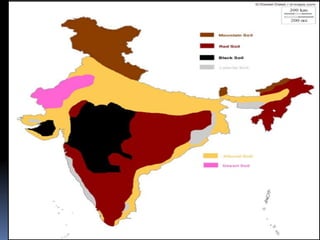
Indian soils come in 6 main types - alluvial, laterite, red, black, mountain, and desert soils. Alluvial soils are fertile soils deposited by river sediments. Laterite soils are found in southern India and are rich in iron oxides but less fertile. Red soils develop in low rainfall areas on granite and are moderately fertile. Black soils are very fertile but sticky clay soils found in central India. Mountain soils are humus-rich but low in nutrients. Desert soils are sandy, drain well but lack nutrients and blow away easily. The type of soil depends on climate, vegetation and underlying rock in each region and influences what crops can be grown.