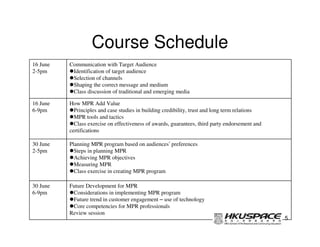
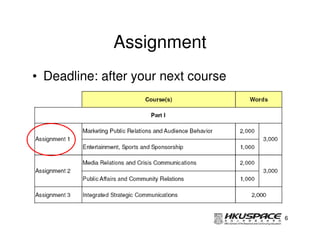
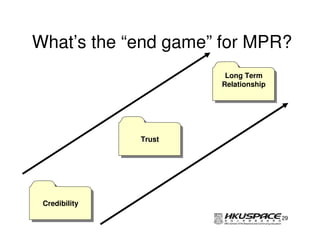
This document provides an overview of a post graduate diploma program in PR and exhibitions management. The first lecture introduces marketing public relations (MPR) and discusses understanding audience behavior and information dissemination. It also covers managing PR activities like trade shows, press conferences, and news articles. The lecture teaches how MPR can add value through building credibility, trust and long-term relationships. The assignment is due after the next course.