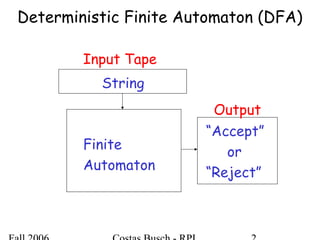
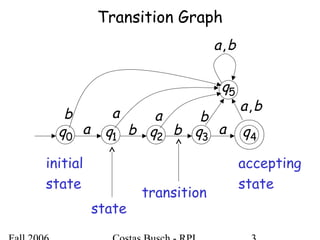
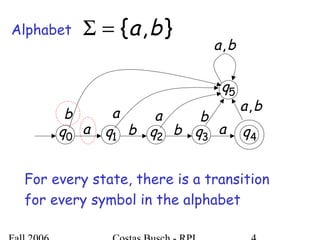
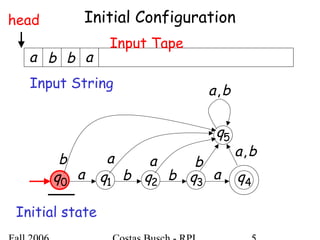
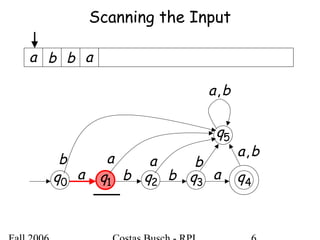
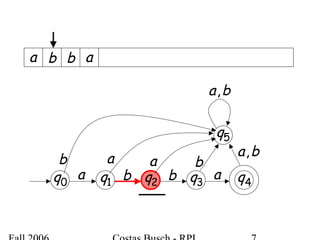
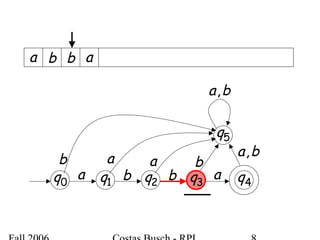
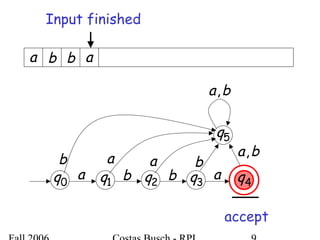
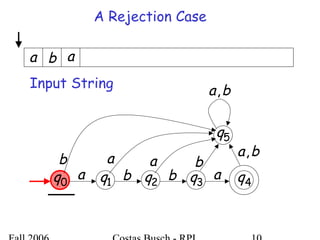
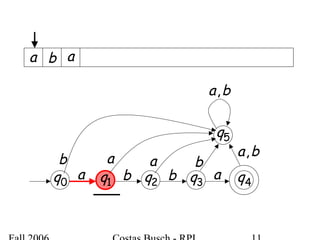
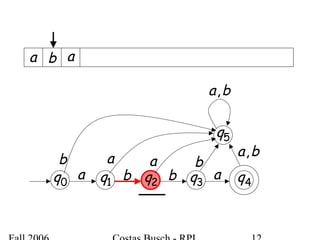
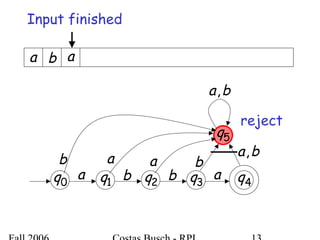
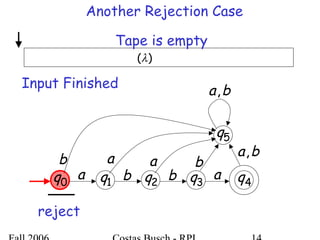
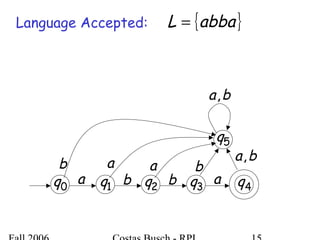
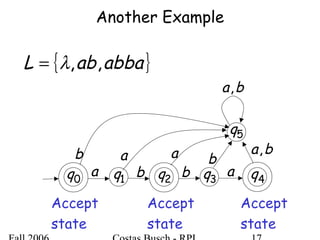
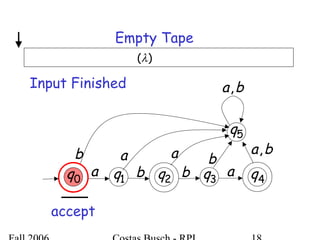
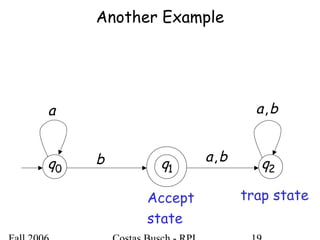
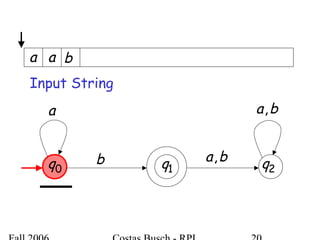
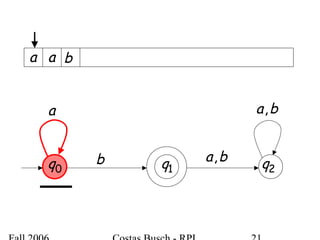
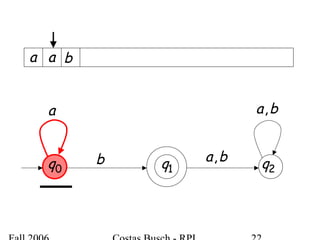
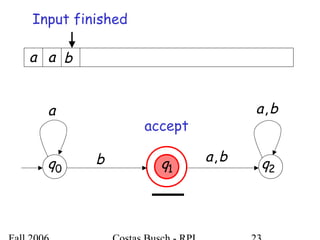
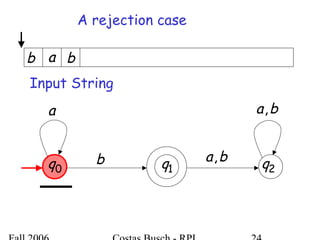
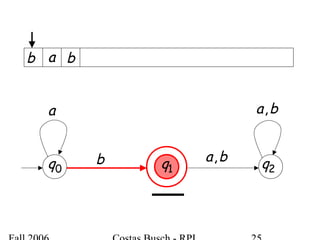
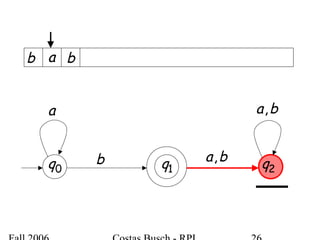
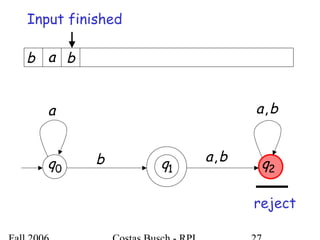
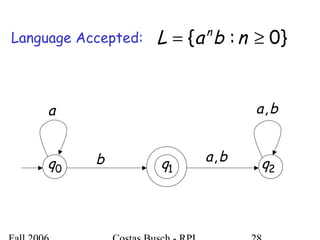
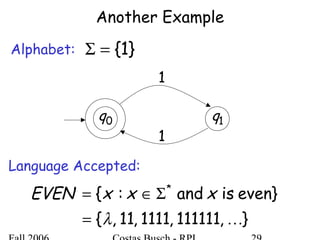
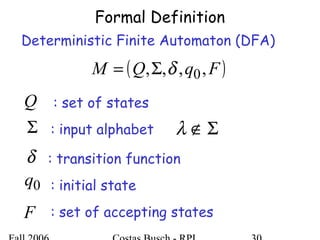
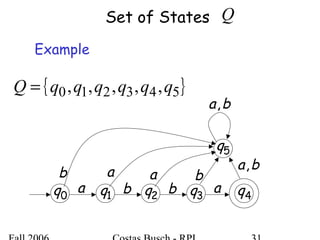
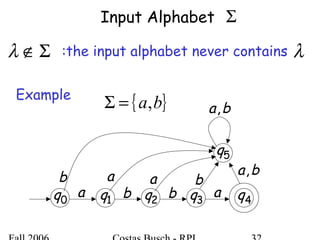
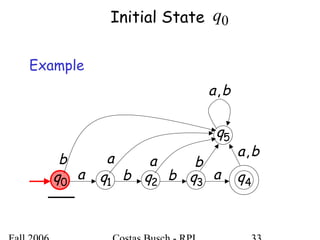
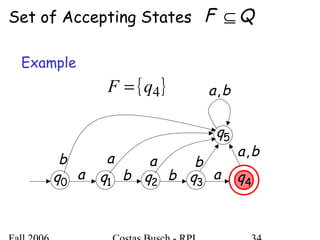
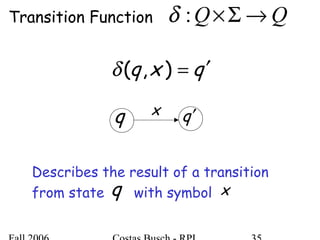
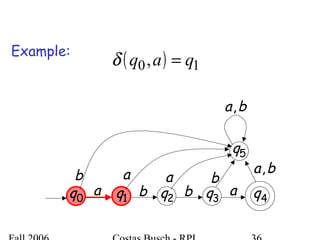
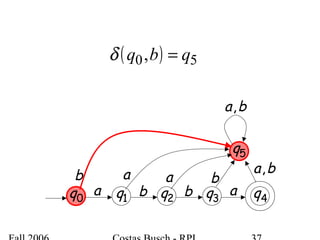
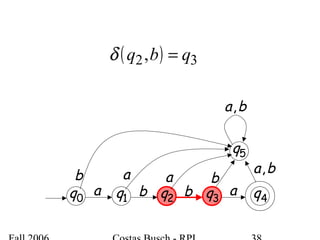
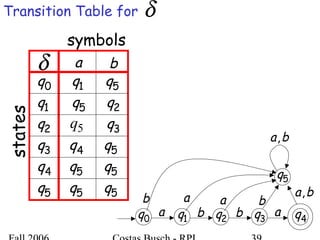
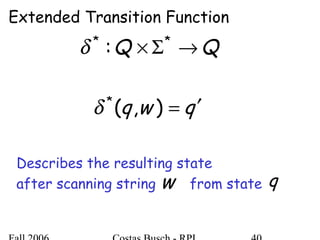
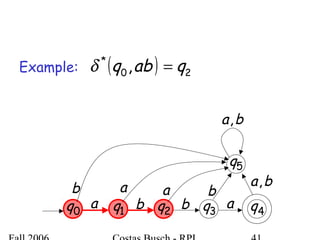
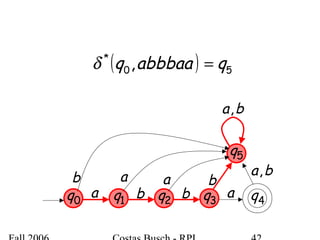
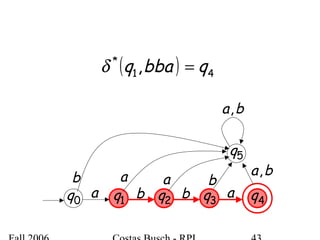
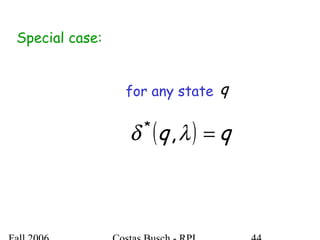
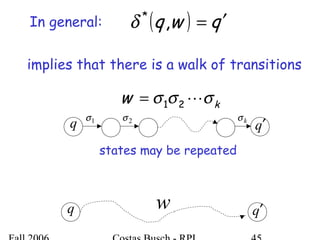
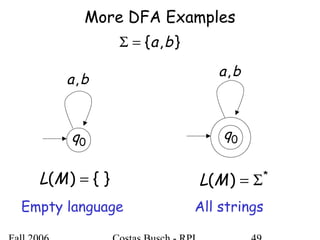
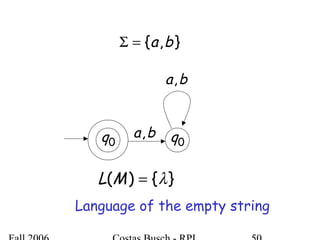
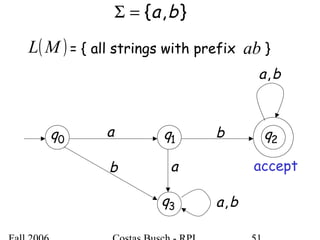
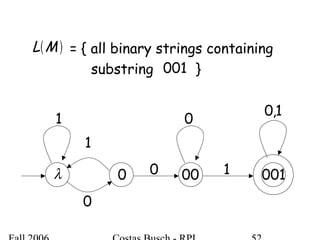
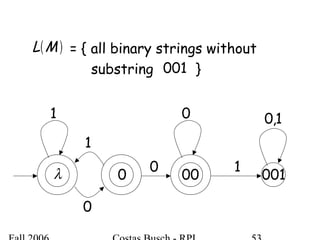
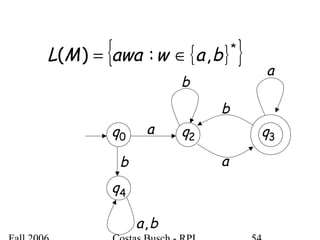
The document discusses deterministic finite automata (DFA) and regular languages. It defines a DFA as a 5-tuple (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states, Σ is an input alphabet, δ is the transition function, q0 is the initial state, and F is a set of accepting states. A language is regular if there exists a DFA that accepts it. The document provides several examples of DFAs and the regular languages they accept.