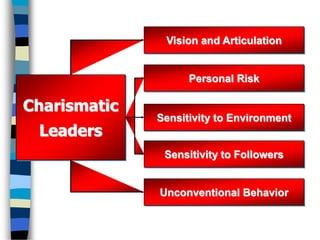
This document discusses different theories of leadership including trait theory, transactional leadership, charismatic leadership, transformational leadership, servant leadership, and superleadership. It explores whether leaders are born or made and defines leadership. Key traits for effective leadership are discussed such as self-confidence, trustworthiness, and emotional intelligence. The document provides tips for developing charisma, team leadership skills, and one's own leadership potential.