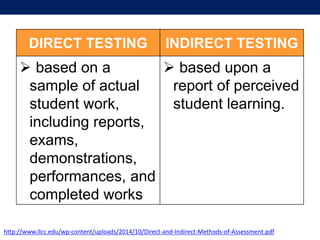
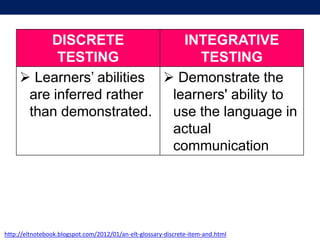
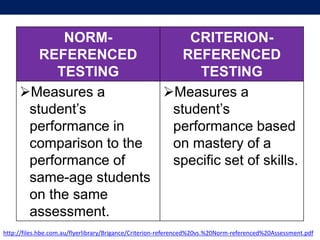
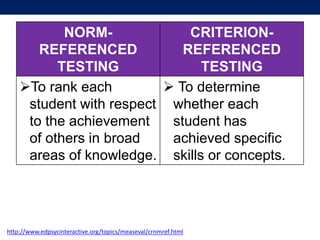
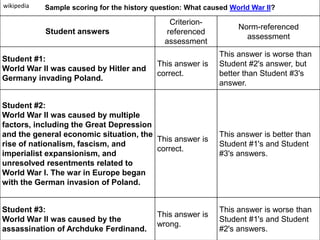
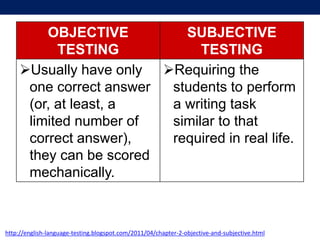
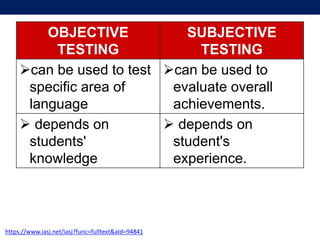
The document discusses language testing techniques, differentiating between direct and indirect assessments, as well as discrete and integrative testing methods. It highlights the differences between norm-referenced and criterion-referenced testing, providing examples for each type. Additionally, the document outlines the distinctions between objective and subjective testing, focusing on their applications in evaluating language proficiency.