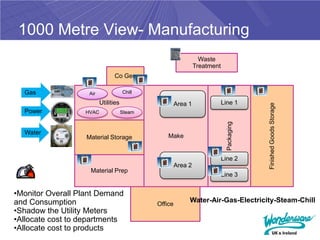
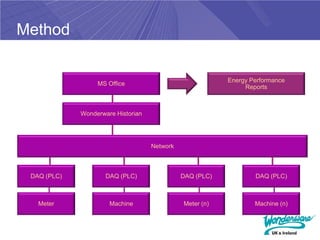
The document discusses the impending increases in energy costs and the need for efficient energy management in industrial settings. It highlights various strategies and technologies, such as lean energy practices and monitoring and targeting (M&T) techniques, to reduce energy waste and improve operational efficiency. Additionally, it emphasizes the benefits of integrating energy management solutions with production systems to enhance decision-making and sustain energy savings.