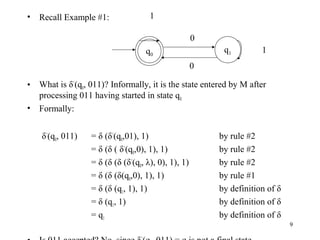
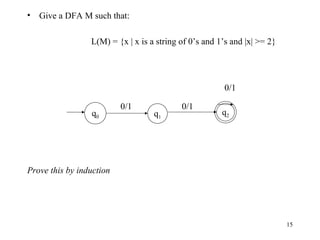
Deterministic Finite State Automata (DFAs) are machines that read input strings and determine whether to accept or reject them based on their state transitions. A DFA is defined as a 5-tuple (Q, Σ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states, Σ is a finite input alphabet, q0 is the starting state, F is the set of accepting states, and δ is the transition function that maps a state and input symbol to the next state. The language accepted by a DFA is the set of strings that cause the DFA to enter an accepting state. Nondeterministic Finite State Automata (NFAs) are similar but δ maps to sets of states rather



































![•
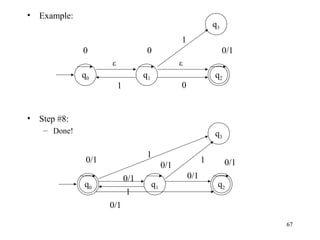
Lemma 2: Let M be an NFA. Then there exists a DFA M’ such that L(M) =
L(M’).
•
Proof: (sketch)
Let M = (Q, Σ, δ,q0,F).
Define a DFA M’ = (Q’, Σ, δ’,q’0,F’) as:
Q’ = 2Q
= {Q0, Q1,…,}
Each state in M’ corresponds to a
subset of states from M
where Qu = [qi0, qi1,…qij]
F’ = {Qu | Qu contains at least one state in F}
q’0 = [q0]
δ’(Qu, a) = Qv iff δ(Qu, a) = Qv
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteautomata-examples-131129064211-phpapp02/85/Finite-automata-examples-41-320.jpg)

![•
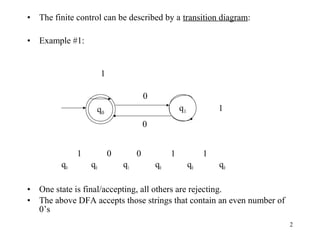
Construct DFA M’ as follows:
1
0/1
[]
1
0
[q0]
[q1]
0
1
[q0, q1]
0
δ({q0}, 0) = {q1}
δ({q0}, 1) = {}
δ({q1}, 0) = {q0, q1} =>
δ({q1}, 1) = {q1}
δ({q0, q1}, 0) = {q0, q1}
δ({q0, q1}, 1) = {q1} =>
δ({}, 0) = {}
δ({}, 1) = {}
=>
δ’([q0], 0) = [q1]
=>
δ’([q0], 1) = [ ]
δ’([q1], 0) = [q0, q1]
=>
δ’([q1], 1) = [q1]
=>
δ’([q0, q1], 0) = [q0, q1]
δ’([q0, q1], 1) = [q1]
=>
δ’([ ], 0) = [ ]
=>
δ’([ ], 1) = [ ]
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteautomata-examples-131129064211-phpapp02/85/Finite-automata-examples-43-320.jpg)