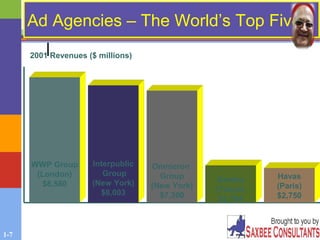
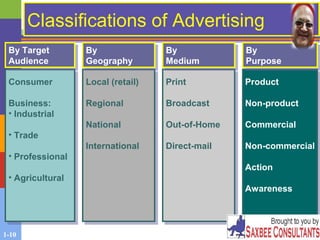
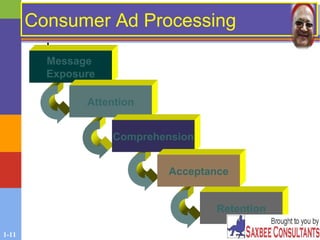
This document provides an overview of advertising and public relations. It discusses the key characteristics of advertising, how people process advertising information, and the different approaches used in developing advertising campaigns. It also outlines how marketers assess advertising effectiveness. Additionally, the document examines the advertising industry and classifications of advertising. It describes the roles of public relations and publicity in marketing communications and the different public relations functions. Finally, it discusses evaluating advertising effectiveness and some of the ethical and legal issues related to advertising.









![1-18
Cost per Thousand (CPM):
CPM = [(magazine page cost x
1,000)/circulation]
Media Vehicle EvaluatonMedia Vehicle Evaluaton](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/marketingtips-141224012649-conversion-gate01/85/Marketing-tips-18-320.jpg)








