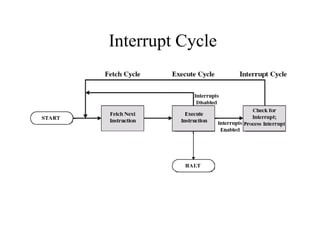
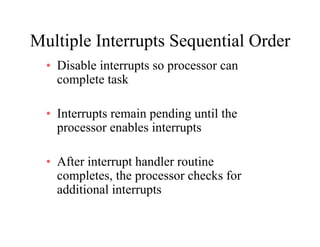
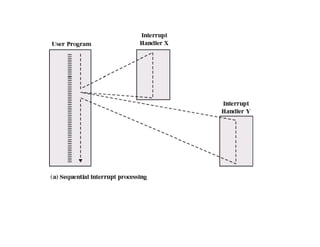
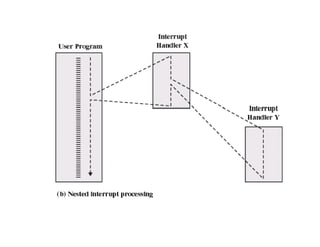
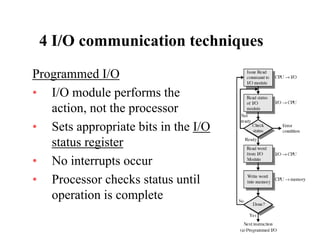
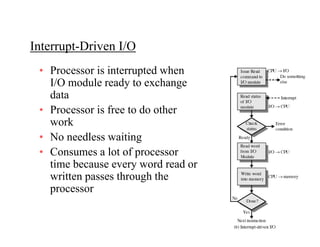
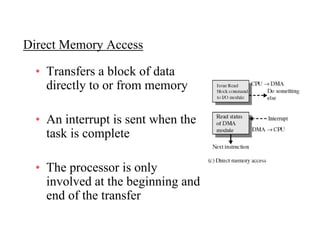
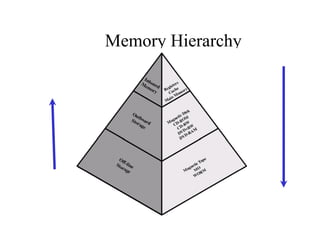
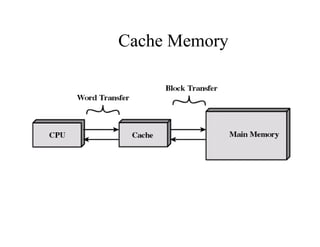
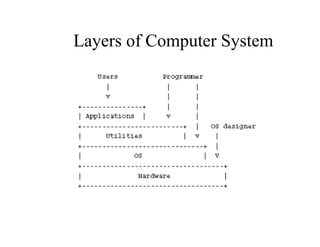
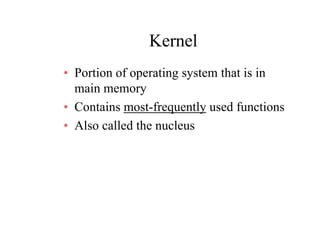
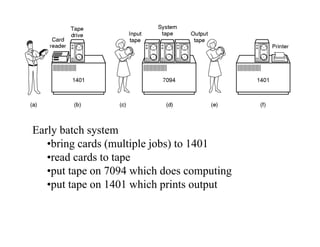
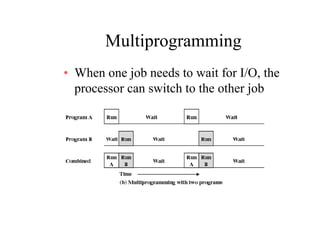
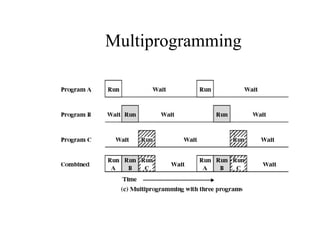
The document discusses operating systems concepts including interrupt cycles, multiple interrupts, multiprogramming, I/O communication techniques, memory hierarchy, cache memory, and an operating systems overview. Interrupt cycles allow the processor to suspend the current program and execute an interrupt handler if an interrupt is pending. Multiple interrupts are handled by prioritizing higher priority interrupts and disabling interrupts while one is being processed. Multiprogramming allows the processor to execute more than one program by switching between programs based on priority and I/O waits. Various I/O communication techniques like programmed I/O, interrupt-driven I/O, and direct memory access are described. The memory hierarchy from fastest to slowest includes cache memory, main memory, and disk