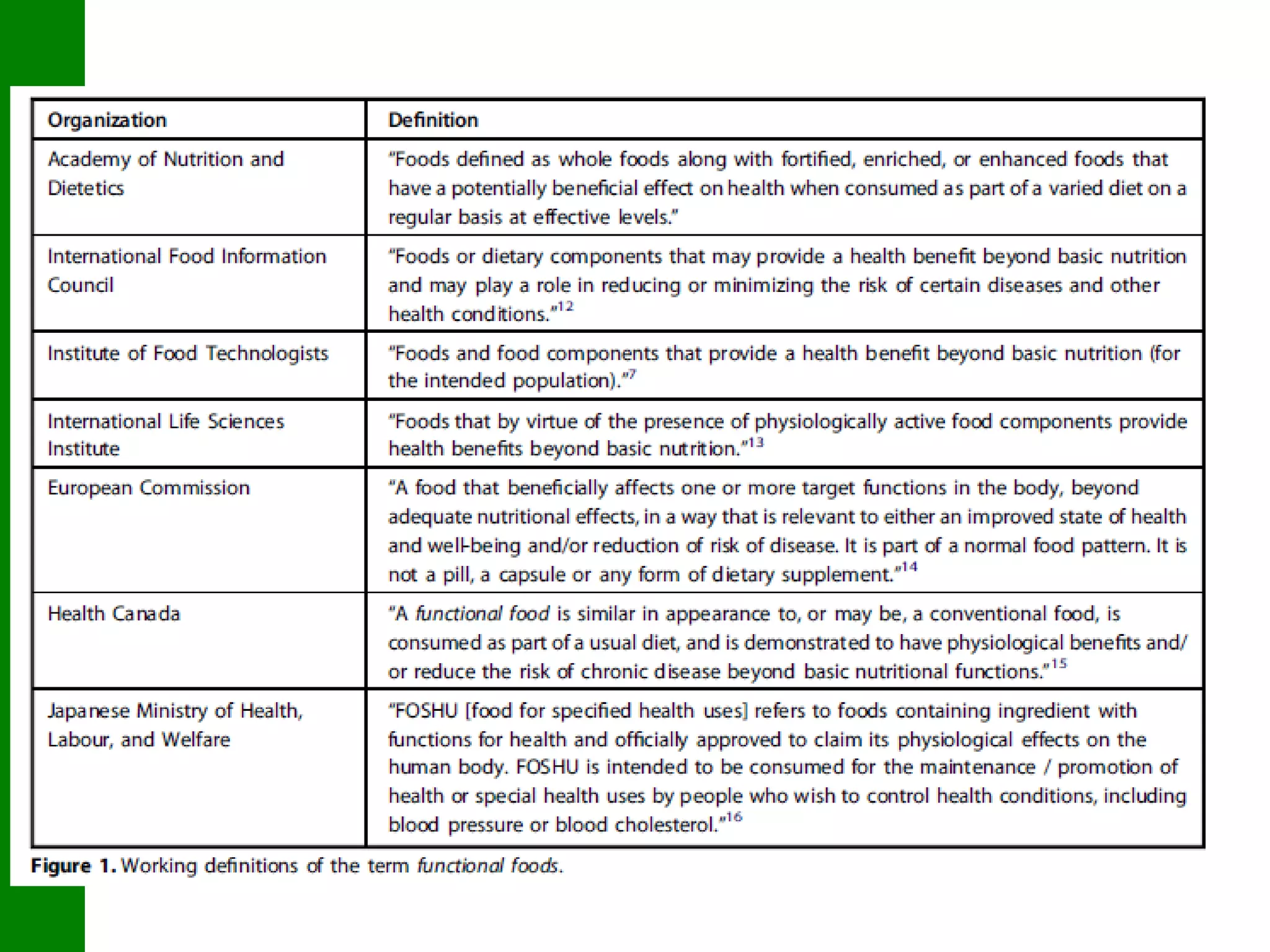
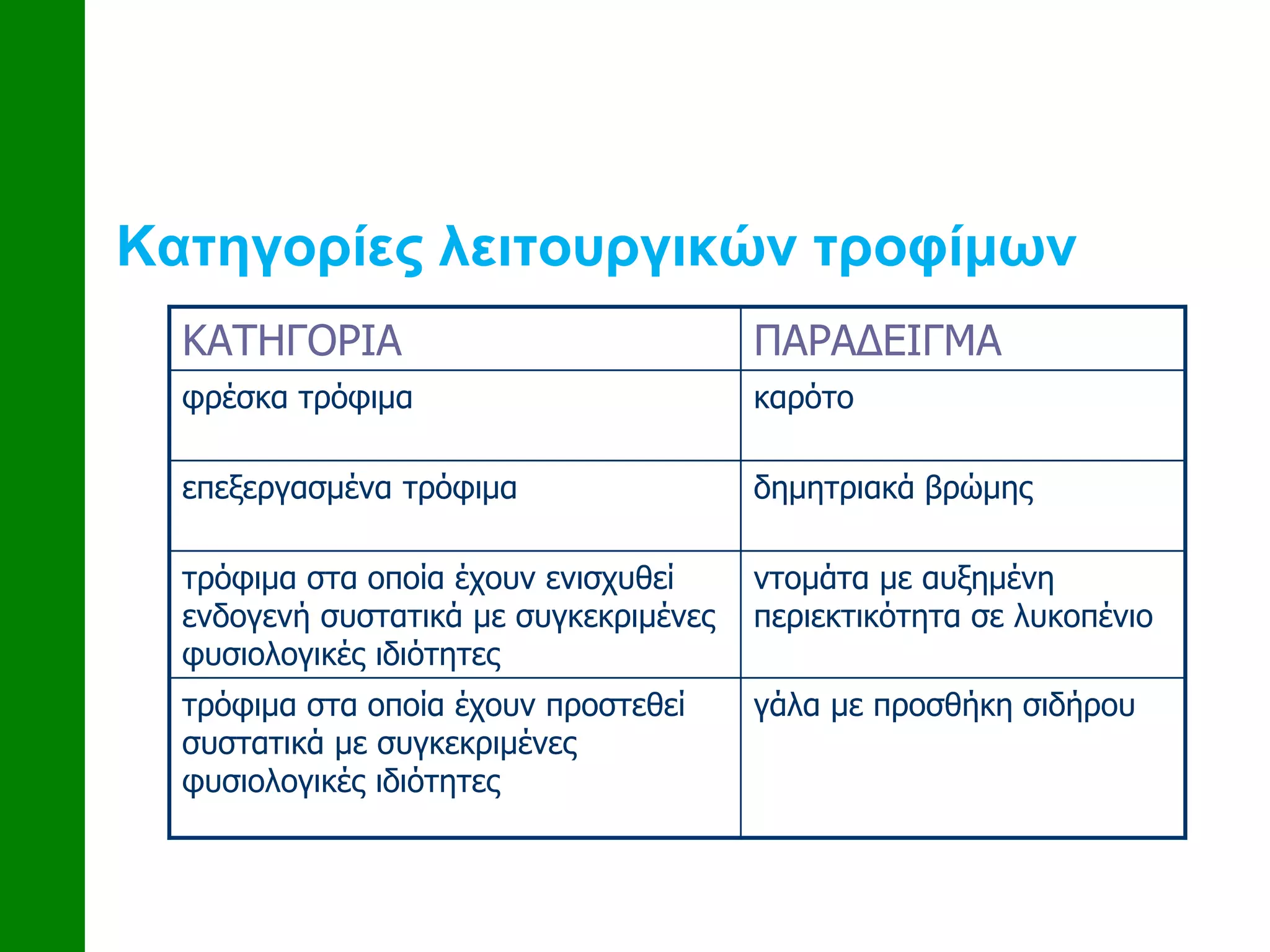
This document discusses functional foods and nutrition. It begins by defining functional foods as foods that are claimed to promote health or provide benefits beyond basic nutrition. Examples mentioned include fresh foods like carrots, processed foods like oats, and modified foods where nutrients have been enhanced or added, such as tomatoes with increased lycopene or iron-fortified milk.
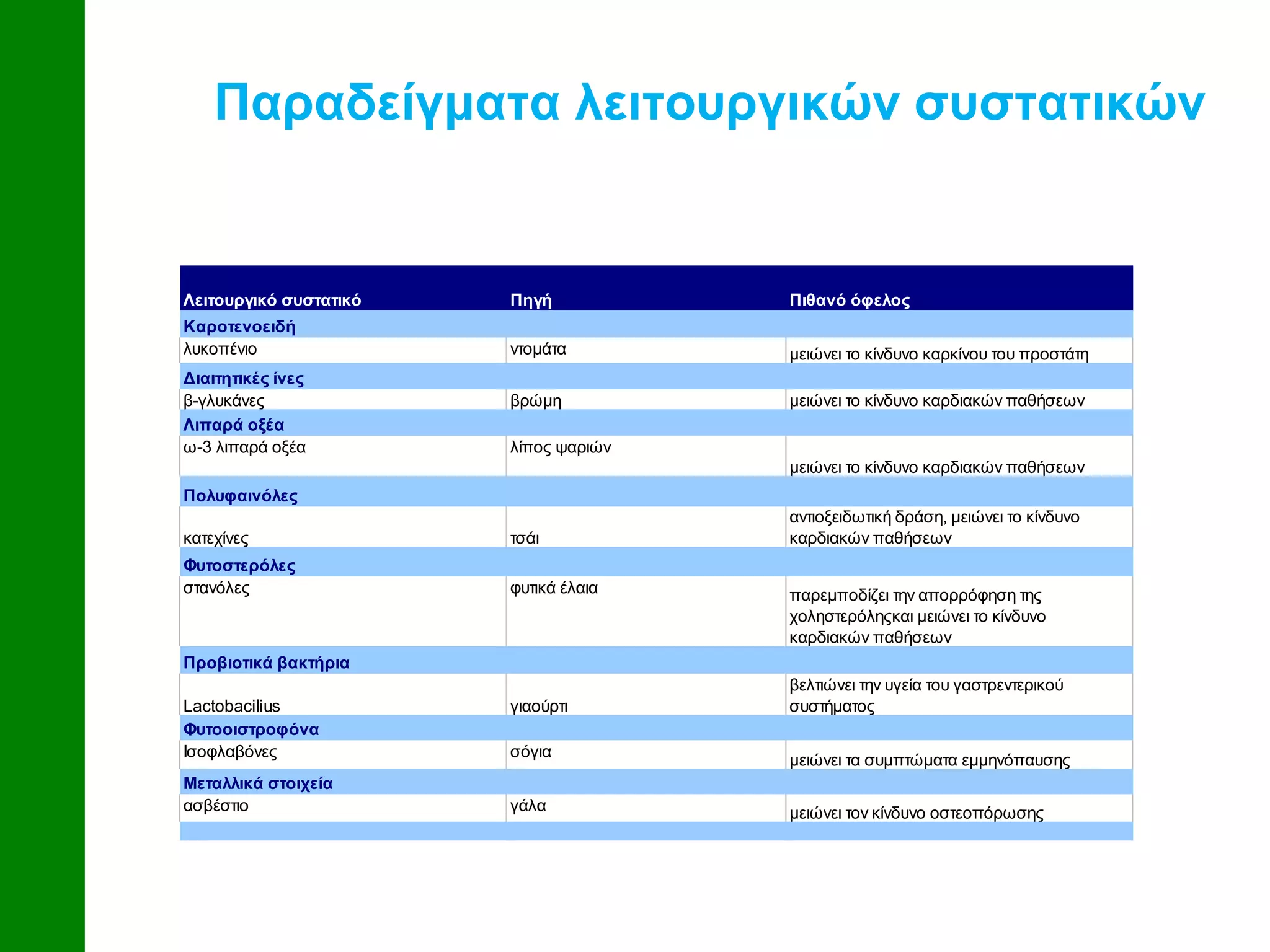
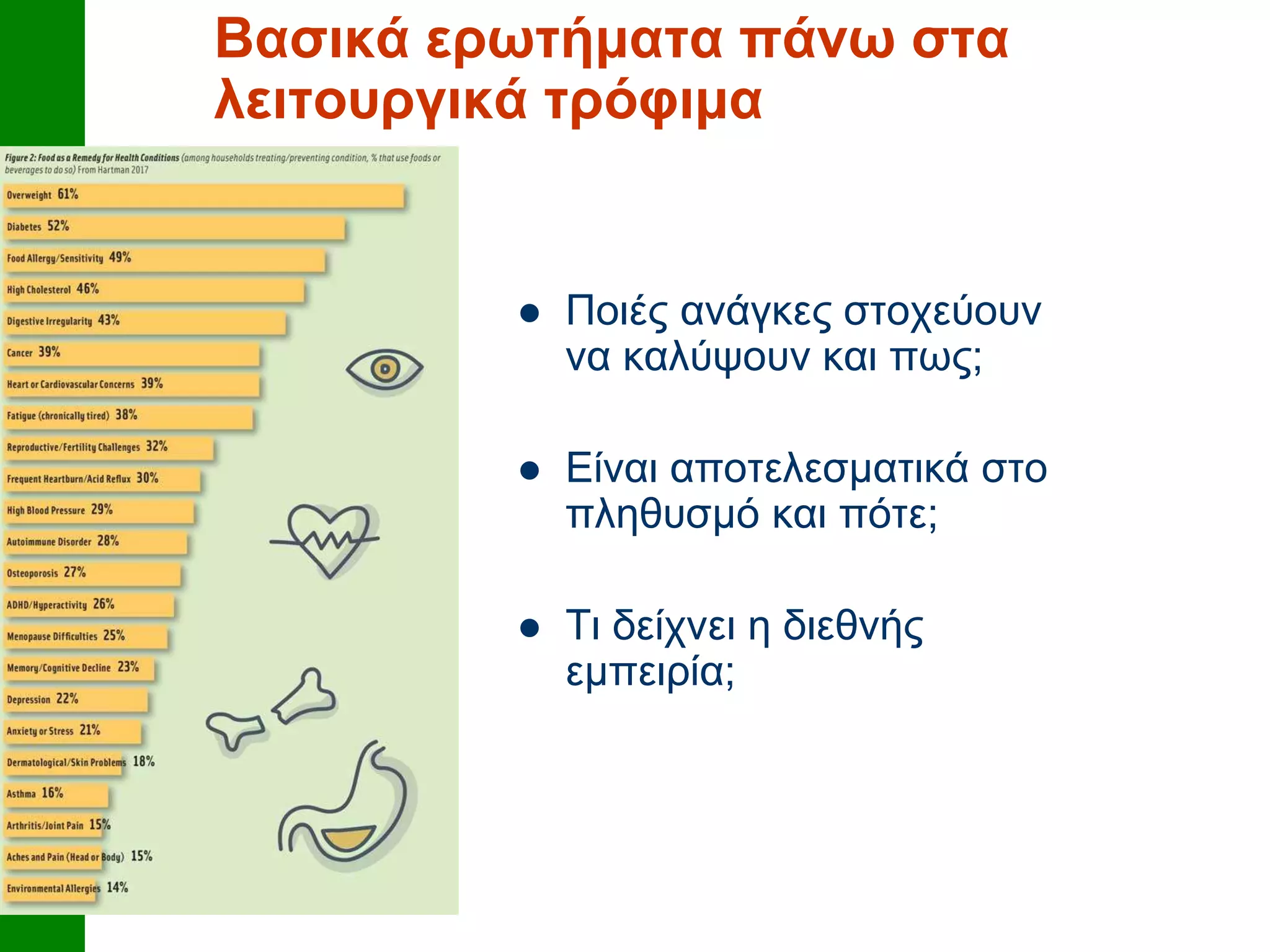
Common functional compounds discussed include lycopene, beta-glucans, omega-3 fatty acids, catechins, stanols, probiotics, isoflavones, and calcium. The development of functional foods is part of a strategy to improve nutritional intake. Key questions raised about functional foods include which needs they aim to meet, how effectively they work in