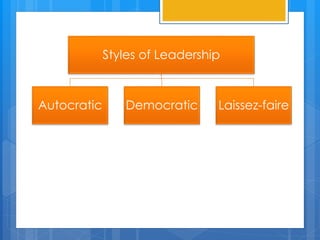
This document discusses three main styles of leadership: autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire. Autocratic leaders make all decisions individually with little input from others. Democratic leaders participate in decision-making and allow group member input, while retaining the final say. Laissez-faire leaders offer no guidance and leave decisions entirely up to group members. Each style has positive and negative effects on teams. The document also provides examples of when each style may be more or less effective and the differences between leadership and management.