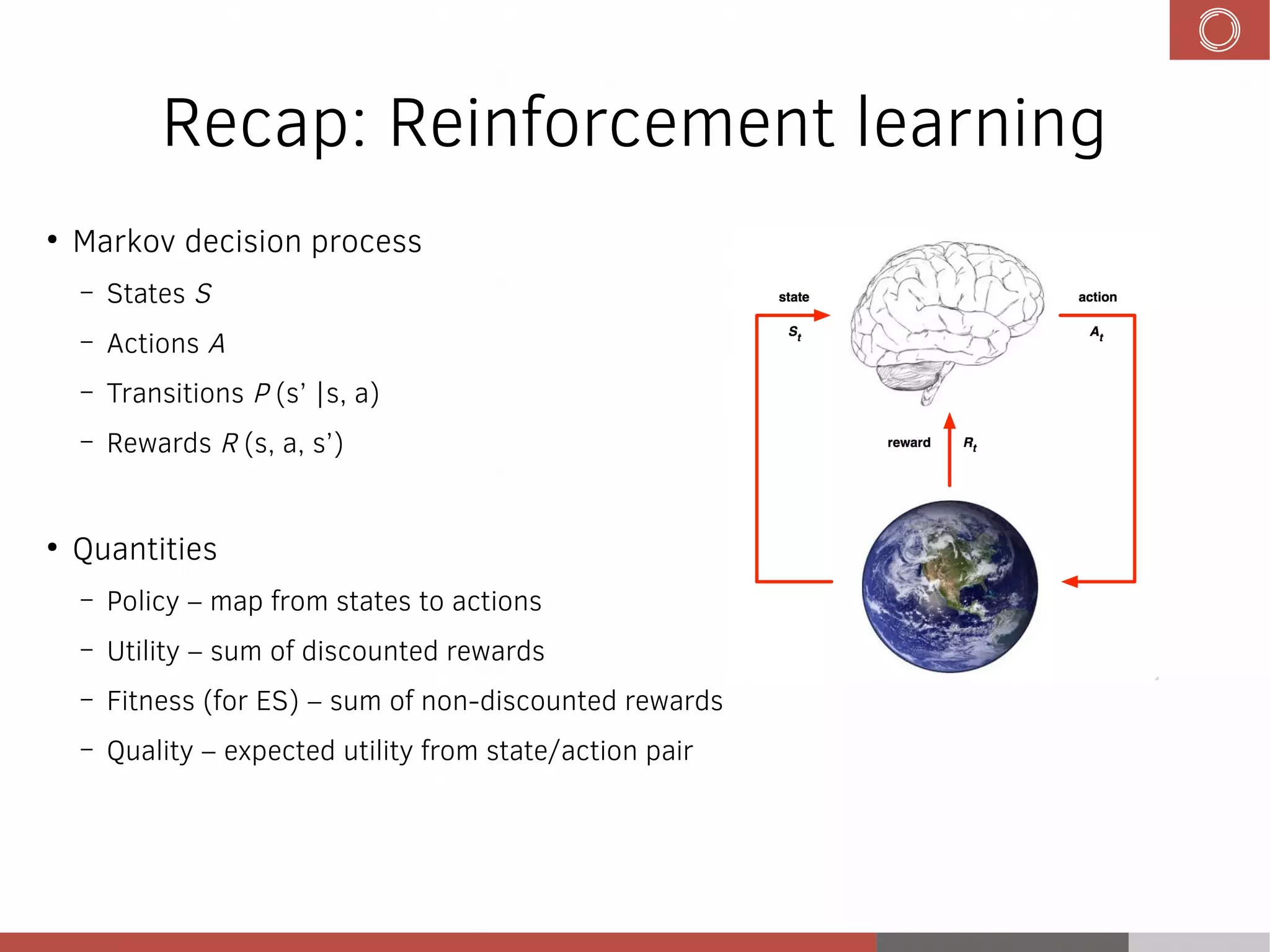
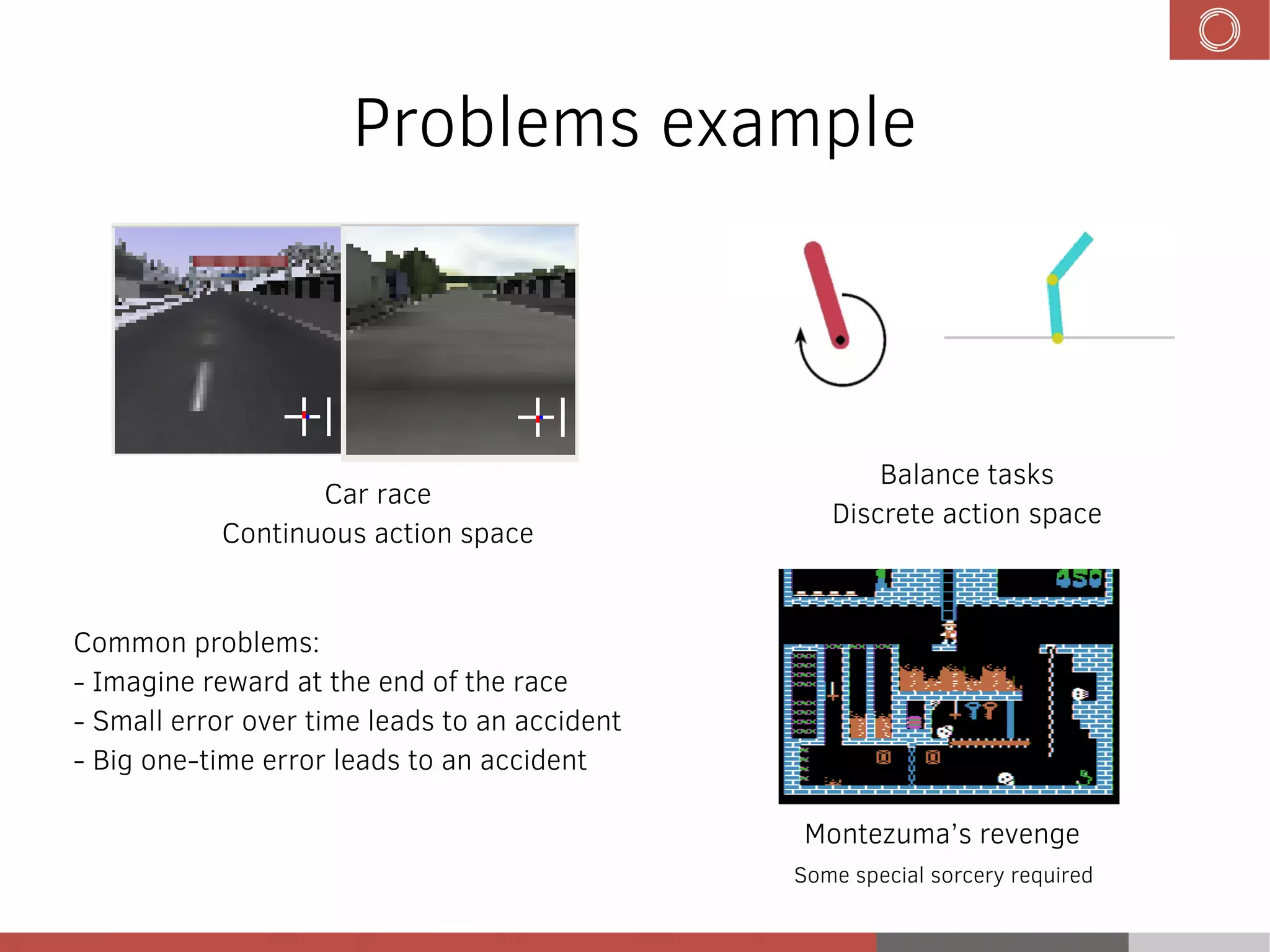
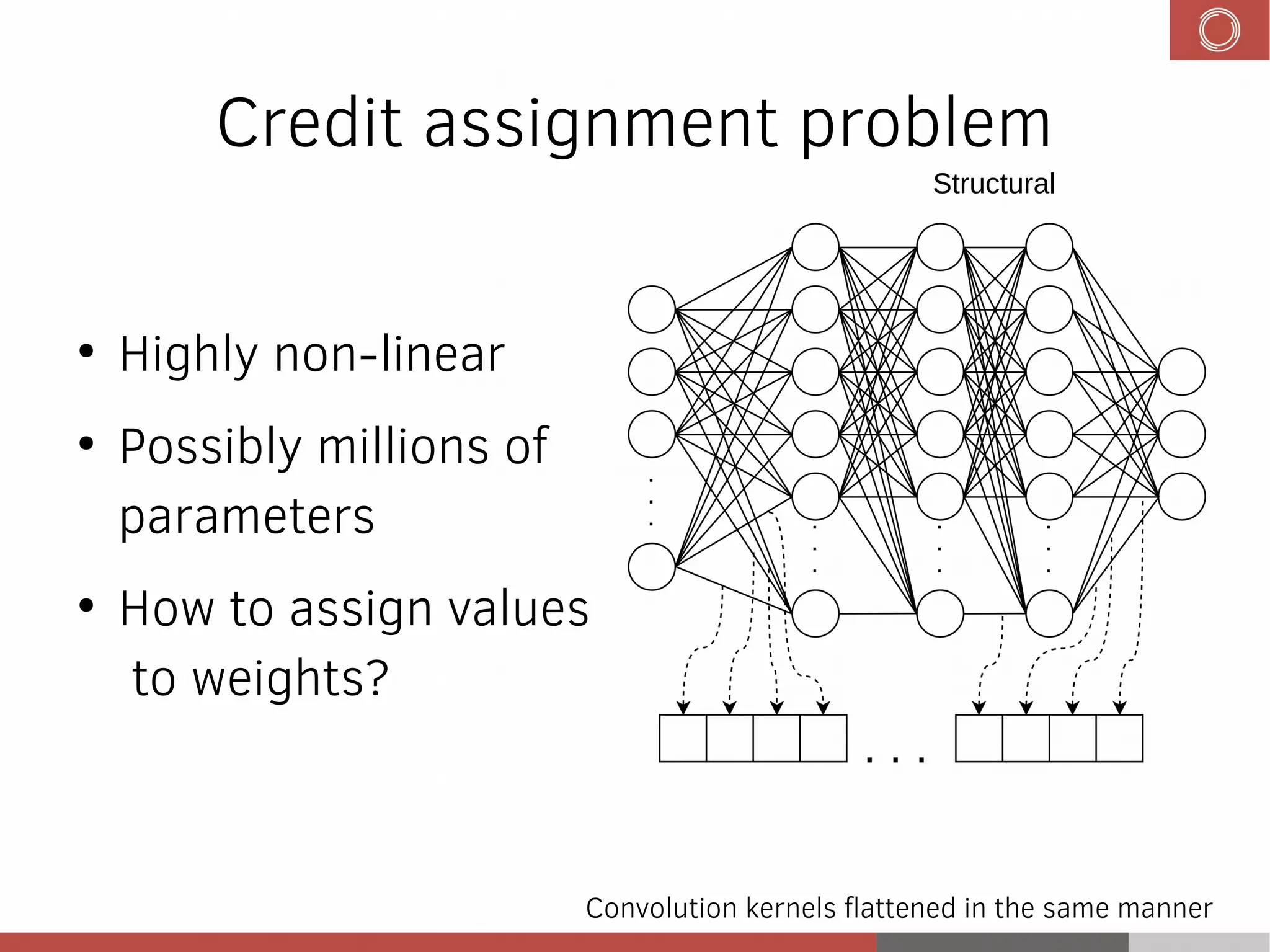
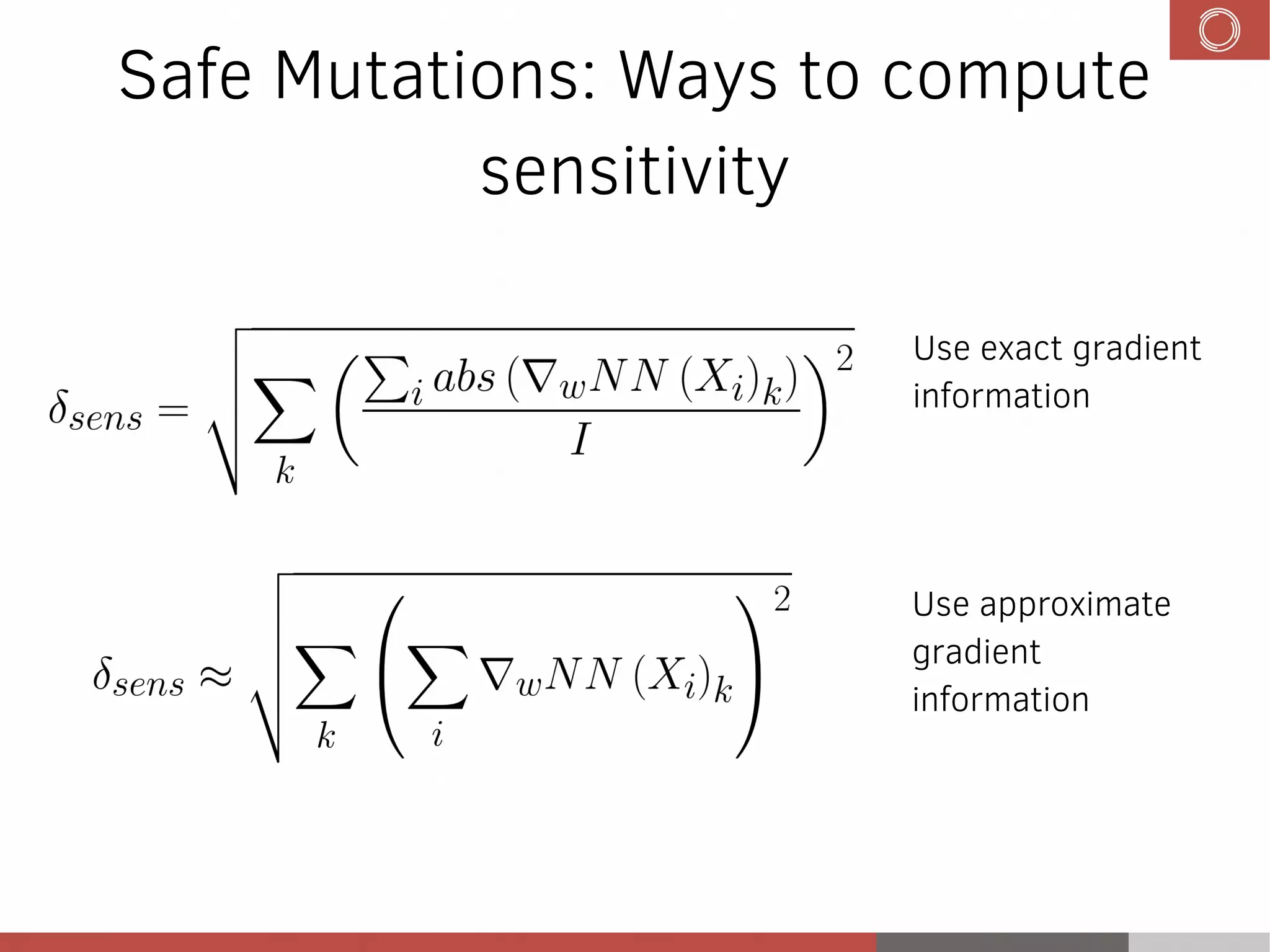
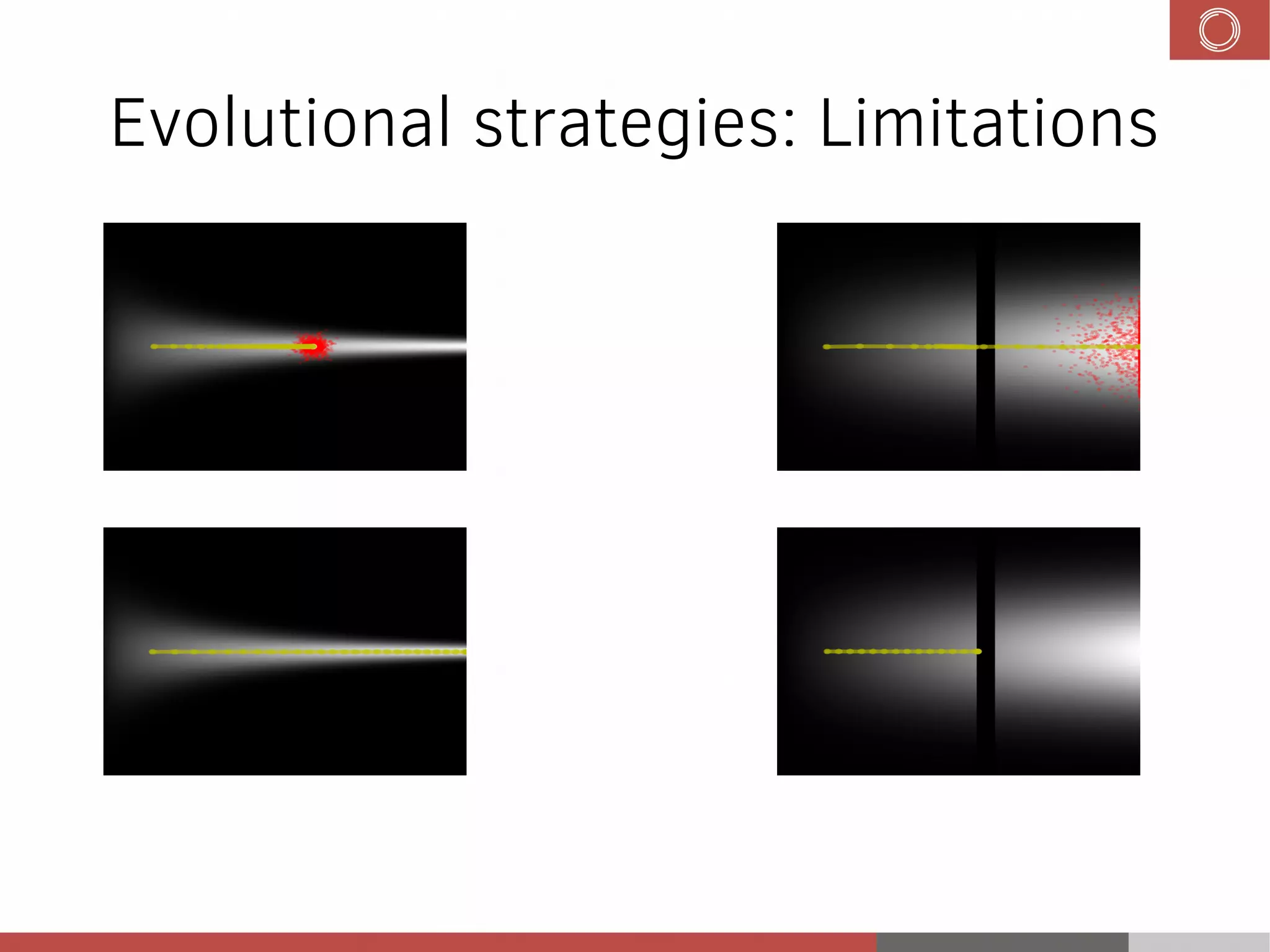
This document discusses evolution strategies in reinforcement learning. It introduces reinforcement learning concepts like Markov decision processes, the credit assignment problem, and the exploration-exploitation tradeoff. It then explains how evolution strategies address some RL challenges by using genetic algorithms and natural evolution techniques to optimize neural network policies without backpropagation. Specifically, it discusses using selection and mutation of the fittest agents along with safe mutations like rescaling perturbations to keep behavioral changes small. While parallelizable and able to handle non-differentiable problems, evolution strategies require large numbers of samples and domain evaluations to work effectively.