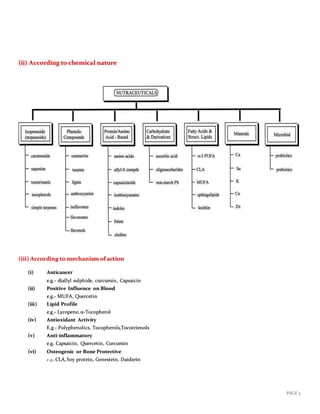
This document provides information on functional foods and nutraceuticals. It begins by defining functional foods and discussing their classification based on source (plant, animal, microbial) and mechanism of action. It then discusses probiotics, prebiotics, polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidant vitamins, polyphenols, and spices as examples of nutraceutical groups. The document concludes by discussing how nutraceuticals can be used to treat various health conditions like cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and more.