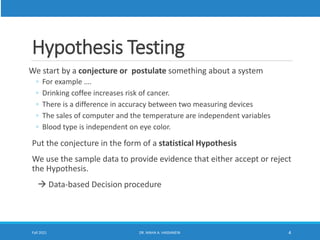
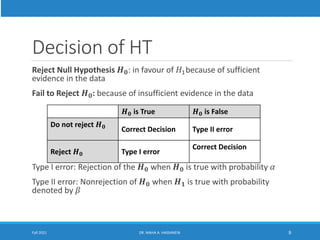
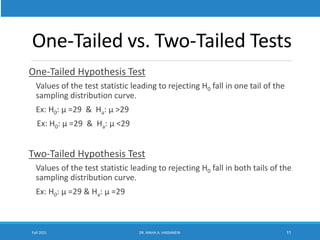
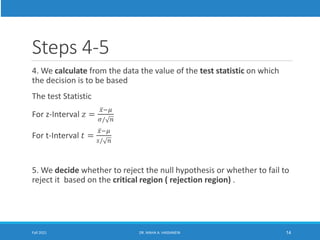
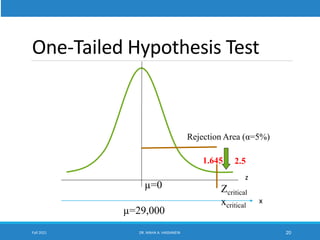
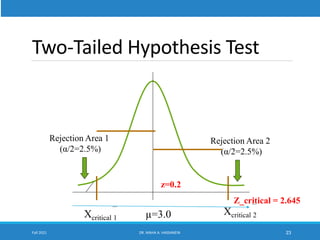
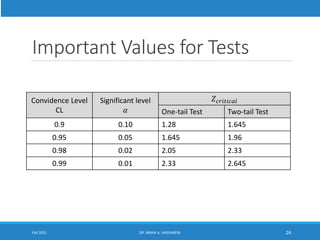
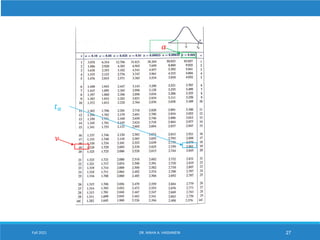
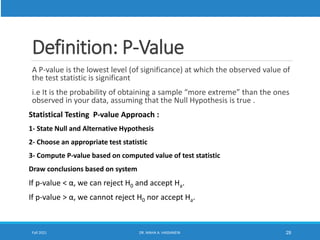
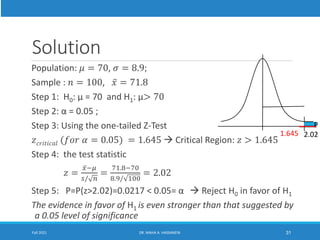
This lecture discusses hypothesis testing. It begins by reviewing confidence intervals and introducing the concepts of the null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (H1). Hypothesis testing involves collecting sample data and using it to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis. Type I and type II errors are defined. Common steps in hypothesis testing are outlined, including specifying the significance level, determining the rejection region, calculating the test statistic, and making a decision. Examples demonstrate one-tailed and two-tailed hypothesis tests using z-tests and t-tests. P-values are also introduced as another method for drawing conclusions in hypothesis testing.