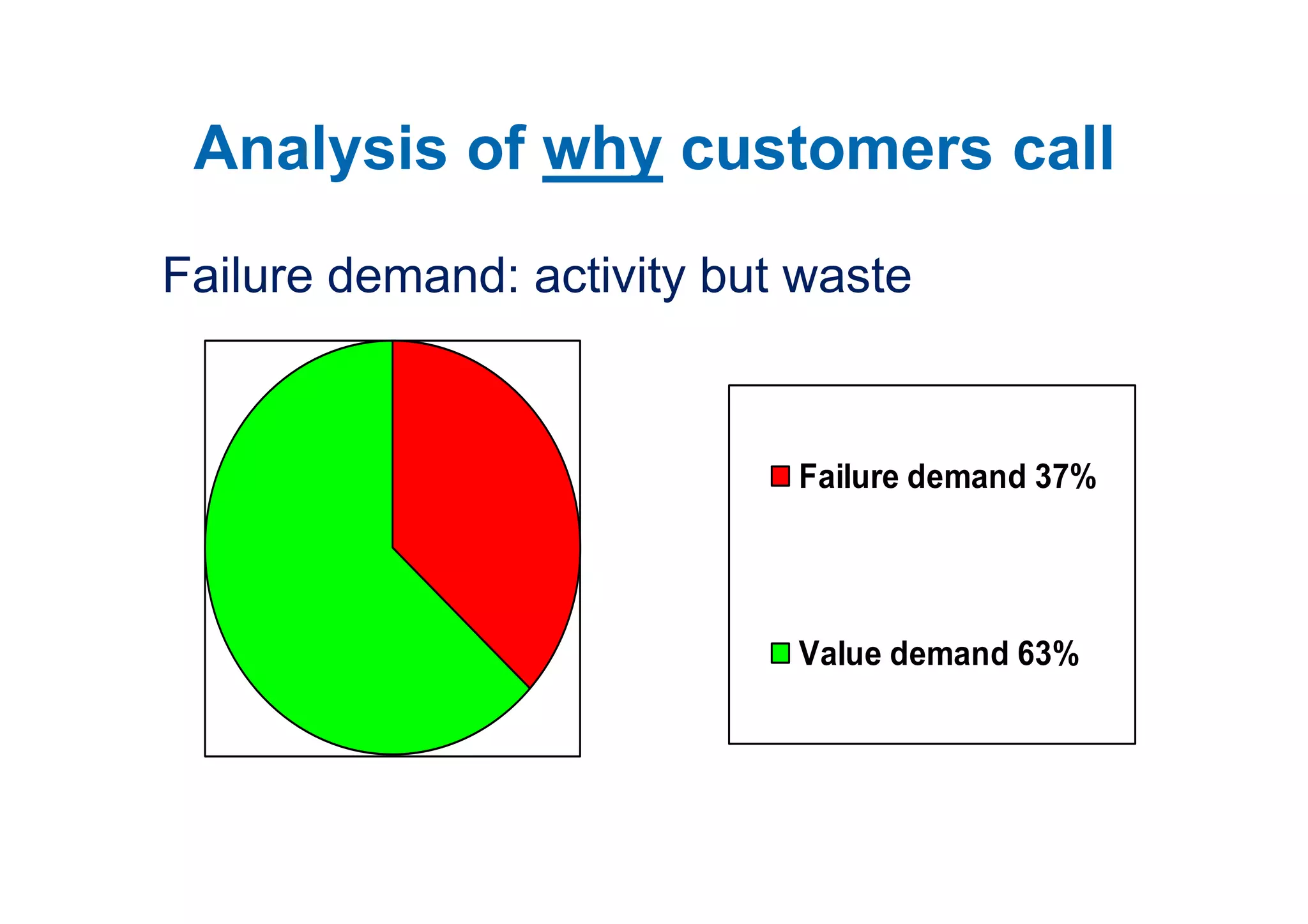
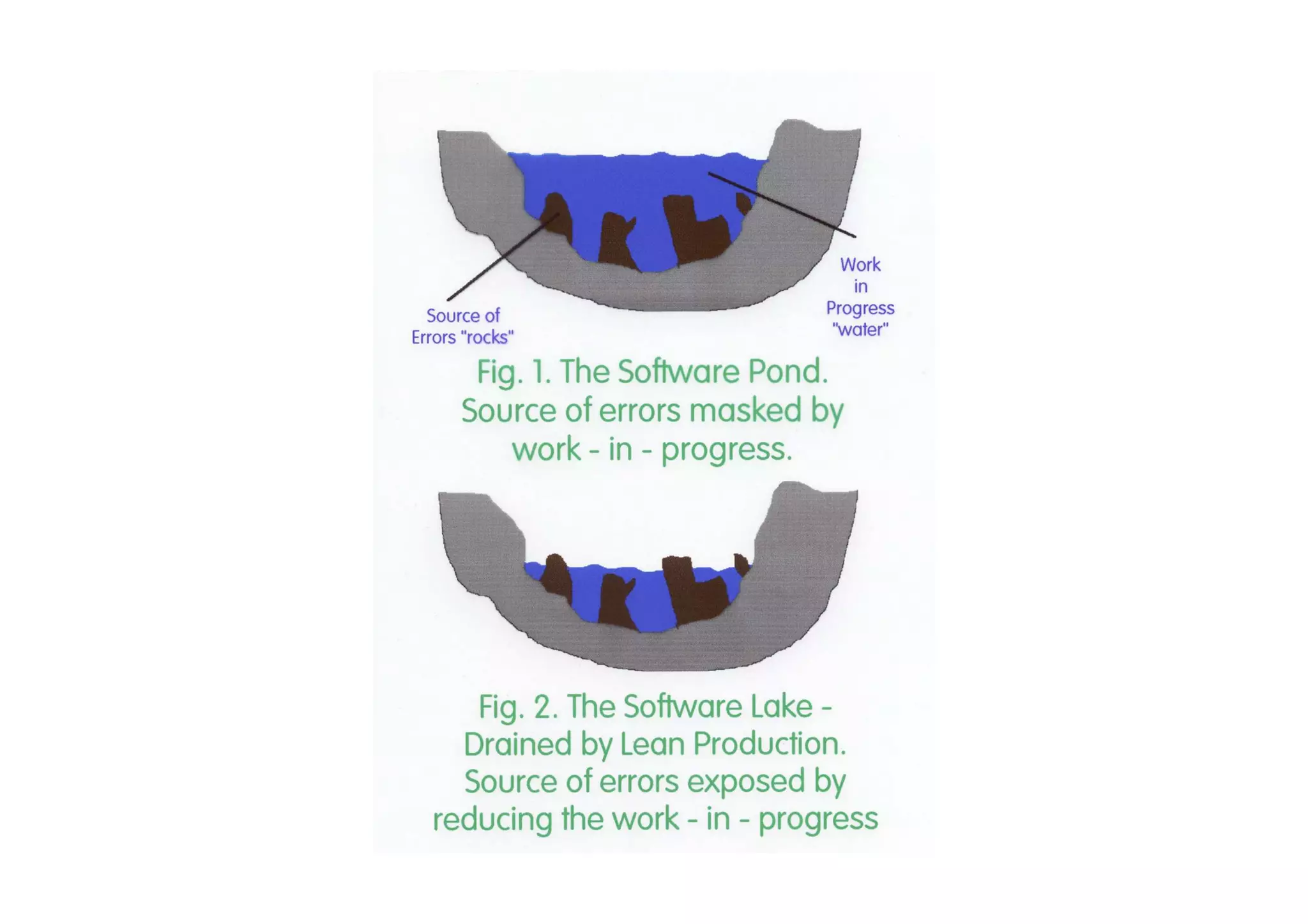
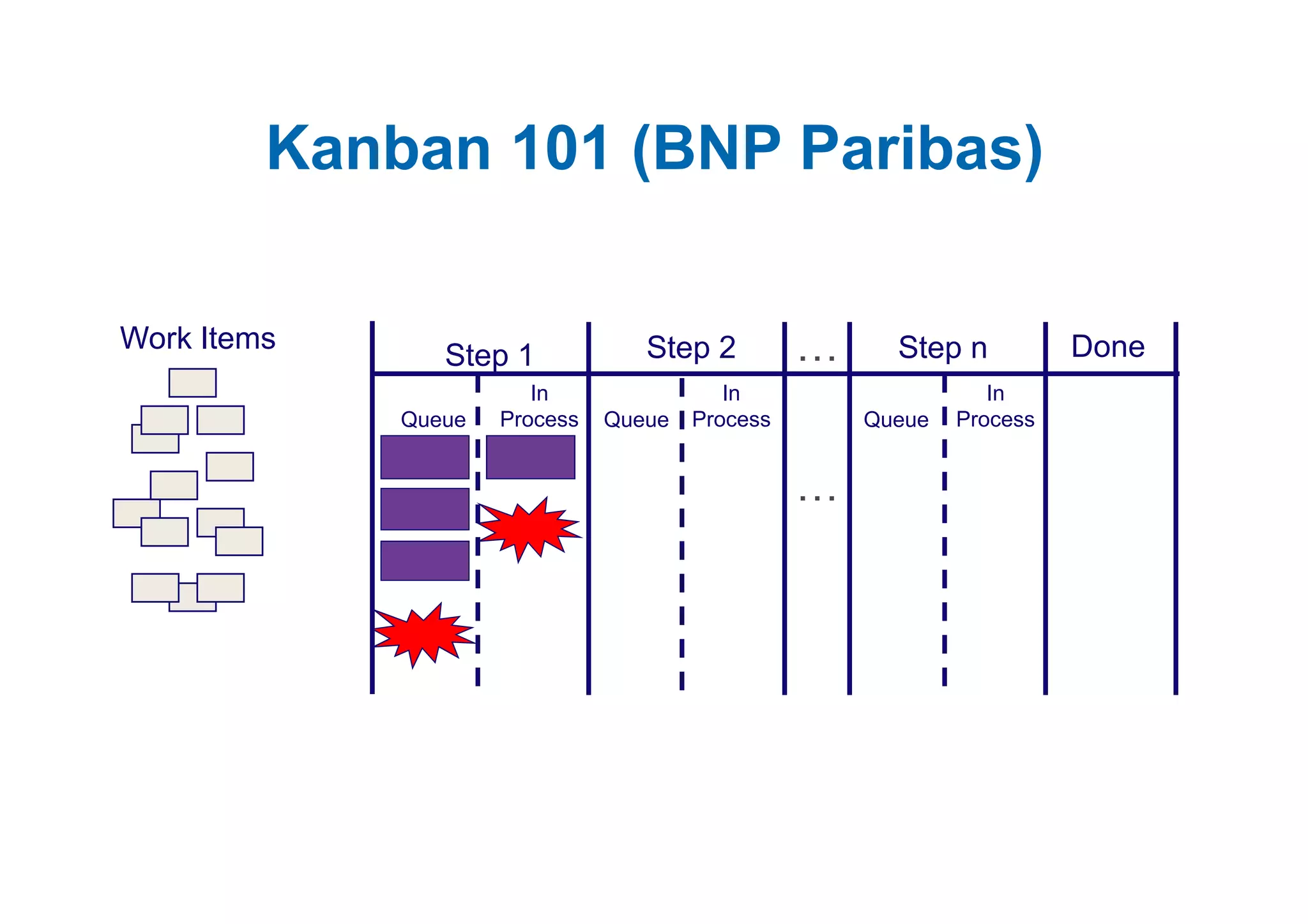
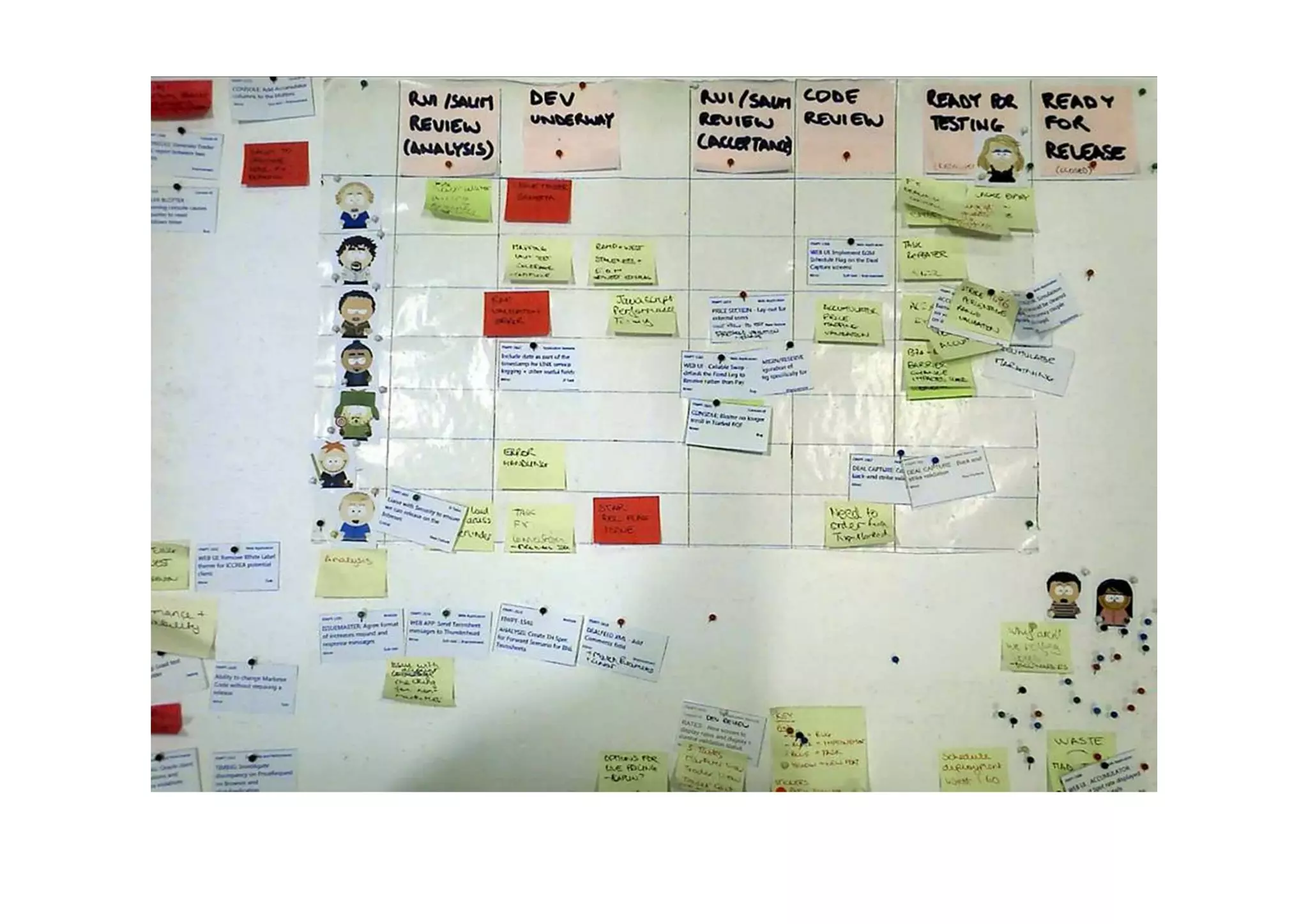
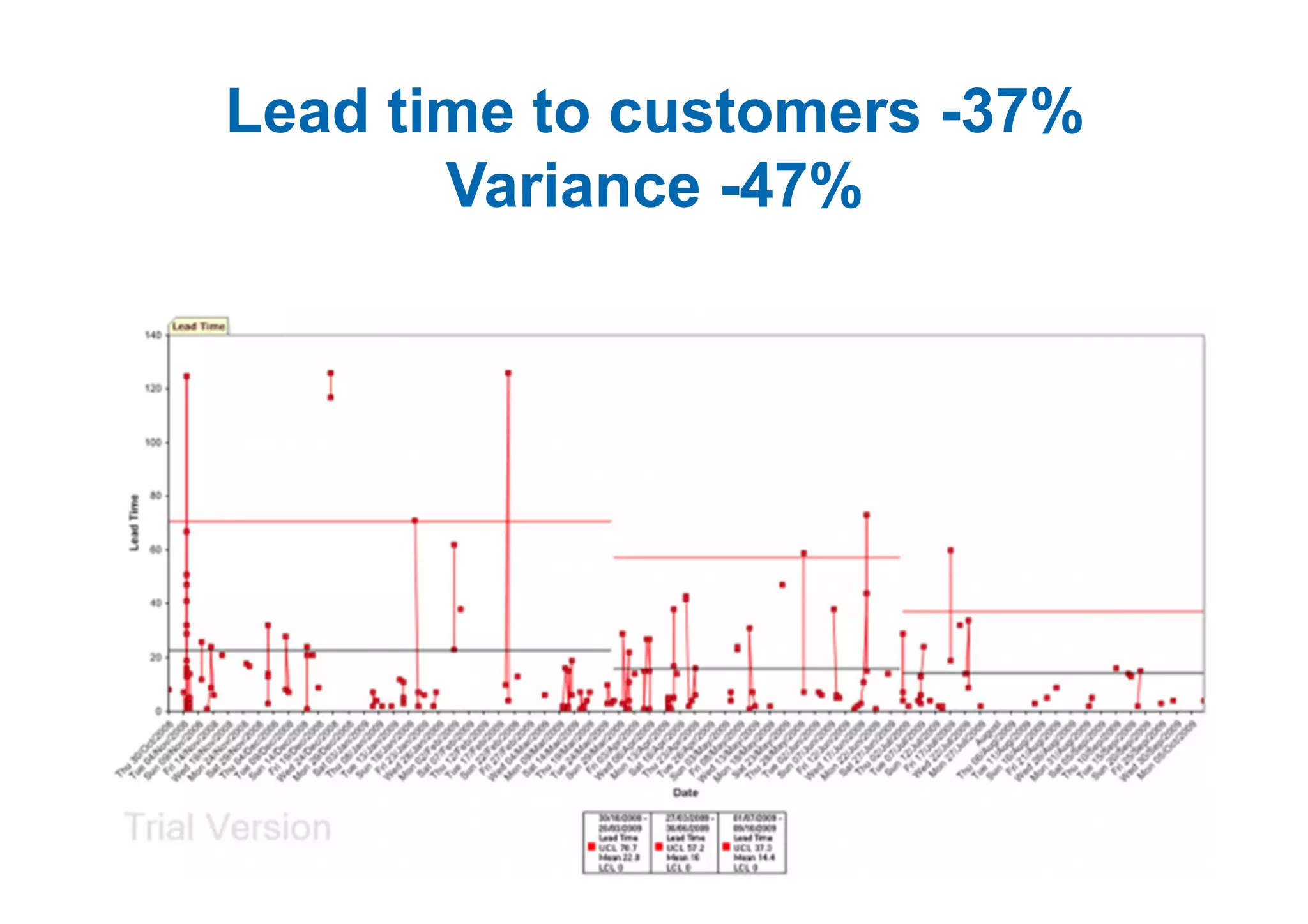
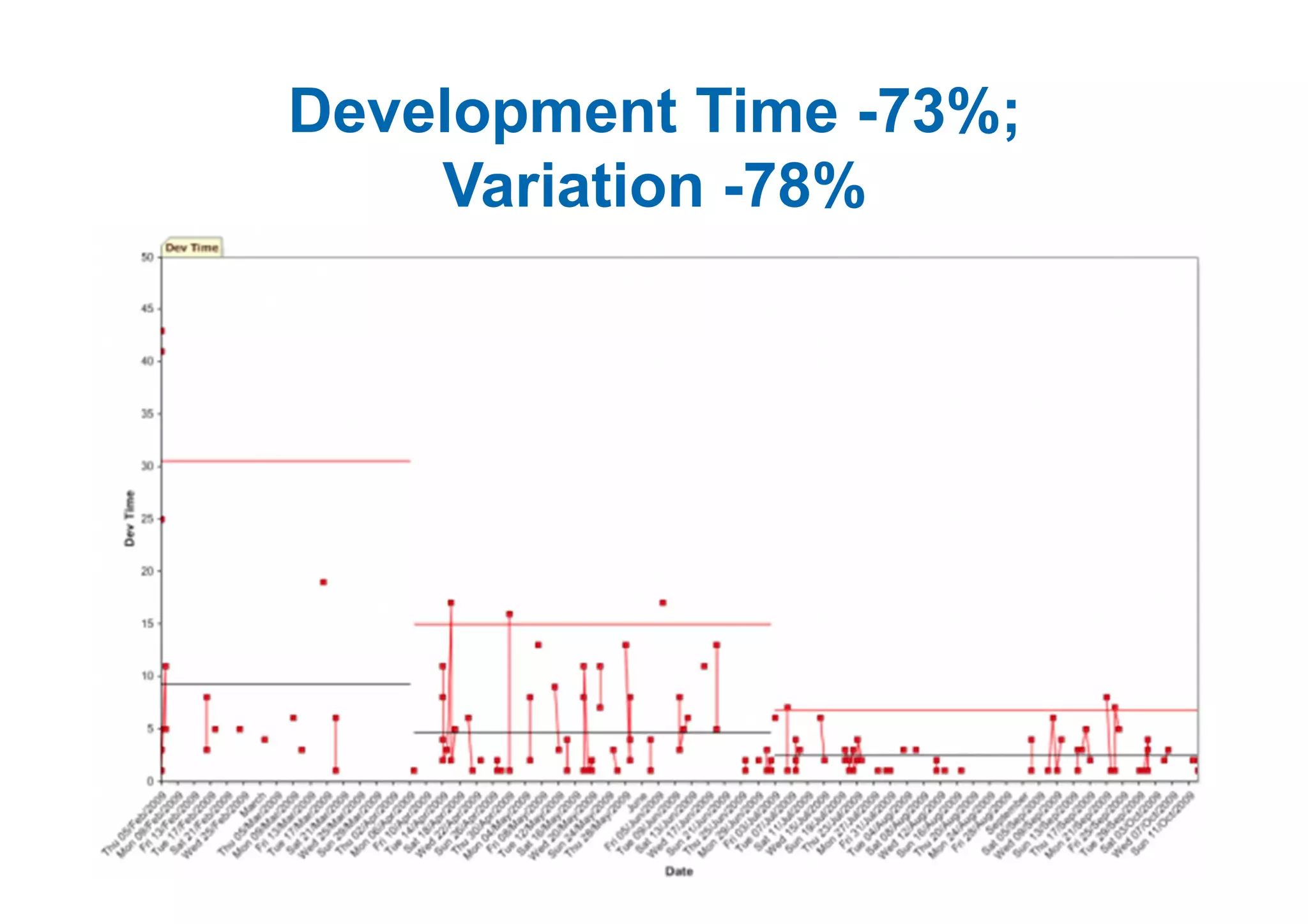
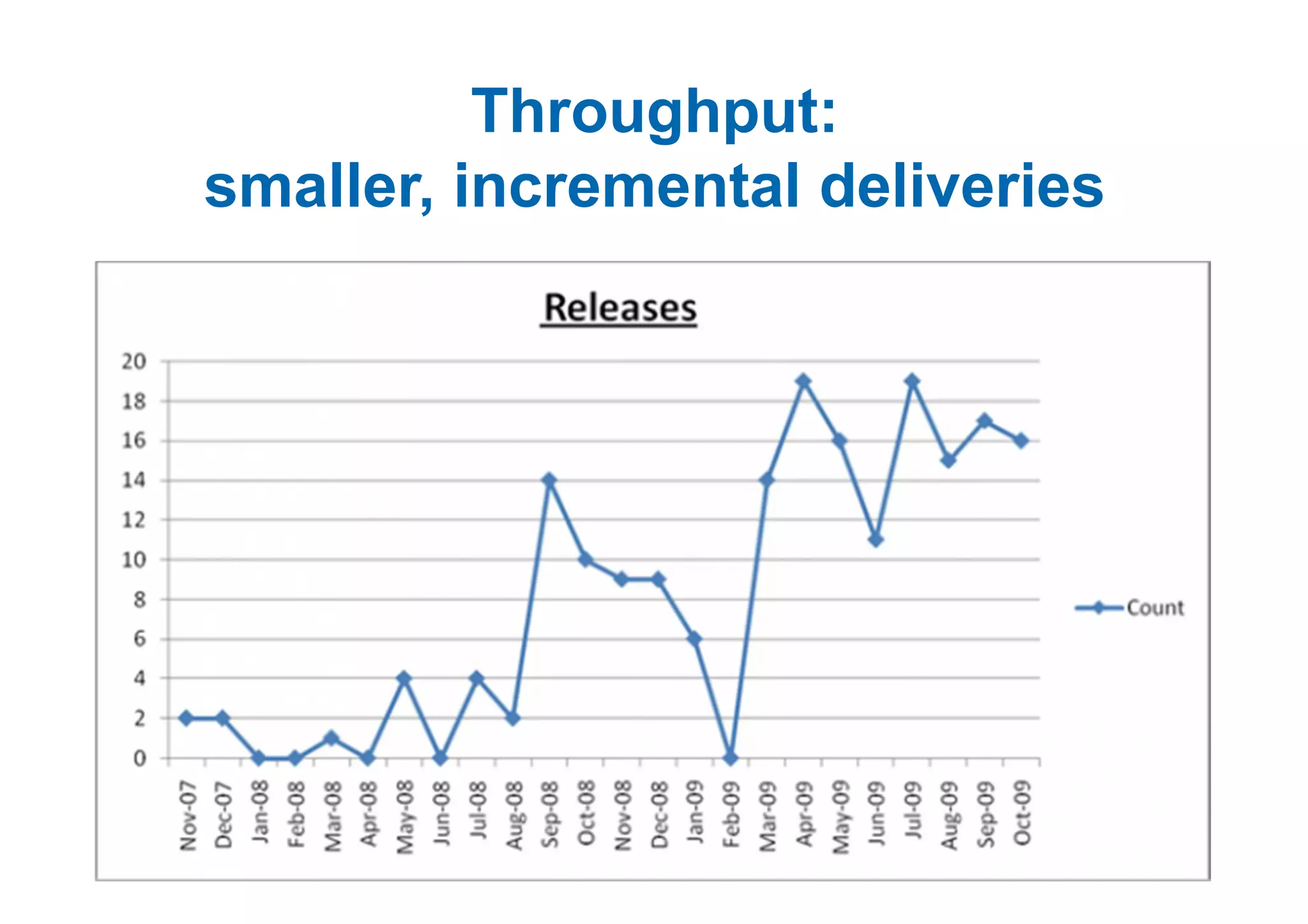
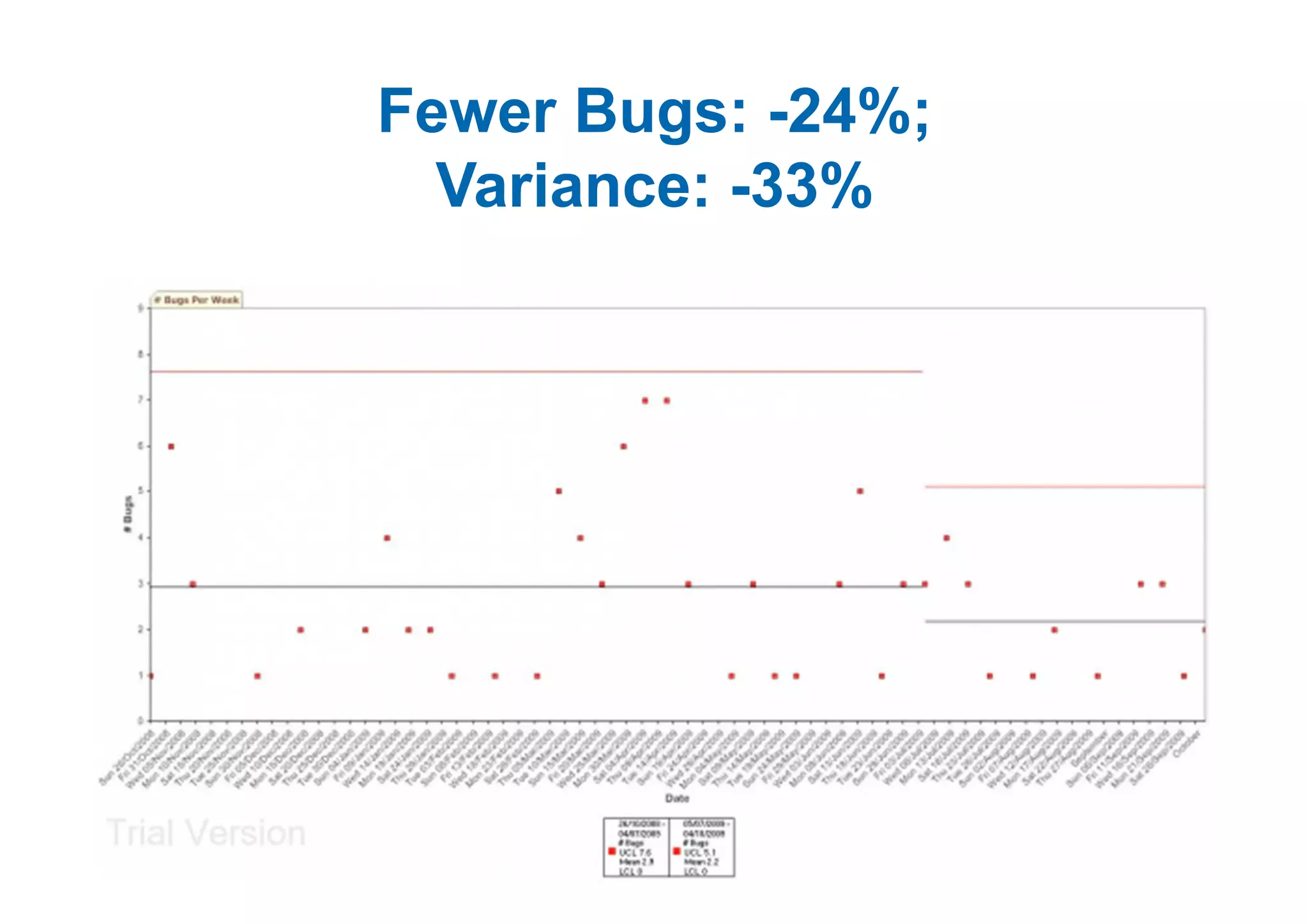
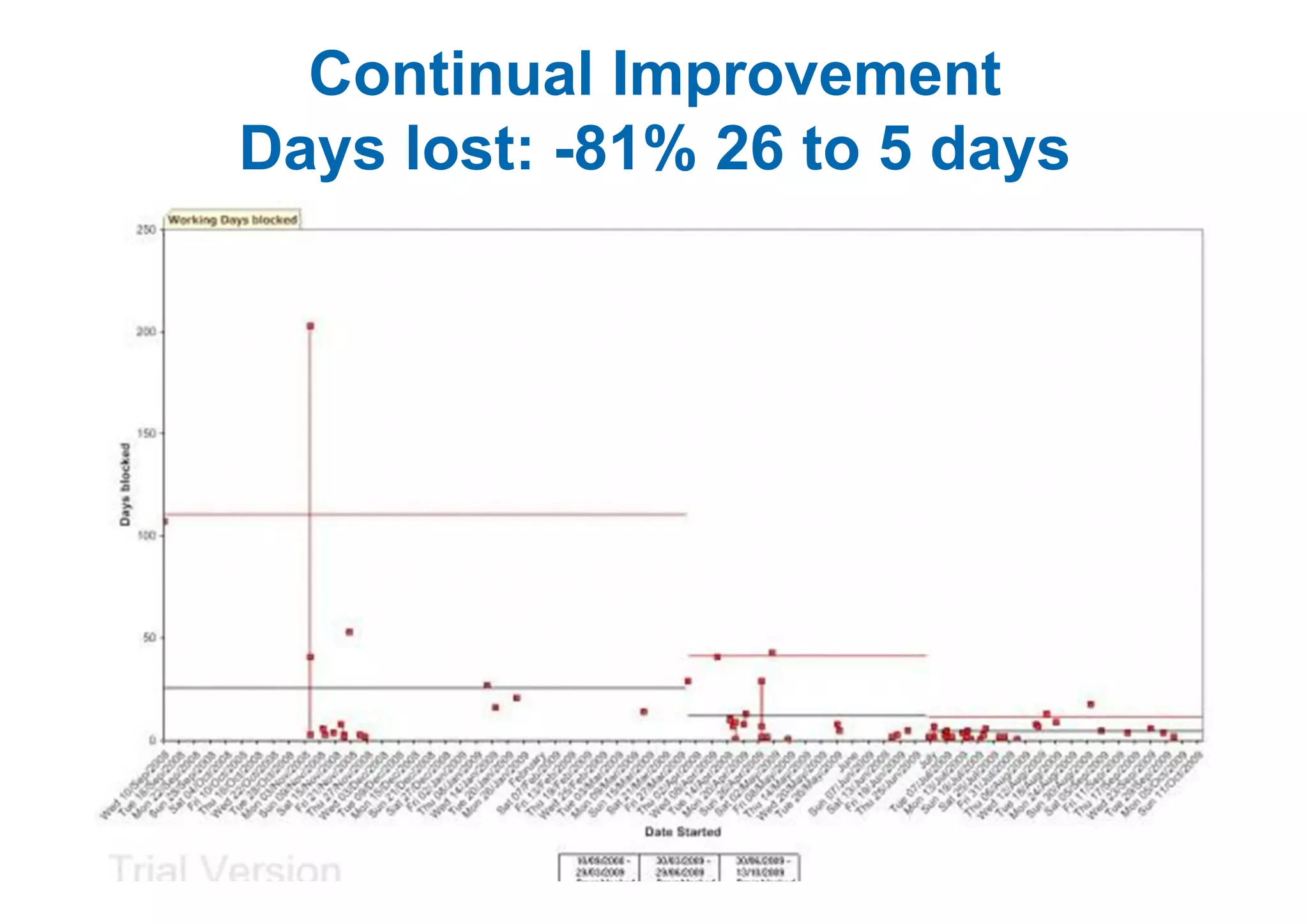
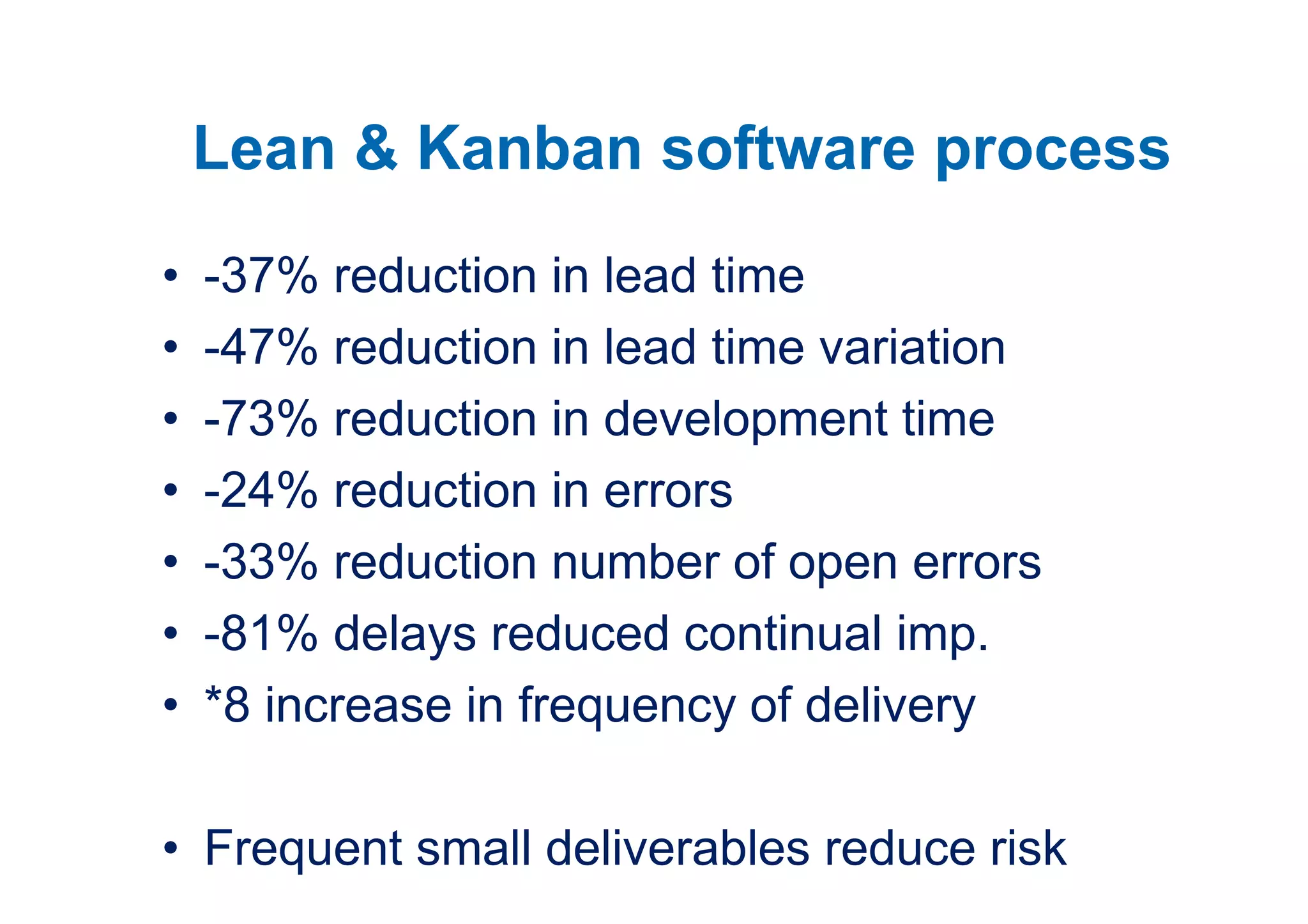
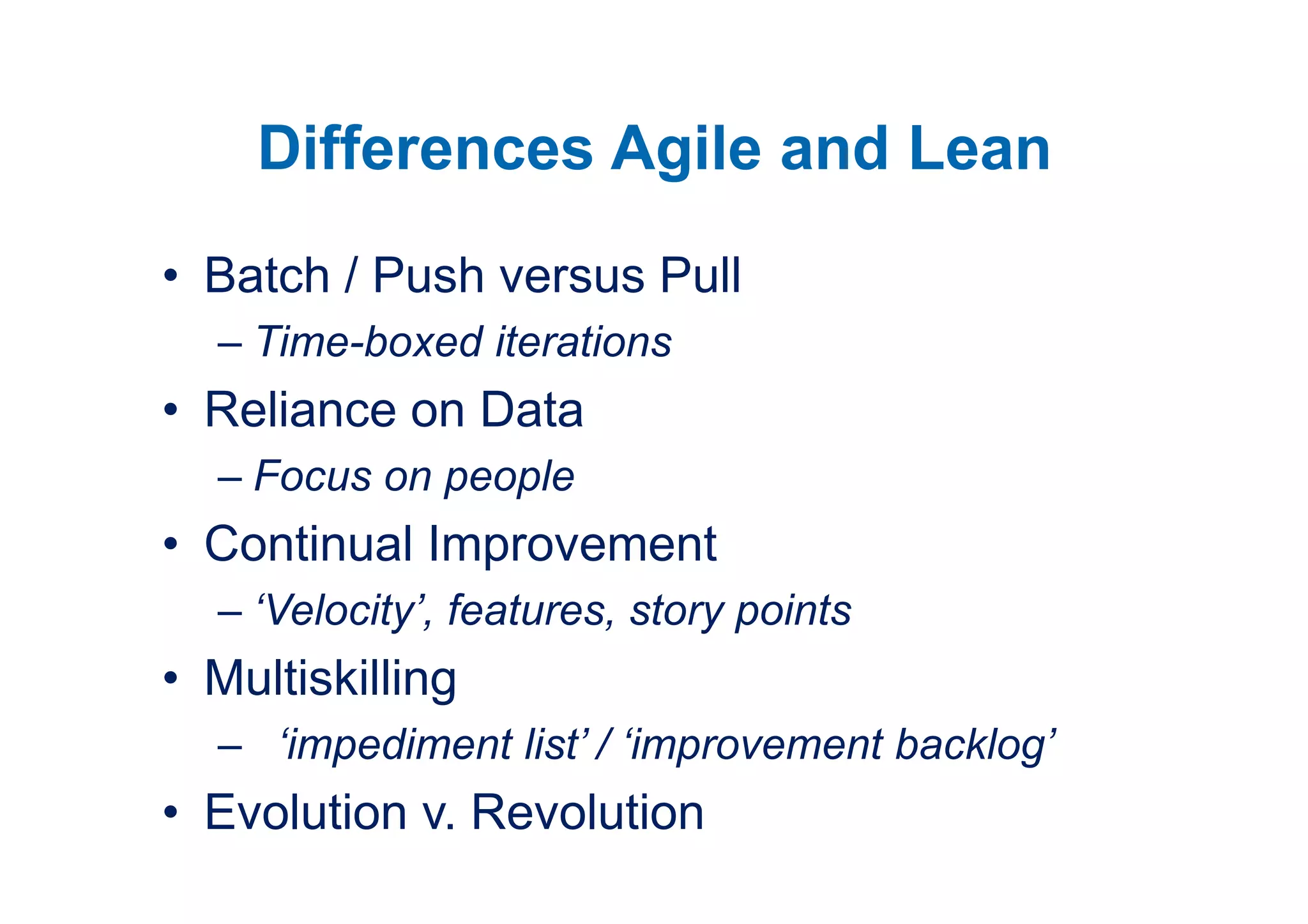
The case study describes the implementation of lean software management practices at BBC Worldwide, highlighting significant reductions in lead time, development time, and errors while increasing the frequency of delivery and valuable asset output. It emphasizes the importance of understanding and addressing 'failure demand' that constitutes a large portion of customer interactions and suggests strategies to optimize workflow and efficiency. The study concludes that lean principles enhance agility and discipline in software management, leading to continual improvement and value delivery.