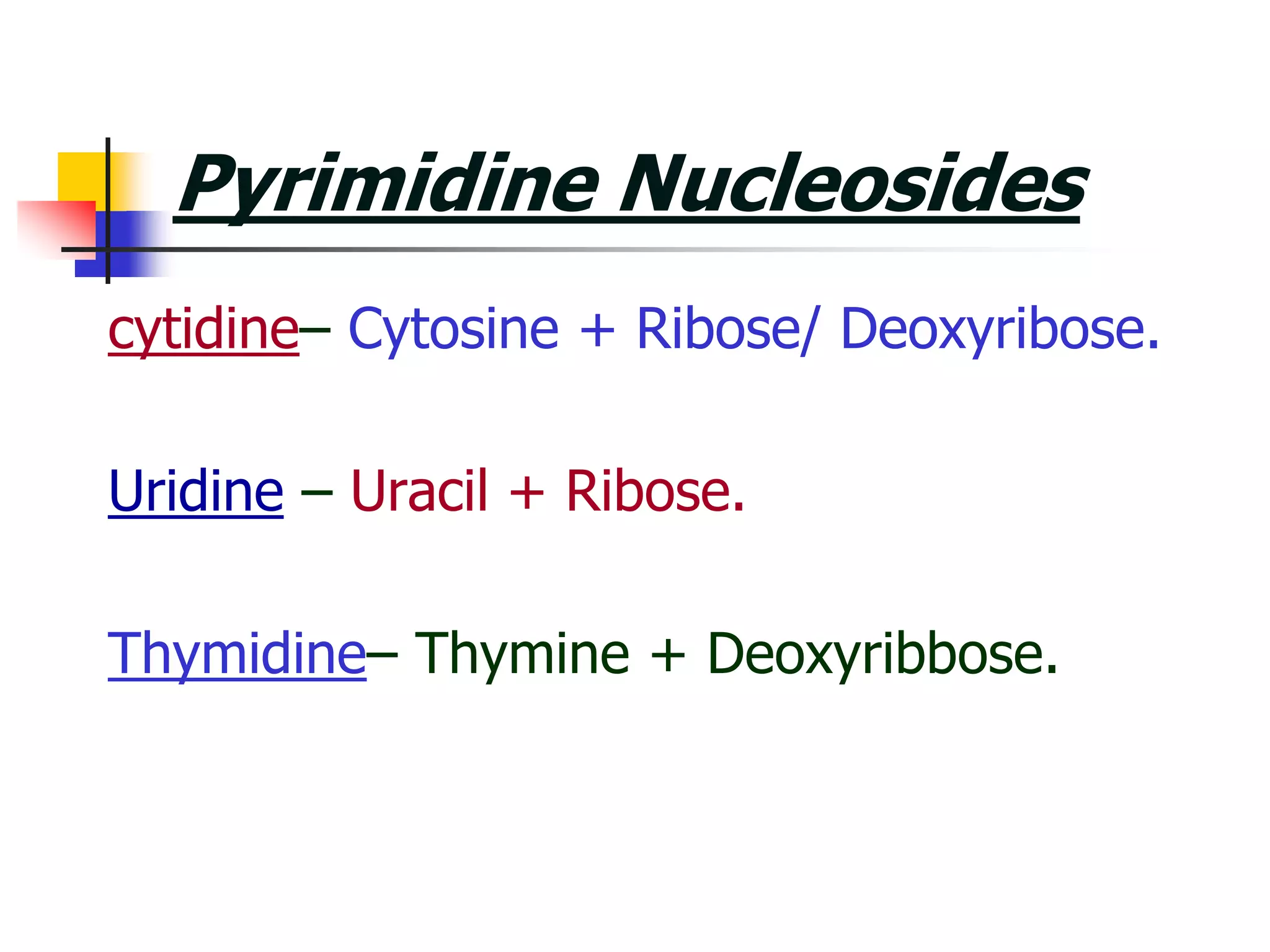
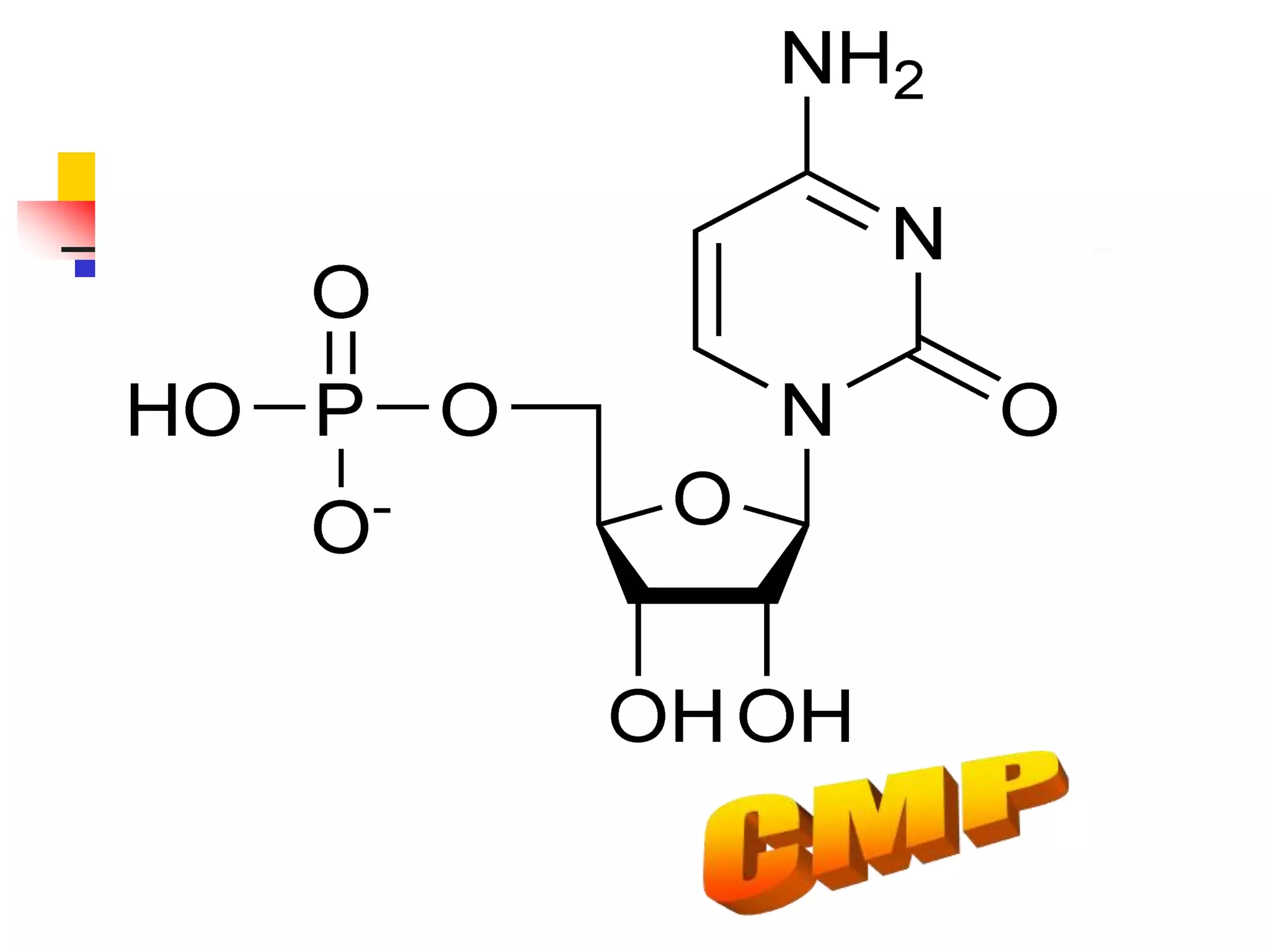
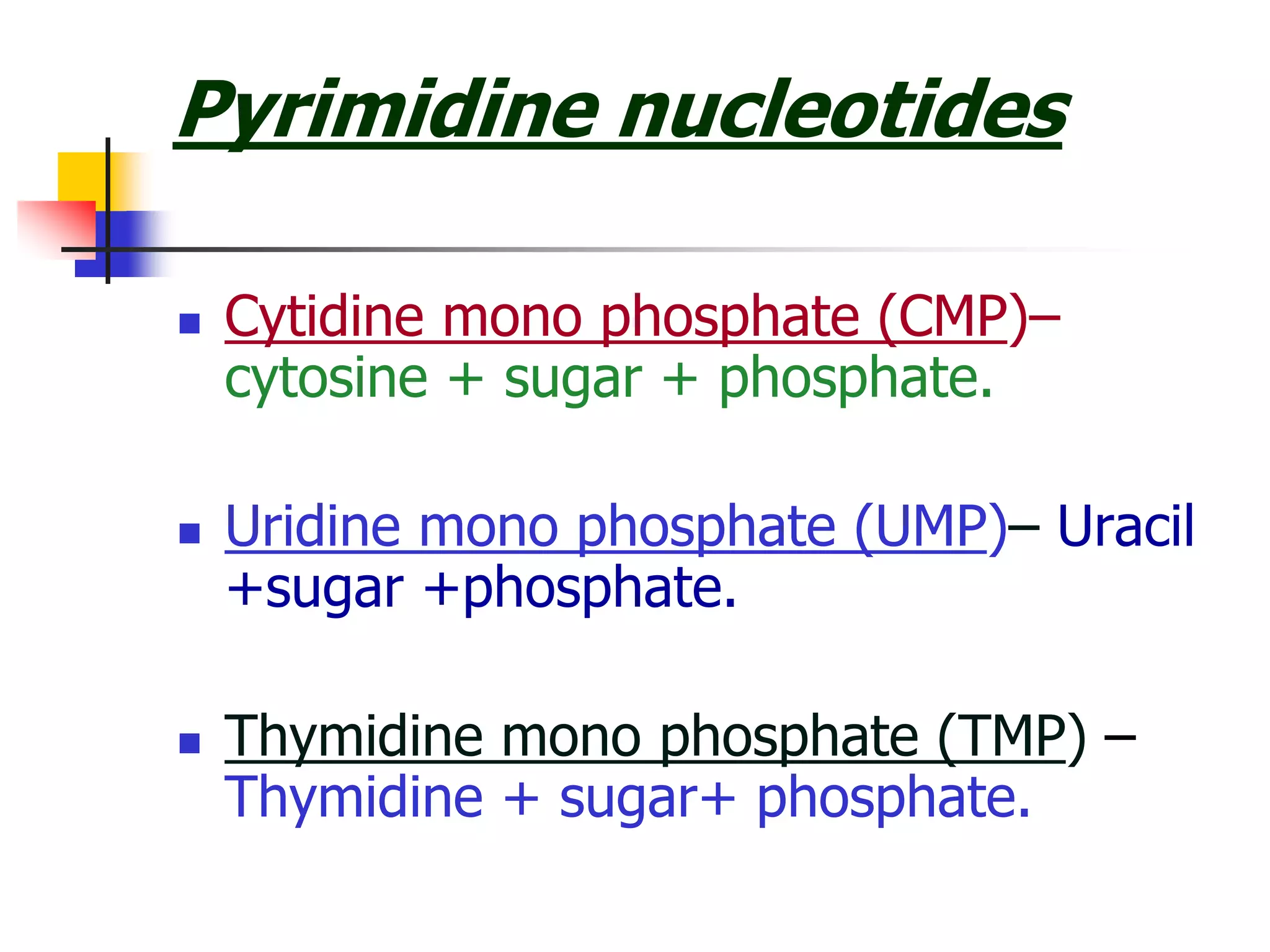
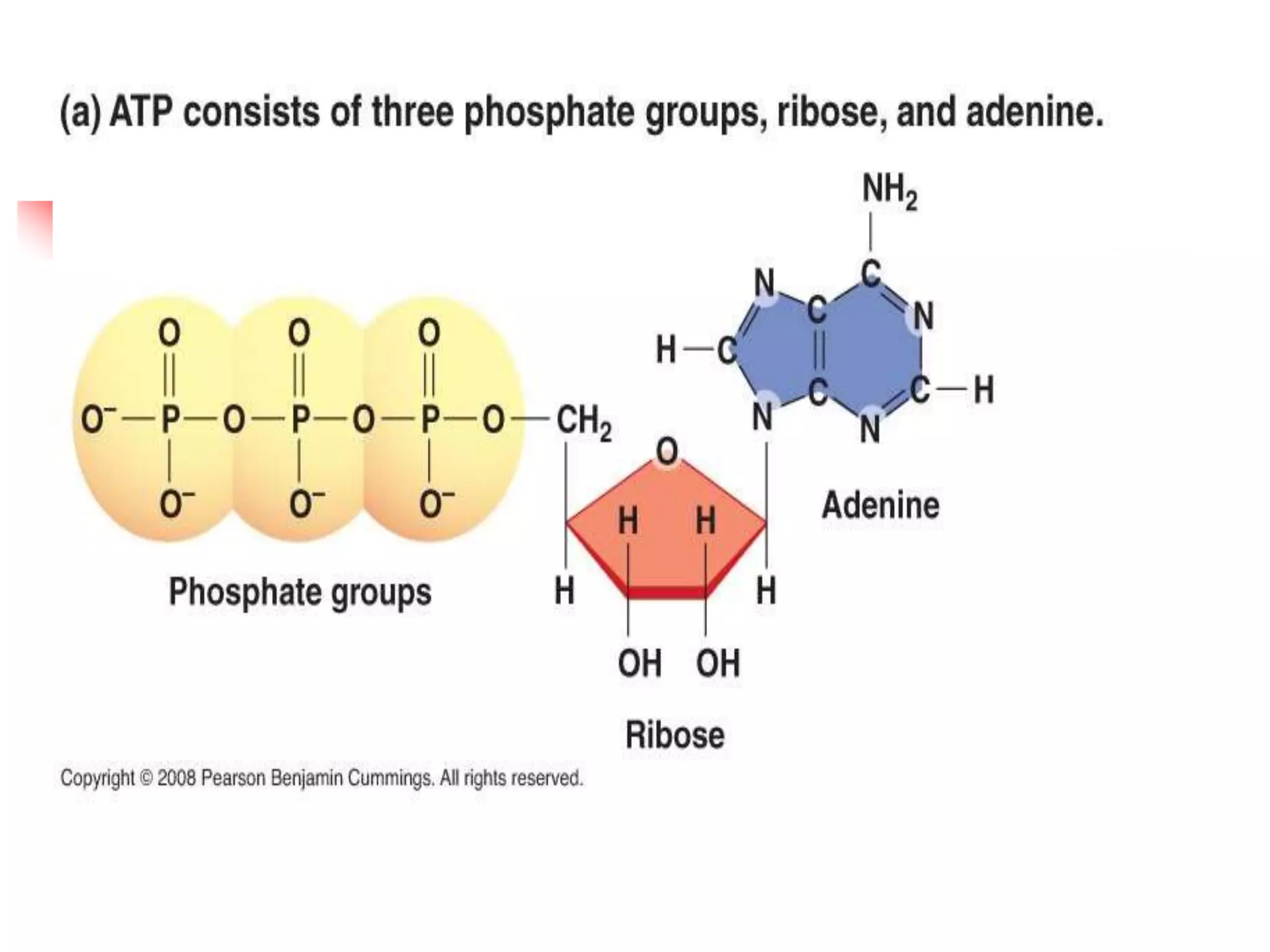
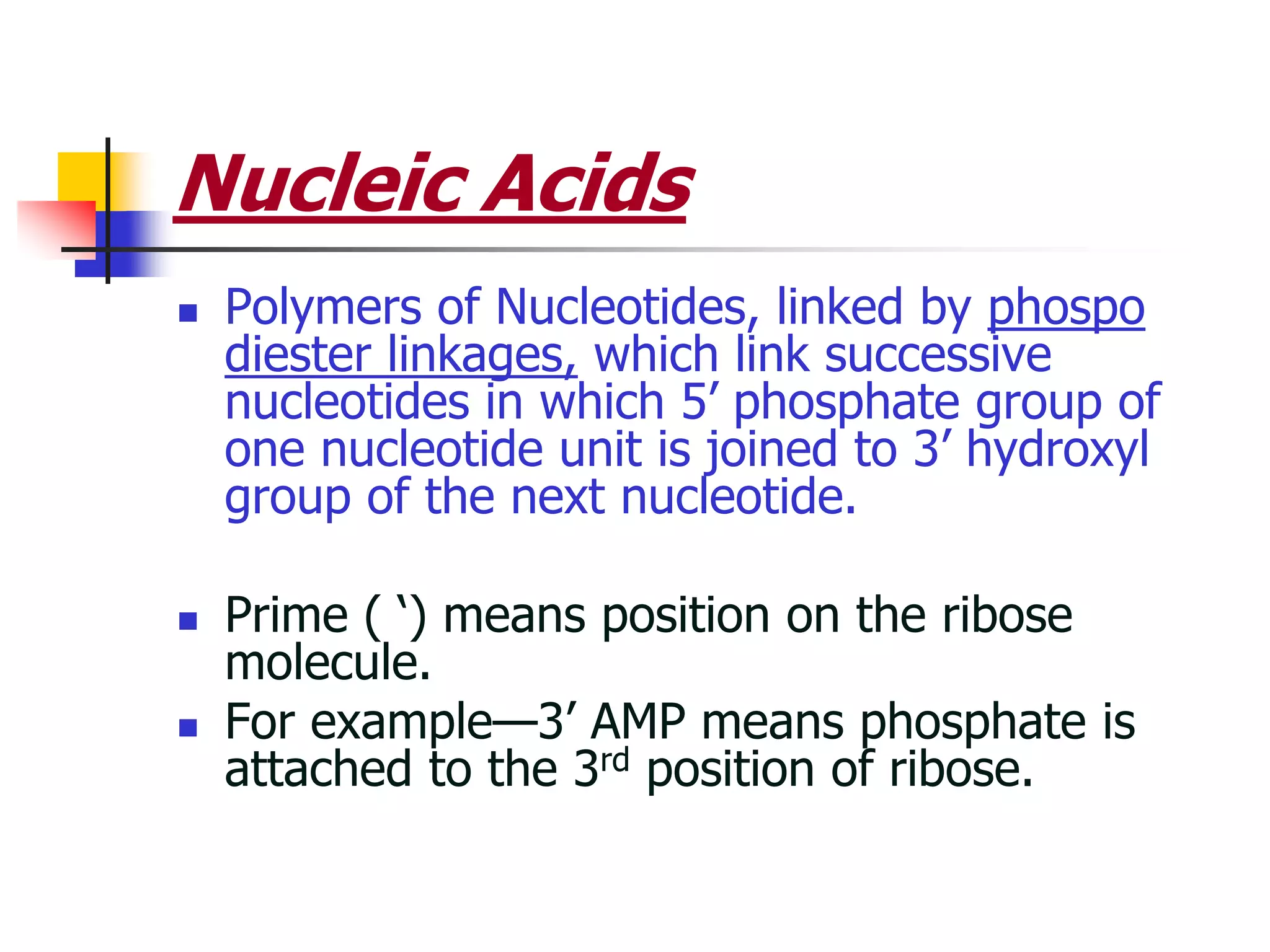
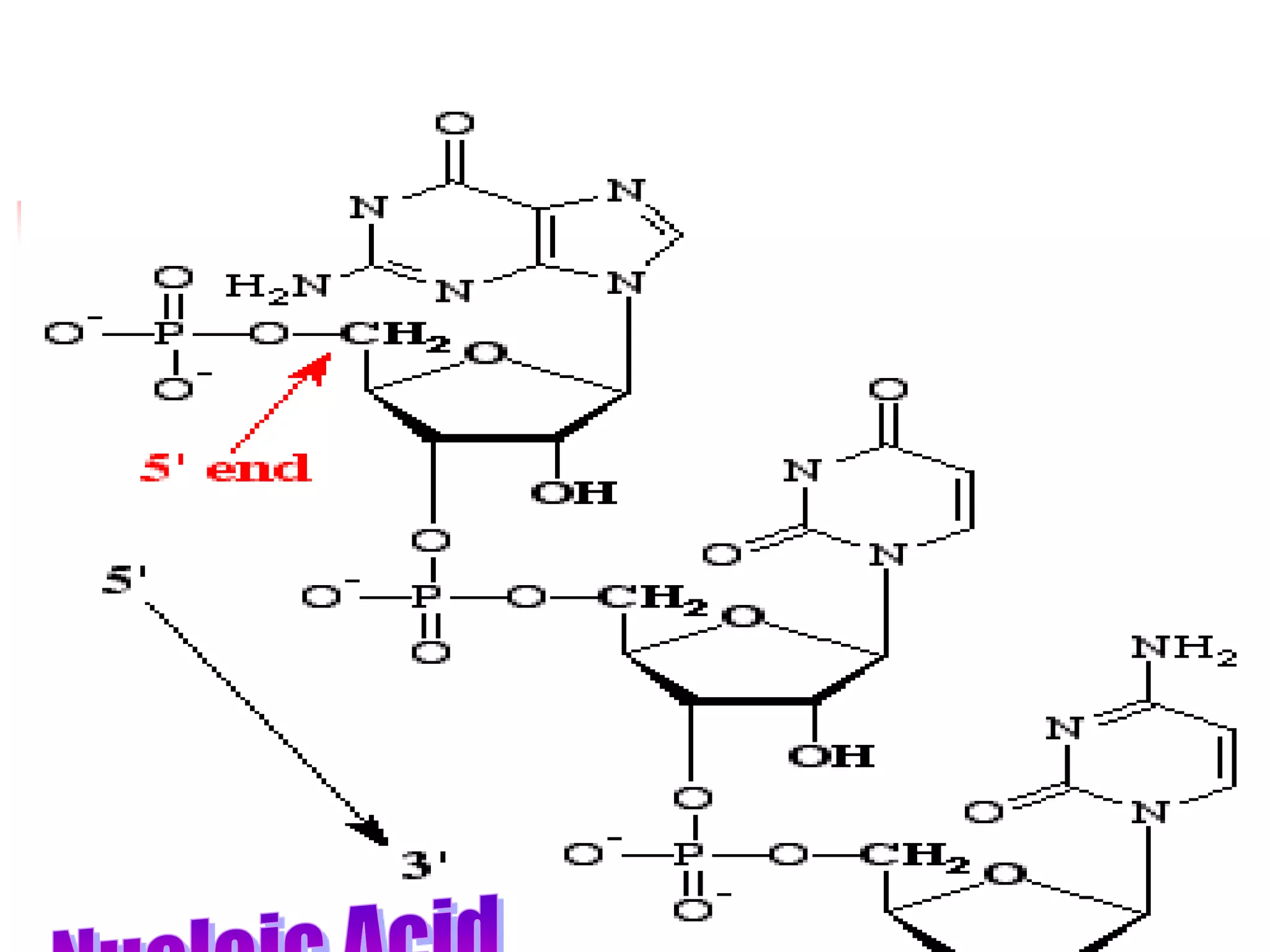
2) Nucleosides consist of a nitrogenous base linked to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar. Nucleotides contain a nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate group.
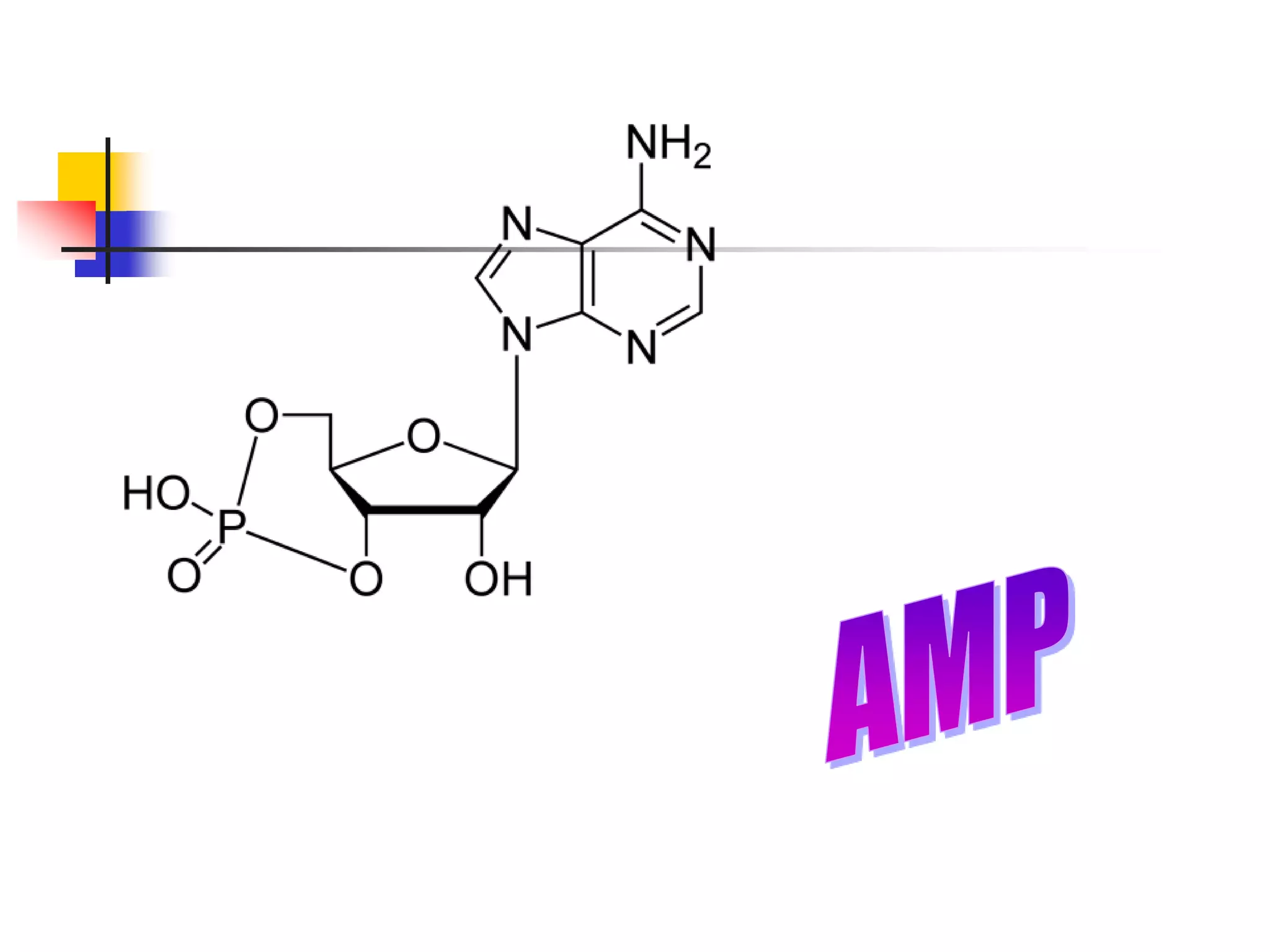
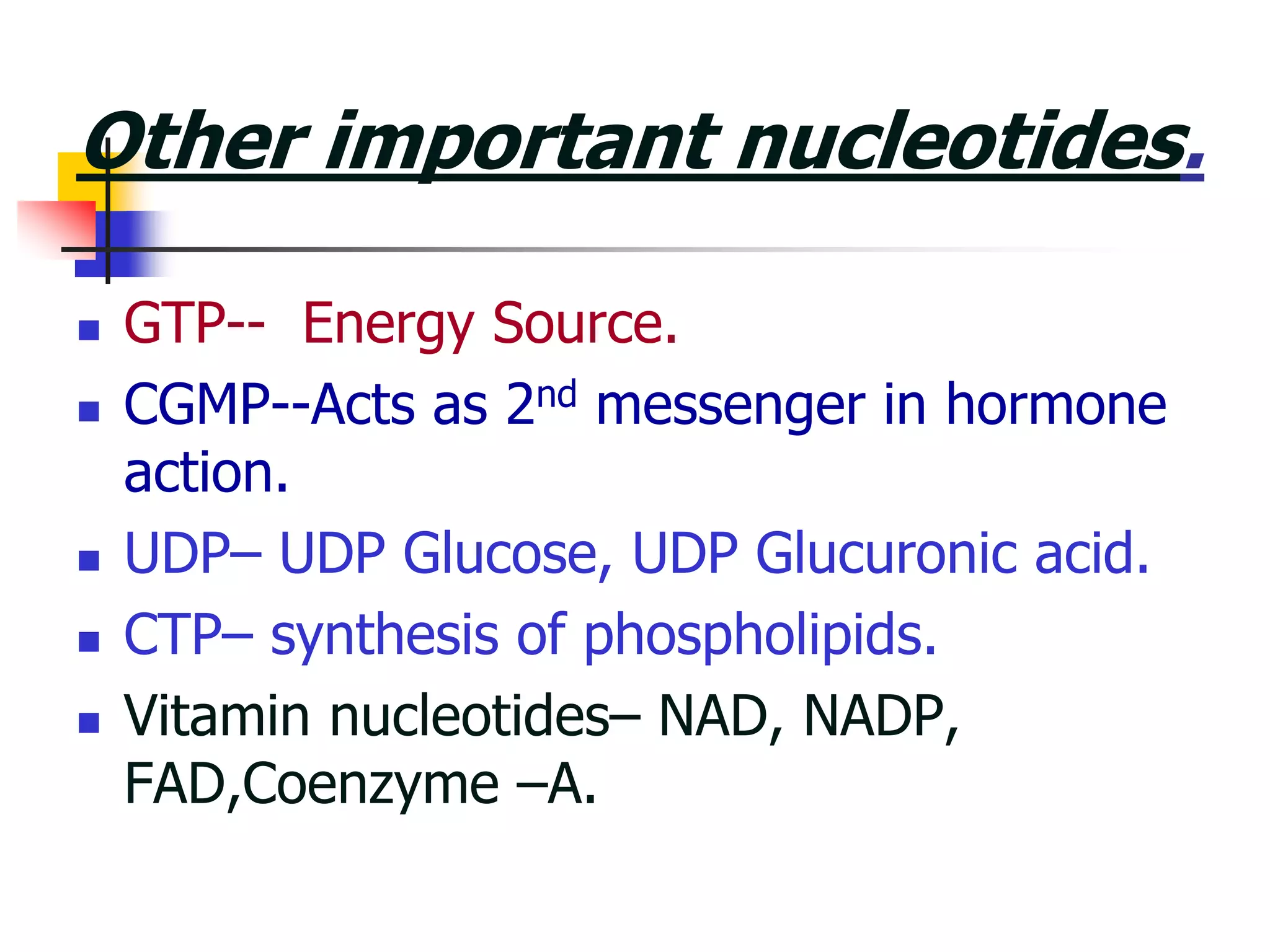
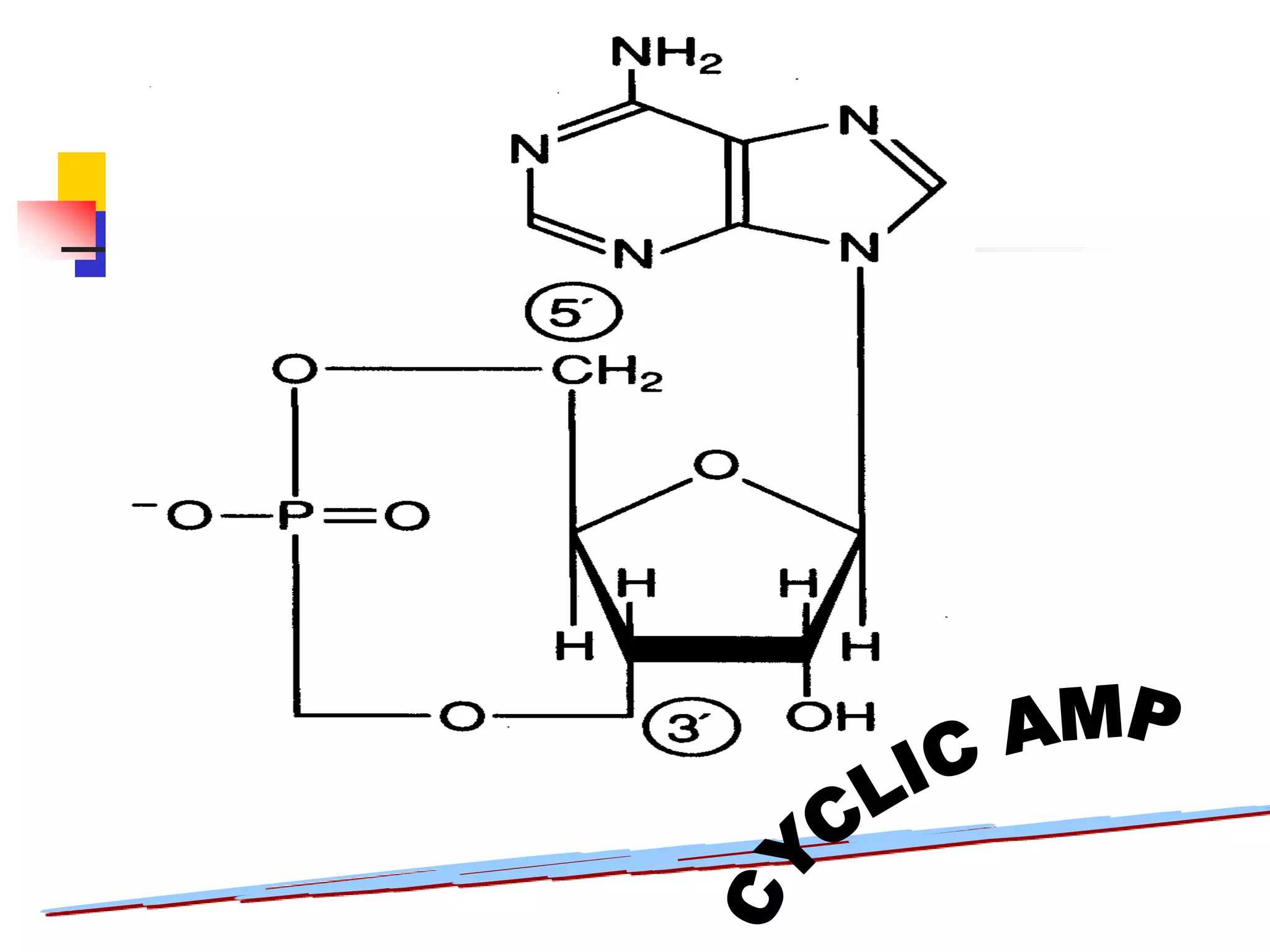
3) Important nucleotides include ATP, ADP, cAMP, GTP, and CTP which play critical roles in cellular energy transfer and signaling. Synthetic analogs are also used experimentally and clinically.