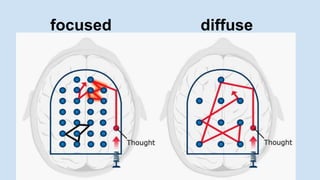
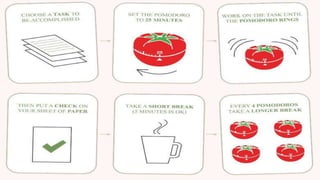
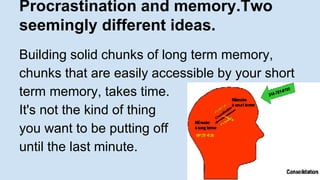
The document discusses various techniques for effective learning, including using both focused and diffuse thinking modes, interleaving topics, avoiding procrastination, using the Pomodoro technique, getting enough sleep, exercising, forming memory chunks, avoiding overconfidence, and studying with friends. Some key recommendations are to space out learning over time instead of cramming, take breaks to allow the diffuse thinking mode to kick in, and catch blind spots by explaining concepts to others.