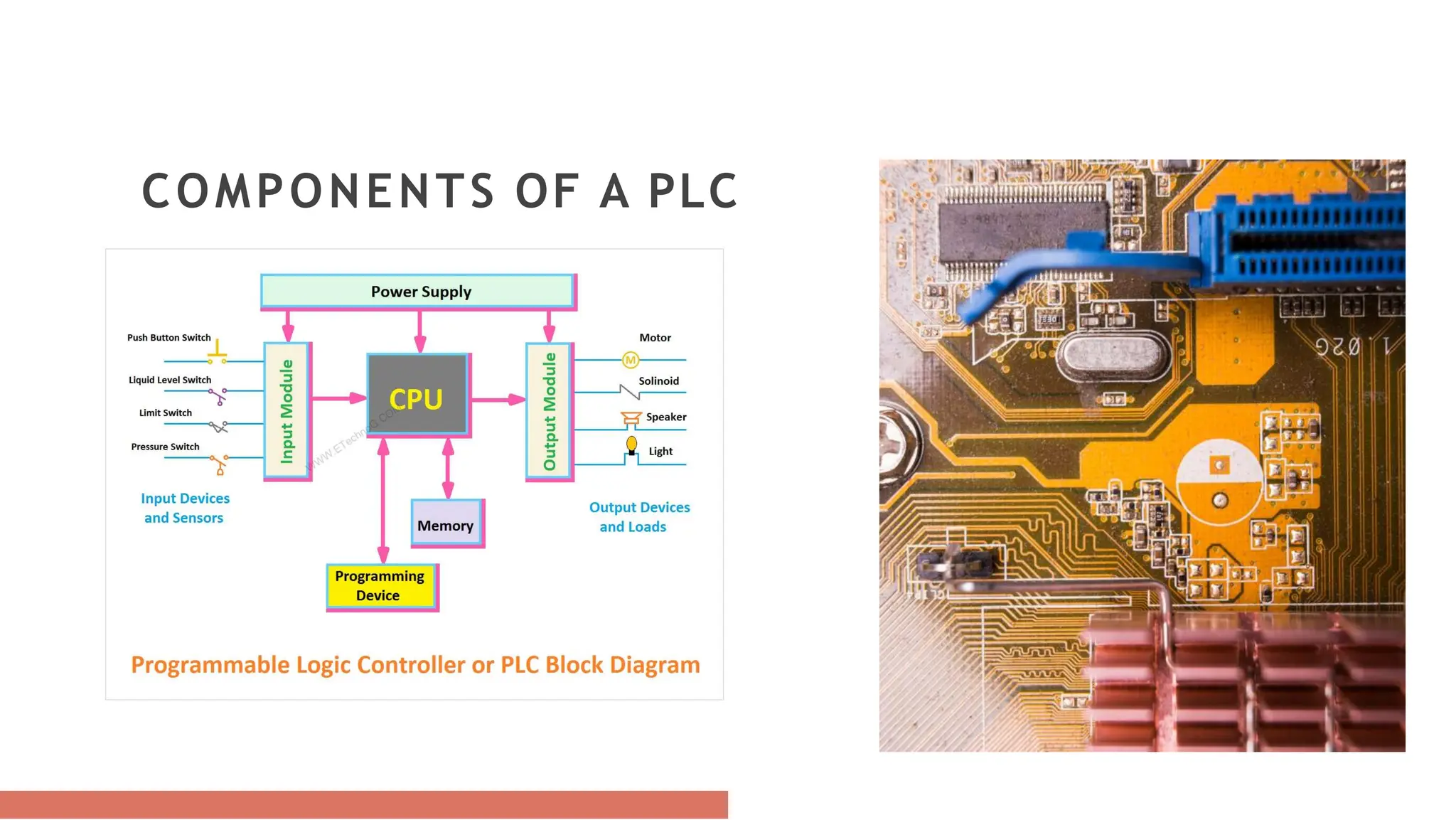
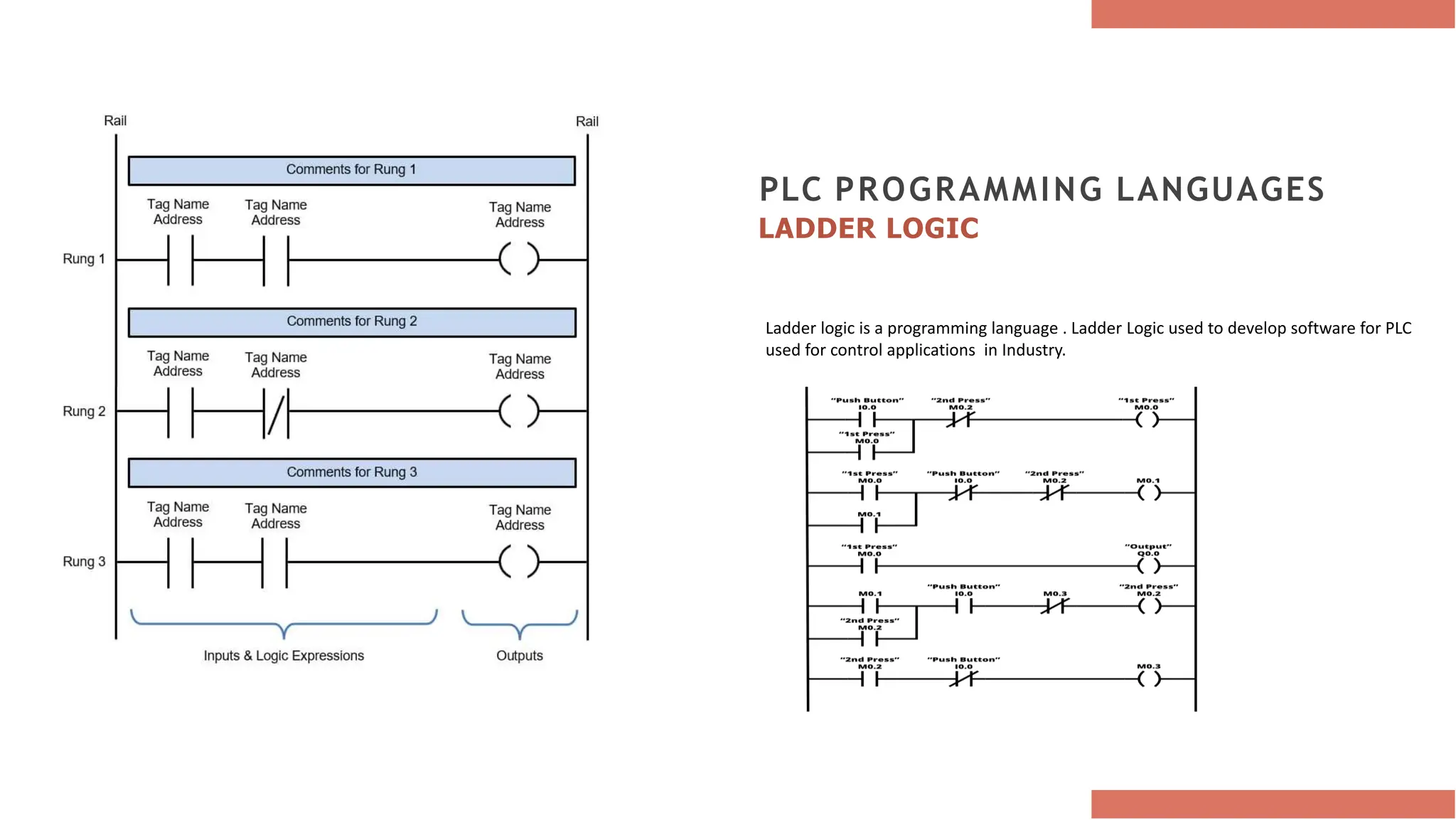
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential industrial computers that automate control functions in various industries, evolving from simple relay systems to advanced microprocessor-based units. Key components include a power supply, I/O modules, processors, and programming devices, with programming languages like ladder logic offering varied advantages for control applications. Despite their benefits such as reliability and flexibility, PLCs also face challenges like proprietary devices and limited design options but remain crucial for modern industrial automation.