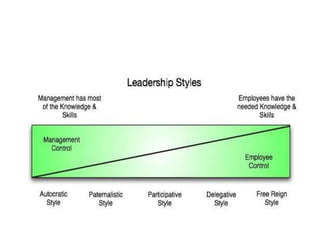
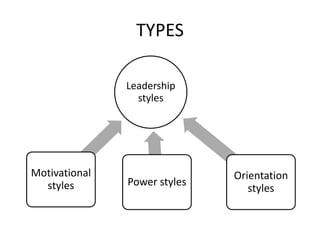
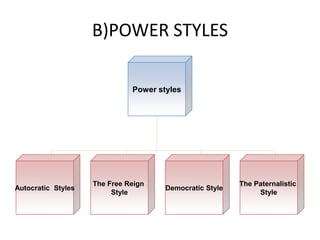
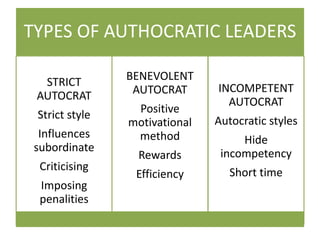
Leadership styles refer to the behavioral patterns that leaders use to direct members of an organization towards achieving goals. There are several types of leadership styles including motivational styles which use positive or negative reinforcement, power styles such as autocratic, democratic, and paternalistic, and orientation styles that are either employee-oriented or task-oriented. Effective leadership requires traits that can be innate or developed like intelligence, motivation skills, communication abilities, and a focus on developing employees as well as completing tasks. While managers focus on processes and directing employees formally, leaders influence others through informal relationships and inspiring enthusiasm to accomplish work.